
- 230 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Optimizing Databricks Workloads
About this book
Accelerate computations and make the most of your data effectively and efficiently on DatabricksKey Features• Understand Spark optimizations for big data workloads and maximizing performance• Build efficient big data engineering pipelines with Databricks and Delta Lake• Efficiently manage Spark clusters for big data processingBook DescriptionDatabricks is an industry-leading, cloud-based platform for data analytics, data science, and data engineering supporting thousands of organizations across the world in their data journey. It is a fast, easy, and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics platform for data science and data engineering in the cloud.In Optimizing Databricks Workloads, you will get started with a brief introduction to Azure Databricks and quickly begin to understand the important optimization techniques. The book covers how to select the optimal Spark cluster configuration for running big data processing and workloads in Databricks, some very useful optimization techniques for Spark DataFrames, best practices for optimizing Delta Lake, and techniques to optimize Spark jobs through Spark core. It contains an opportunity to learn about some of the real-world scenarios where optimizing workloads in Databricks has helped organizations increase performance and save costs across various domains.By the end of this book, you will be prepared with the necessary toolkit to speed up your Spark jobs and process your data more efficiently.What you will learn• Get to grips with Spark fundamentals and the Databricks platform• Process big data using the Spark DataFrame API with Delta Lake• Analyze data using graph processing in Databricks• Use MLflow to manage machine learning life cycles in Databricks• Find out how to choose the right cluster configuration for your workloads• Explore file compaction and clustering methods to tune Delta tables• Discover advanced optimization techniques to speed up Spark jobsWho this book is forThis book is for data engineers, data scientists, and cloud architects who have working knowledge of Spark/Databricks and some basic understanding of data engineering principles. Readers will need to have a working knowledge of Python, and some experience of SQL in PySpark and Spark SQL is beneficial.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Section 1: Introduction to Azure Databricks
- Chapter 1, Discovering Databricks
- Chapter 2, Batch and Real-Time Processing in Databricks
- Chapter 3, Learning about Machine Learning and Graph Processing in Databricks
Chapter 1: Discovering Databricks
- Introducing Spark fundamentals
- Introducing Databricks
- Learning about Delta Lake
Technical requirements
- An Azure subscription
- Azure Databricks
Introducing Spark fundamentals
- DataFrames: Fundamental data structures consisting of rows and columns.
- Machine Learning (ML): Spark ML provides ML algorithms for processing big data.
- Graph processing: GraphX helps to analyze relationships between objects.
- Streaming: Spark's Structured Streaming helps to process real-time data.
- Spark SQL: A SQL to Spark engine with query plans and a cost-based optimizer.
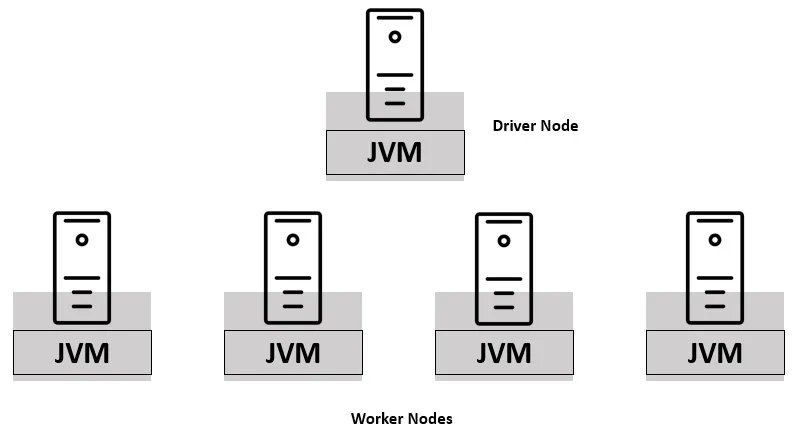
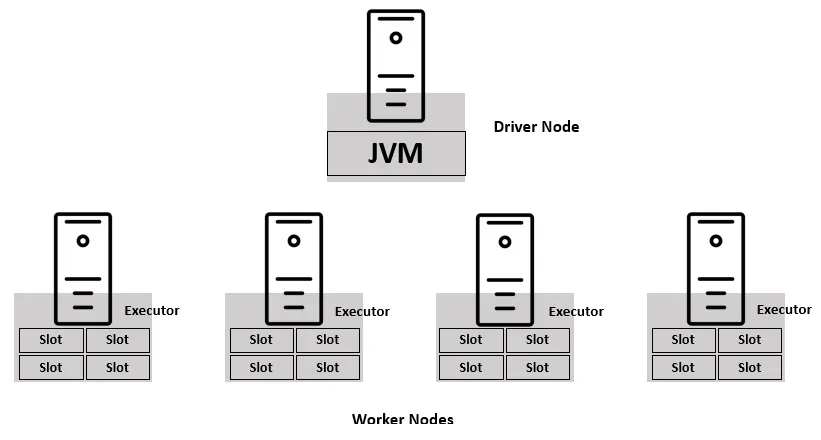
- Cache
- Computation
- Vertical parallelism: Scaling the number of slots in the executors
- Horizontal parallelism: Scaling the number of executors in a Spark cluster
Table of contents
- Optimizing Databricks Workloads
- Contributors
- Preface
- Section 1: Introduction to Azure Databricks
- Chapter 1: Discovering Databricks
- Chapter 2: Batch and Real-Time Processing in Databricks
- Chapter 3: Learning about Machine Learning and Graph Processing in Databricks
- Section 2: Optimization Techniques
- Chapter 4: Managing Spark Clusters
- Chapter 5: Big Data Analytics
- Chapter 6: Databricks Delta Lake
- Chapter 7: Spark Core
- Section 3: Real-World Scenarios
- Chapter 8: Case Studies
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app