
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This book provides 300 practice MCQs divided into three practice papers. Correct answers follow, accompanied by short referenced notes drawing from recent important journal articles, major critical care textbooks and selected internet resources. Since there is no other dedicated intensive care MCQ book on the market, this book is relevant to the following groups: junior intensive care trainees, senior intensive care nursing staff wishing to enhance their medical knowledge, intensive care consultants as a teaching aid and trainees preparing for professional examinations. This MCQ book will also be ideal in preparation for the European Diploma in Intensive Care Medicine (EDIC) Part 1 examination, as the questions are matched as closely as possible in style and difficulty to those in the EDIC Part 1. The EDIC is an internationally recognised qualification for medical trainees in intensive care, set by the European Society for Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM). It is a two-part examination consisting of a 100-question multiple choice paper (Part 1) and a clinical and viva voce examination (Part 2). To ensure relevance, the questions are designed with reference to the training syllabus provided by the ESICM.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
| a. | Infusion of potassium should not normally exceed 40mmol/h. |
| b. | Daily sodium requirement is 1-2mmol/kg. |
| c. | Most calcium in the extracellular fluid is protein-bound. |
| d. | 1g of magnesium sulphate contains 4mmol magnesium. |
| e. | The normal range for phosphate in the plasma is 0.8-1.5mmol/L (2.5-4.6mg/dL). |
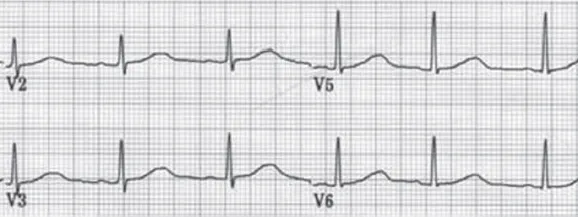
| a. | Hyperkalaemia. |
| b. | Hypocalcaemia. |
| c. | Hypothermia. |
| d. | Acute anterolateral myocardial infarction. |
| e. | Hyponatraemia. |
| a. | Mains isolating transformer. |
| b. | Earth leakage circuit breaker. |
| c. | Use of a common earth. |
| d. | Ensuring the patient has a good earth connection. |
| e. | Use of Class II equipment. |
| a. | Cold air blanket. |
| b. | Ice water bodily immersion. |
| c. | Extracorporeal heat exchange. |
| d. | Rapid infusion of 30ml/kg bolus of crystalloid at 4°C. |
| e. | Central venous cooling catheter. |
| a. | Extensive pulmonary contusion. |
| b. | Cardiac tamponade. |
| c. | Myocardial infarction. |
| d. | Fat embolism. |
| e. | Ruptured spleen. |
| a. | Human albumin 4% will be no more effective than crystalloid for fluid resuscitation. |
| b. | Blood substitutes should be used in preference to crystalloid for initial resuscitation if available. |
| c. | Level 1 evidence supports the use of hypotensive resuscitation in this setting. |
| d. | A transfusion trigger of 7-9g/dl should be used. |
| e. | A central venous catheter should be placed immediately to guide further fluid therapy. |
| a. | Female gender. |
| b. | Her age. |
| c. | A dilated unreactive pupil. |
| d. | Her GCS after resuscitation. |
| e. | Subarachnoid blood on CT scan. |
| a. | Tuberculous meningitis. |
| b. | Viral meningitis. |
| c. | Pneumococcal meningitis. |
| d. | Cryptococcal meningitis. |
| e. | None of the above. |
| a. | Right atrial pressure is usually <10mmHg. |
| b. | It usually signifies occlusion in a branch of the right coronary artery. |
| c. | Right to left shunting is a recognised complication. |
| d. | Inferior myocardial infarction is usually present. |
| e. | Right corona... |
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- Foreword
- Abbreviations
- How to use this book
- Paper 1
- Paper 2
- Paper 3