
- 154 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Advances in Controlled Delivery of Drugs
About this book
The development of improved methods of drug delivery has received significant attention over the last two decades. Most important is a non-toxic level of the drug at a particular body organ or body locale. To reach this goal, many variations of controlled release have been researched worldwide. This edited volume of papers from the Journal of Biomaterials Applications details many exciting technical advances in controlled release drug delivery systems. Some of the important developments described in the book include implantable delivery systems, delivery of topical drugs, and ultrasonic drug delivery.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Advances in Controlled Delivery of Drugs by Melvyn Kohudic in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Medicine & Chemistry. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Implantable Drug Delivery
Medical Student 4th Year
University of Nevada at Reno
School of Medicine
Reno, NV 89557
University of Nevada at Reno
School of Medicine
Reno, NV 89557
Director of Research
Section Head: Pharmaceutical Sciences
Associate Professor of Pharmaceutics
St. Louis College of Pharmacy
4588 Parkview Place
St. Louis, MO 63110
Section Head: Pharmaceutical Sciences
Associate Professor of Pharmaceutics
St. Louis College of Pharmacy
4588 Parkview Place
St. Louis, MO 63110
INTRODUCTION
Conventional drug delivery utilizes routes of administration, namely, oral, rectal, intravenously, and topical, that deliver drug substances that are immediately released in bolus fashion. For a time, the drug concentration will be adequate for therapeutic effectiveness, but eventually the drug concentration falls below the minimum effective concentration and another dose of the drug is required. The increased frequency of dosing to sustain a therapeutic concentration may be several times daily, which not only results in variable drug concentrations, but also noncompliance by the patient unable to maintain this regimen. The ideal drug concentration profile would be a sustained therapeutic level without variation or the need for repeated dosing (Figure 1).
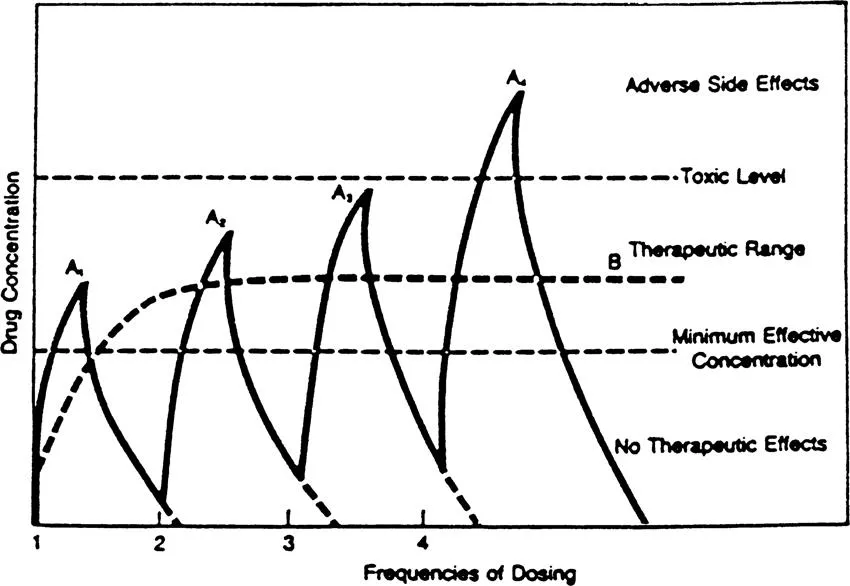
Pharmaceutical companies continue to develop new drugs with the goal of augmenting the duration of action and thus, reducing the frequency of dosing. It was not until recently that the delivery systems themselves were modified in order to facilitate controlled-release drug delivery that would also sustain the duration of action within the therapeutic range. These advancements in drug delivery have afforded many new and exciting areas of research and development aimed to optimize pharmaceutically-related therapy for many diseases. These technical advances in drug delivery are rapidly progressing to reality and it is anticipated that they will be used more frequently in clinical practice over the next decade. Major advances have already been made in the area of contraception with the development of the Norplant implantable system [1]. In addition, the insulin pump for diabetes is being perfected by several investigators and is widely reported in the literature [2].
Implantable pumps and infusion systems are two of the several innovative technologies developed in drug delivery over the past two decades. These systems employ a mechanism involving a reservoir of drug substance and an energy source to drive drug release. Each mechanism offers unique opportunities for rate and duration for controlled delivery of drug substances directly into the bloodstream either locally or systemically. Further, the control of drug delivery in this manner reduces the adverse effects of drugs and improves overall efficacy and compliance by avoiding repeated insertions of needles into peripheral vasculature.
The implantable device is surgically introduced and completely subcutaneous with nominal chance of infection. Fluids or drugs are injected into the portal chamber and flow through the catheter directly into the bloodstream. The needle may be removed or an external pump, many of which are ambulatory, may be attached for continuous infusion.
Overall, there are several advantages to these systems including the psychological benefit to the patient who experiences less pain, less anxiety and less disruption of daily routines while remaining ambulatory during treatment. In addition, implantable systems are valuable because they enable drug substances to overcome the absorption barriers encountered by oral and peripheral intravenous administration, specifically: plasma proteins, first pass hepatic effects, gastrointestinal absorption, and the blood brain barrier. Each of these biological barriers prevents a percentage of drug substance from reaching its target site and active receptor. Implantables, whether for local or systemic administration, can also protect healthy tissue by eliminating peaks and troughs resulting from periodic dosing, thus minimizing toxic side effects.
Unfortunately, there are potential problems with the use of implantable systems. These include: biocompatibility, biodegradability, the need for a minor surgical procedure for ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Ultrasonically Mediated Drug Delivery
- Implantable Drug Delivery
- Polyethylene-Starch Extrudates as Erodible Carriers for Bioactive Materials: I. Erodibility and in vitro Dye Release Studies
- Bioactive Polymers: In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Controlled Release Neomycin
- Polymer Entrapment Powders for Topical Delivery
- Bioactive Polymers 68–Controlled Release of Neomycine-Furazolidone Bicomponent System from Xanthan Hydrogel
- Effect of Controlled Local Acetylsalicylic Acid Release on in vitro Platelet Adhesion to Vascular Grafts
- Materials Used in Controlled Release Technology–A Primer