
- 594 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Mastering ROS for Robotics Programming
About this book
Design, build, and simulate complex robots using the Robot Operating SystemKey Features• Become proficient in ROS programming using C++ with this comprehensive guide• Build complex robot applications using the ROS Noetic Ninjemys release to interface robot manipulators with mobile robots• Learn to interact with aerial robots using ROSBook DescriptionThe Robot Operating System (ROS) is a software framework used for programming complex robots. ROS enables you to develop software for building complex robots without writing code from scratch, saving valuable development time. Mastering ROS for Robotics Programming provides complete coverage of the advanced concepts using easy-to-understand, practical examples and step-by-step explanations of essential concepts that you can apply to your ROS robotics projects. The book begins by helping you get to grips with the basic concepts necessary for programming robots with ROS. You'll then discover how to develop a robot simulation, as well as an actual robot, and understand how to apply high-level capabilities such as navigation and manipulation from scratch. As you advance, you'll learn how to create ROS controllers and plugins and explore ROS's industrial applications and how it interacts with aerial robots. Finally, you'll discover best practices and methods for working with ROS efficiently. By the end of this ROS book, you'll have learned how to create various applications in ROS and build your first ROS robot.What you will learn• Create a robot model with a 7-DOF robotic arm and a differential wheeled mobile robot• Work with Gazebo, CoppeliaSim, and Webots robotic simulators• Implement autonomous navigation in differential drive robots using SLAM and AMCL packages• Interact with and simulate aerial robots using ROS• Explore ROS pluginlib, ROS nodelets, and Gazebo plugins• Interface I/O boards such as Arduino, robot sensors, and high-end actuators• Simulate and perform motion planning for an ABB robot and a universal arm using ROS-Industrial• Work with the motion planning features of a 7-DOF arm using MoveItWho this book is forIf you are a robotics graduate, robotics researcher, or robotics software professional looking to work with ROS, this book is for you. Programmers who want to explore the advanced features of ROS will also find this book useful. Basic knowledge of ROS, GNU/Linux, and C++ programming concepts is necessary to get started with this book.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Section 1 – ROS Programming Essentials
- Chapter 1, Introduction to ROS
- Chapter 2, Getting Started with ROS Programming
Chapter 1: Introduction to ROS
- Why should we learn ROS?
- Understanding the ROS filesystem level.
- Understanding ROS computation graph level.
- ROS community level.
Technical requirements
Why should we use ROS?
- High-end capabilities: ROS comes with ready-to-use functionalities. For example, the Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) and Adaptive Monte Carlo Localization (AMCL) packages in ROS can be used for having autonomous navigation in mobile robots, while the MoveIt package can be used for motion planning for robot manipulators. These capabilities can directly be used in our robot software without any hassle. In several cases, these packages are enough for having core robotics tasks on different platforms. Also, these capabilities are highly configurable; we can fine-tune each one using various parameters.
- Tons of tools: The ROS ecosystem is packed with tons of tools for debugging, visualizing, and having a simulation. The tools, such as rqt_gui, RViz, and Gazebo, are some of the strongest open source tools for debugging, visualization, and simulation. A software framework that has this many tools is very rare.
- Support for high-end sensors and actuators: ROS allows us to use different device drivers and the interface packages of various sensors and actuators in robotics. Such high-end sensors include 3D LIDAR, laser scanners, depth sensors, actuators, and more. We can interface these components with ROS without any hassle.
- Inter-platform operability: The ROS message-passing middleware allows communication between different programs. In ROS, this middleware is known as nodes. These nodes can be programmed in any language that has ROS client libraries. We can write high-haveance nodes in C++ or C and other nodes in Python or Java.
- Modularity: One of the issues that can occur in most standalone robotic applications is that if any of the threads of the main code crash, the entire robot application can stop. In ROS, the situation is different; we are writing different nodes for each process, and if one node crashes, the system can still work.
- Concurrent resource handling: Handling a hardware resource via more than two processes is always a headache. Imagine that we want to process an image from a camera for face detection and motion detection; we can either write the code as a single entity that can do both, or we can write a single-threaded piece of code for concurrency. If we want to add more than two features to threads, the application behavior will become complex and difficult to debug. But in ROS, we can access devices using ROS topics from the ROS drivers. Any number of ROS nodes can subscribe to the image message from the ROS camera driver, and each node can have different functionalities. This can reduce the complexity in computation and also increase the debugging ability of the entire system.
Understanding the ROS filesystem level
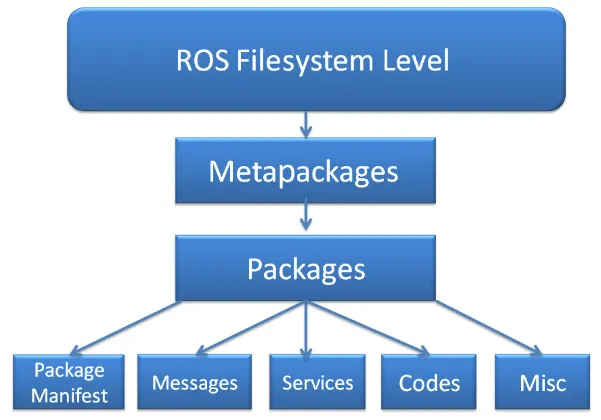
- Packages: The ROS packages are a central element of the ROS softwar...
Table of contents
- Mastering ROS for Robotics Programming Third Edition
- Contributors
- Preface
- Section 1 – ROS Programming Essentials
- Chapter 1: Introduction to ROS
- Chapter 2: Getting Started with ROS Programming
- Section 2 – ROS Robot Simulation
- Chapter 3: Working with ROS for 3D Modeling
- Chapter 4: Simulating Robots Using ROS and Gazebo
- Chapter 5: Simulating Robots Using ROS, CoppeliaSim, and Webots
- Chapter 6: Using the ROS MoveIt! and Navigation Stack
- Chapter 7: Exploring the Advanced Capabilities of ROS MoveIt!
- Chapter 8: ROS for Aerial Robots
- Section 3 – ROS Robot Hardware Prototyping
- Chapter 9: Interfacing I/O Board Sensors and Actuators to ROS
- Chapter 10: Programming Vision Sensors Using ROS, OpenCV, and PCL
- Chapter 11: Building and Interfacing Differential Drive Mobile Robot Hardware in ROS
- Section 4 – Advanced ROS Programming
- Chapter 12: Working with pluginlib, nodelets, and Gazebo Plugins
- Chapter 13: Writing ROS Controllers and Visualization Plugins
- Chapter 14: Using ROS in MATLAB and Simulink
- Chapter 15: ROS for Industrial Robots
- Chapter 16: Troubleshooting and Best Practices in ROS
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app