
Deep Learning Approaches to Cloud Security
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Deep Learning Approaches to Cloud Security
About this book
Covering one of the most important subjects to our society today, cloud security, this editorial team delves into solutions taken from evolving deep learning approaches, solutions allowing computers to learn from experience and understand the world in terms of a hierarchy of concepts, with each concept defined through its relation to simpler concepts.
Deep learning is the fastest growing field in computer science. Deep learning algorithms and techniques are found to be useful in different areas like automatic machine translation, automatic handwriting generation, visual recognition, fraud detection, and detecting developmental delay in children. However, applying deep learning techniques or algorithms successfully in these areas needs a concerted effort, fostering integrative research between experts ranging from diverse disciplines from data science to visualization. This book provides state of the art approaches of deep learning in these areas, including areas of detection and prediction, as well as future framework development, building service systems and analytical aspects. In all these topics, deep learning approaches, such as artificial neural networks, fuzzy logic, genetic algorithms, and hybrid mechanisms are used. This book is intended for dealing with modeling and performance prediction of the efficient cloud security systems, thereby bringing a newer dimension to this rapidly evolving field.
This groundbreaking new volume presents these topics and trends of deep learning, bridging the research gap, and presenting solutions to the challenges facing the engineer or scientist every day in this area. Whether for the veteran engineer or the student, this is a must-have for any library.
Deep Learning Approaches to Cloud Security:
- Is the first volume of its kind to go in-depth on the newest trends and innovations in cloud security through the use of deep learning approaches
- Covers these important new innovations, such as AI, data mining, and other evolving computing technologies in relation to cloud security
- Is a useful reference for the veteran computer scientist or engineer working in this area or an engineer new to the area, or a student in this area
- Discusses not just the practical applications of these technologies, but also the broader concepts and theory behind how these deep learning tools are vital not just to cloud security, but society as a whole
Audience: Computer scientists, scientists and engineers working with information technology, design, network security, and manufacturing, researchers in computers, electronics, and electrical and network security, integrated domain, and data analytics, and students in these areas
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Biometric Identification Using Deep Learning for Advance Cloud Security
AbstractA few decades ago, biometric identification was a staple technology of highly advanced security systems in movies, but today, it exists all around us. Biometric technologies have the potential to revolutionize approaches to identity verification worldwide.This chapter discusses the prevailing Biometric modalities, their classification, and their working. It goes on to discuss the various approaches used for Facial Biometric Identification such as feature selection, extraction, face marking, and the Nearest Neighbor Approach.Here, we propose a system that compares an input image with that of the database in order to detect the presence of any similarities. Moreover, we use fiducially point analysis to extract facial landmarks and compare them with the database using data mining and use the Nearest Neighbor Approach for identifying similar images.The chapter ends with deliberations on the future extent of Biometric technologies and the need to put in ample safeguards for data protection and privacy.Keywords: Biometric, feature extraction, facial recognition, nearest neighbor approach
1.1 Introduction
- • Behavioral Biometrics: gestures, vocal recognition, handwritten texts, walking patterns, etc.
- • Physical Biometrics: fingerprints, iris, vein, facial recognition, DNA, etc.
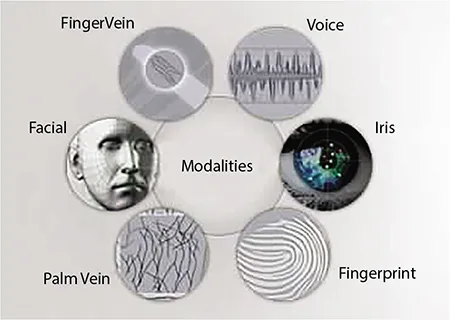
1.2 Techniques of Biometric Identification
1.2.1 Fingerprint Identification
- 1. Optical Readers’ sensors work using a 2D image of the fingerprint. Algorithms can be utilized to discover novel patterns of lines and edges spread across lighter and hazier zones of the picture
- 2. Capacitive Readers use electrical signals to form the image of fingerprints. As the charges differ in the air gap between the ridges and lines in the finger set over the capacitive plate, it causes a difference in the fingerprint patterns.
- 3. Ultrasound Readers use high frequency sound waves to infiltrate the external layer of the skin which is used to capture a 3D depiction of the fingerprint. It involves the use of ultrasonic pulses using ultrasonic transmitters and receivers.
- 4. Thermal Readers sense the temperature difference between fingerprint valleys and ridges on making a contact. Higher power consumption and a performance reliant on the surrounding temperature are impediments for these readers.
1.2.2 Iris Recognition
- 1. Scan an individual’s eyes with subtle infrared illumination to obtain detailed patterns of iris.
- 2. Isolate iris pattern from the rest of the picture, analyze, and put in a system of coordinates.
- 3. Coordinates are removed using computerized data and in this way an iris mark is produced.
1.2.3 Facial Recognition
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Foreword
- Preface
- 1 Biometric Identification Using Deep Learning for Advance Cloud Security
- 2 Privacy in Multi-Tenancy Cloud Using Deep Learning
- 3 Emotional Classification Using EEG Signals and Facial Expression: A Survey
- 4 Effective and Efficient Wind Power Generation Using Bifarious Solar PV System
- 5 Background Mosaicing Model for Wide Area Surveillance System
- 6 Prediction of CKD Stage 1 Using Three Different Classifiers
- 7 Classification of MRI Images to Aid in Diagnosis of Neurological Disorder Using SVM
- 8 Convolutional Networks
- 9 Categorization of Cloud Computing & Deep Learning
- 10 Smart Load Balancing in Cloud Using Deep Learning
- 11 Biometric Identification for Advanced Cloud Security
- 12 Application of Deep Learning in Cloud Security
- 13 Real Time Cloud Based Intrusion Detection
- 14 Applications of Deep Learning in Cloud Security
- About the Editors
- Index
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app