
Big Data for Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Development
- 206 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Big Data for Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Development
About this book
This book provides insight for researchers and decision-makers on the application of data in the entrepreneurship and sustainable development sector. This book covers how Big Data for Industry 4.0 and entrepreneurship are effective in resolving business, social, and economic problems.
The book discusses how entrepreneurs use Big Data to cut costs and minimize the waste of time. It offers how using Big Data can increase efficiency, enables the studying of competitors, can improve the pricing of products, increase sales and loyalty, and can ensure the right people are hired. The book presents how decision-makers can make use of Big Data to resolve economic and social problems. Analyze the development of the economy and enhance the business climate.
This book is for researchers, PhD students, and entrepreneurs and can also be of interest for transforming governments as well as businesses.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1Entrepreneurship and Social Innovation in Big Data Era A Particular Focus on the Internet of Things
- 1.1Introduction
- 1.2Big Data
- 1.2.1History of Big Data and Background Behind It: Data Era
- 1.2.1.1First Industrial Revolution
- 1.2.1.2Second Industrial Revolution
- 1.2.1.3Third Industrial Revolution
- 1.2.1.4Fourth Industrial Revolution
- 1.2.2Data Era and Technologies
- 1.2.3What Can Big Data Solve
- 1.2.3.1Availability and Capability
- 1.2.4Successful Stories
- 1.2.5Internet of Events
- 1.2.6The Four Vs and Challenges of Big Data
- 1.3Big Data, Entrepreneurs, and Innovation
- 1.3.1Importance of Entrepreneurship and Sustainability
- 1.3.1.1Sustainability
- 1.3.1.2Sustainability and Entrepreneurs
- 1.3.2Importance of Innovation
- 1.3.3Entrepreneurship, a Path of Innovation in Big Data Era
- 1.3.3.1The New Entrepreneurial Context
- 1.3.3.2Opportunities
- 1.3.3.3Big Data and Open Innovation
- 1.3.3.4The Use of Big Data for Social Innovation
- 1.4Internet of Things
- 1.4.1What is IoT?
- 1.4.2Opportunities to Innovate with IoT
- 1.4.2.1Business Innovation Framework
- 1.4.2.2Foundational Capability
- 1.4.2.3IoT Business Innovation Model; Orchestrating Value Networks
- 1.4.3IoT for an Enriched World
- 1.5Conclusion
- Notes
- References
1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 BIG DATA
1.2.1 History of Big Data and Background behind It: Data Era
1.2.1.1First Industrial Revolution
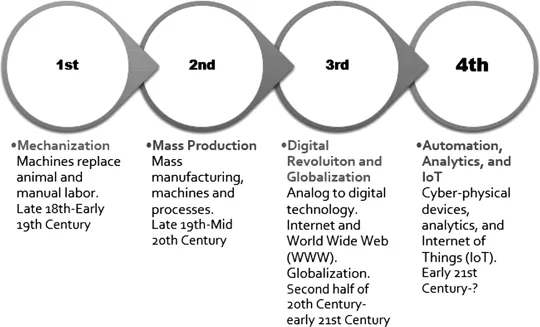
1.2.1.2 Second Industrial Revolution
1.2.1.3Third Industrial Revolution
1.2.1.4Fourth Industrial Revolution
1.2.2 Data Era and Technologies
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Table of
- Foreword
- Preface
- Contributors
- Editor Biographies
- Chapter 1 Entrepreneurship and Social Innovation in Big Data Era: A Particular Focus on the Internet of Things
- Chapter 2 Big Data for Entrepreneurship Towards CSR and Sustainable Development
- Chapter 3 Finance, Digital Disruption, and Sustainability: Issues, Challenges, and Future Directions
- Chapter 4 Disruptive Financial Innovation and Big Data Implications in Digital Finance
- Chapter 5 Cybersecurity Aids Financial Institutions Performance
- Chapter 6 Sustainability-Oriented Cost Management Tools and Big Data Analytics: An Organizing Framework for Enhancing Sustainable Decision Making
- Chapter 7 Industry 4.0 and Digital Supply-Chain Management: ERP-SCM Implementation
- Chapter 8 New Forms of Effective Collaboration: How to Enhance Big Data for Innovative Ideas in the Online Environment
- Chapter 9 Rethinking Tourism Entrepreneurship Amidst COVID-19 Through the Lens of Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analytics
- Chapter 10 The New Trends Technology of Entrepreneurship in the Incubators: A Case Study of Cyberpark Sidi Abdallah
- Index