
eBook - ePub
Reinventing Manufacturing and Business Processes Through Artificial Intelligence
- 176 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Reinventing Manufacturing and Business Processes Through Artificial Intelligence
About this book
This edited book describes how newly emerging Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies will provide unprecedented opportunities to penetrate technology and automation into everything we do, and at the same time, provide a huge playing field for businesses to develop newer models to capture market share.
It establishes a milestone in understanding global transformational changes occurring in the manufacturing and corporate world due to AI and tries to find powerful and sophisticated solutions that will improve and streamline operations.
Reinventing Manufacturing and Business Processes Through Artificial Intelligence will be of interest to students, researchers, and professionals of the AI community as well as interdisciplinary researchers.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Reinventing Manufacturing and Business Processes Through Artificial Intelligence by Geeta Rana, Alex Khang, Ravindra Sharma, Alok Kumar Goel, Ashok Kumar Dubey, Geeta Rana,Alex Khang,Ravindra Sharma,Alok Kumar Goel,Ashok Kumar Dubey in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Management. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Adopting Green HRM Practices
DOI: 10.1201/9781003145011-1
CONTENTS
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Review of Literature
1.2.1 Artificial Intelligence
1.2.2 Green Human Resource Management
1.2.3 Determinants of GHRM Adoption
1.3 Role of AI in Adopting GHRM Practices
1.4 Conclusion
References
1.1 INTRODUCTION
Artificial intelligence (AI) is constantly trying to meet the criteria of Industry 4.0 by transforming traditional organizations into smart factories where human efforts can be minimized and their talent can be leveraged for attaining organizational sustainability (Kshetri, 2021). However, business organizations in developing economies are struggling both internally and externally. On one hand, while organizations have to meet the demands of Industry 4.0 by transforming themselves into smart factories, they on the other hand also have to be responsive to the changing expectations of their customers and environment. With the increasing pressures of maintaining the environment, reducing waste and implementing cleaner production policies, organizations are shifting their focus to implement green human resource management (green HRM) practices (Pham et al., 2019). In order to both meet the ends and satisfy the organizational stakeholders, both internally and externally, companies are relying on AI (Garg et al., 2018). AI supports organizations with the advanced digital technologies, cloud computing and data storage facilities, decision-making applications and smart analytical tools (Kshetri, 2021). This chapter will explain the role of AI in adopting and implementing green HRM practices. The next section will discuss the literature carried out on green HRM and artificial intelligence. The latest examples and cases from the industry will be discussed in the chapter.
1.2 REVIEW OF LITERATURE
1.2.1 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
AI is a not a new concept anymore for developing or developed economies. AI is the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs (McCarthy, 1989). AI is an innovative tool used for transforming the role of management and organizational practices (Kshetri, 2021; Sharma & Rana, 2021). It is a subpart of computer science, which is concerned with making computers sophisticated so that they can act smartly (Nilson, 1980). It includes various intelligent tasks performed by computers on behalf of human beings such as recognition, reasoning and learning (Hilker, 1986). AI has changed the pattern of work and decision-making abilities for many organizations with its smart technological approach such as genetic algorithms, neural networks, data mining, text mining, sentiment analysis and interactive voice recognition applications (Lauterbach, 2019; Strohmeier & Piazza, 2015). It improves the decision-making ability and cost-effectiveness of the organizations by making decisions on real-time data (Kahraman et al., 2011; Rana & Sharma, 2017; Lawler & Elliot, 1996). However, the question arises: What is artificial intelligence? Is it a tool, an application, software, a methodology or a thought? AI cannot be defined in terms of a written definition, but various researchers defined artificial intelligence in technical and sociological terms.
A review study tries to explain artificial intelligence through the lens of social sciences and technology (Lauterbach, 2019). As per social sciences, AI has been described as artificial narrow intelligence, artificial general intelligence and artificial super intelligence. Artificial narrow intelligence (ANI) focuses on specializing one task or one function of the organization, which might be scheduling a meeting, recognizing voices, or human touch. Statistical machine learning in games (chess, Go and Jeopardy!), self-driving cars, automated assistants (Apple Siri, Amazon Alexa, Google Now and Microsoft Cortana) are few examples of ANI (Bundy, 2017). Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is interdisciplinary in nature and provides multiple solutions for single problems which help the decision-makers to select the appropriate solution out of the available ones (Voss, 2007). AGI applications use sensory data (visual or auditory) and deal with attributes to present simplified data for researchers and analysts. Artificial super intelligence (ASI) is defined as, “an intellect that is much smaller than the best human brains in practically every field, including scientific creativity, general wisdom and social skills” (Bostrom, 2014, pp. 109–114).
On the other hand, AI has also been explained through technological background. Technological AI is further disseminated in machine learning technologies and perception technologies. Machine learning technologies (MLT) focus on copying the human skills and thinking to presume in order to provide better analytical results. It helps in improving the efficiency and performance automatically for a given task by observing the relevant data. It is mostly used for research and development projects, speech recognition, lie detection, image recognition and several other tasks which depend on human intelligence and decision-making skills. Perception technologies include computer vision and natural language processing. Computer vision is a form of machine learning which includes recognition of faces, developing predictions, collecting and tagging data, assessing and analyzing data for manufacturing and service industries. Natural language processing is a form of AI whereby individuals can speak with machines and get their work done; for example, the virtual personal assistant Alexa (Amazon Echo), and call center agents.
The form of artificial intelligence defined here is shown in Figure 1.1.
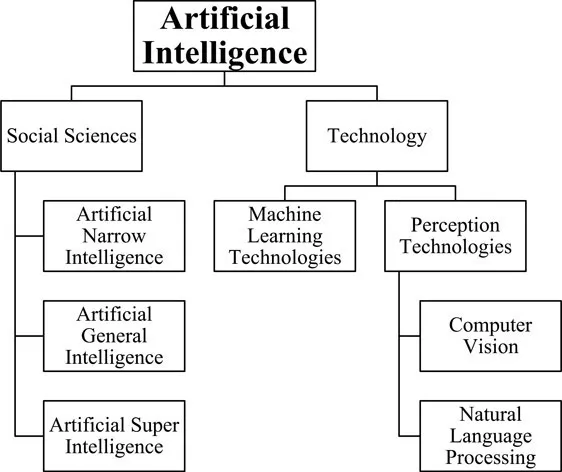
Figure 1.1 explains the different dimensions of AI which are adopted and implemented by organizations to improve their processes and services. These AI technologies are not only changing human effort, but also generating more opportunities to leverage the human skills. AI is not limited to manufacturing or service organizations but is also implemented for improving organizational efficiency and effectiveness. Companies are employing AI tools and techniques for various administrative and HRM functions including recruitment, training and development, performance appraisal, career development and talent retention.
Modern management theories management by objective (MBO) and management by exception (MBE) are focusing more on green environment issues (Chan & Chan, 2004; Chan et al., 2014; Mařík & Lažanský, 2007). Therefore, along with the challenge to sustain in this competitive scenario, companies also have to maintain green HRM practices and functions. With smart and innovative applications, AI helps the organizations attain green HRM functions and practices (Sekhri & Cheema, 2019). In the era of Industry 4.0 when organizations are transforming into digitalized systems, AI plays a great role in turning imagination into reality. With its smart and digitally equipped applications, AI is of great help for organizations to adopt and implement green HRM practices and functions. Applications like chat boats, digital attendance, job intelligence maestros, automation, distance assistants and e-pass systems are the major AI tools which have been employed by organizations to improve their HRM functions and processes. Similarly, as per the scenario AI tools and applications are used by organizations to adopt green HRM (GHRM) functions and processes. The next section will discuss the main GHRM functions practiced in organizations.
1.2.2 GREEN HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
With the constantly increasing pressure of environmentalists to maintain and preserve a pollution-free environment, organizations cannot avoid the implementation of GHRM practices (Jabbour, 2013; Pham et al., 2019). Another reason for the same is increasing customer awareness and concern of job seekers about the organizational policies toward maintaining a sustainable and green environment (Teixeira et al., 2012). Organizations cannot attain sustainable competitive advantage without leveraging the talent of their employees, and talented employees can only be retained with effective HRM policies. Therefore, GHRM has attracted the interest of various scholars, researchers, policymakers and academics after the research initiated by a small group of researchers (Jabbour & Santos, 2008; Tomer & Rana, 2020; Jackson et al., 2011; Pham et al., 2019; Renwick et al., 2016; Yong et al., 2019a, 2019b). Implementation of GHRM practices also helped organizations to minimize carbon emissions, go for paperless approaches and deduct waste production in manufacturing units (Ahmad, 2015; Yong et al., 2019a). GHRM has been considered as a sustainable change for the organizations (Sawang & Kivits, 2014).
GHRM can be defined as HRM-related aspects of environmental management (EM) and focuses on the role of HRM in preventing environmental pollution using organizational procedures (Renwick et al., 2008; Renwick et al., 2013). GHRM practices have been considered a combination of original HRM practices and strategic HRM measures of organizations to preserve and sustain green environment (Gholami et al., 2016). GHRM practices depend on three components: developing green ability, motivating green employees and facilitating green opportunity to the employees (Renwick et al., 2013). These practices and measures revolve around the main HRM functions which are disseminated into recruitment and selection, training and development, performance management, compensation and reward management, and finally talent retention. HRM functions support organizations in implementing environmental measures by formulating environmental goals (Cohen, 2012). HRM also serves as a partner to formulate environment-based corporate values and design strategies to attain sustainability. Therefore, HRM functions are further divided on the basis of antecedents of GHRM practices. Table 1.1 divides the HRM functions as per the factors of GHRM practices.
| No | Antecedents of GHRM Practices | HRM Functions | Research Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Developing green ability |
| Jabbour et al. (2010); Jabbour (2013); Renwick et al. (2013); Pham and Paillé (2019); Ren et al. (2018); Zaid et al. (2018); Chaudhary (2018); Chaudhary (2019a); Roscoeetal. (2019) |
| 2 | Motivating green employees |
| Masri and Jaaron (2017); Gupta (2018); Longoni et al. (2018); Aboramadan (2020) |
| 3 | Facilitating green opportunities |
| Jabbour and Santos (... |
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Half Title Page
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents Page
- Preface Page
- Acknowledgments Page
- Editors Page
- Contributors Page
- Chapter 1 The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Adopting Green HRM Practices
- Chapter 2 The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Blockchain Applications
- Chapter 3 The Rise of Artificial Intelligence in Modern Healthcare Sector
- Chapter 4 Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing
- Chapter 5 Customer Behavior Prediction for E-Commerce Sites Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Investigation
- Chapter 6 The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Global Business Practices
- Chapter 7 Road Map for Implementation of IoT in Metal Cutting for the Process Monitoring System to Improve Productivity
- Chapter 8 Reinventing HR with Conversational Artificial Intelligence: A Conceptual Framework
- Chapter 9 AI and Business Sustainability: Reinventing Business Processes
- Index