
Step-by-Step Design of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Step-by-Step Design of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants
About this book
How to design a solar power plant, from start to finish
In Step-by-Step Design of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants, a team of distinguished engineers delivers a comprehensive reference on PV power plants—and their design—for specialists, experts, and academics. Written in three parts, the book covers the detailed theoretical knowledge required to properly design a PV power plant. It goes on to explore the step-by-step requirements for creating a real-world PV power plant, including parts and components design, mathematical formulations and calculations, analyses, evaluations, and planning.
The book concludes with a discussion of a sample solar plant design, as well as tips on how to avoid common design mistakes, and how to handle the operation and maintenance of PV power plants.
Step-by-Step Design of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants also includes:
- Thorough introductions to the basic requirements of design, economic analyses, and investment revenue
- Comprehensive explorations of the requirements for feasibility study and grid connection study
- Introducing solar resource, and determining optimum tilt angle and module inter-row spacing
- Presenting methodology for design of large-scale PV plant, requirements of engineering document, and optimal design algorithm
- In-depth examinations for selecting PV module, inverter, string, and DC side equipment
- Practical discussions of system losses, as well as estimation of yearly electrical energy production, capacity factor, and performance ratio of large-scale PV plant
Perfect for professionals in the solar power industry, Step-by-Step Design of Large-Scale Photovoltaic Power Plants will also earn a place in the libraries of equipment manufacturers and university professors seeking a one-stop resource for the design of PV power plants.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1
Introduction
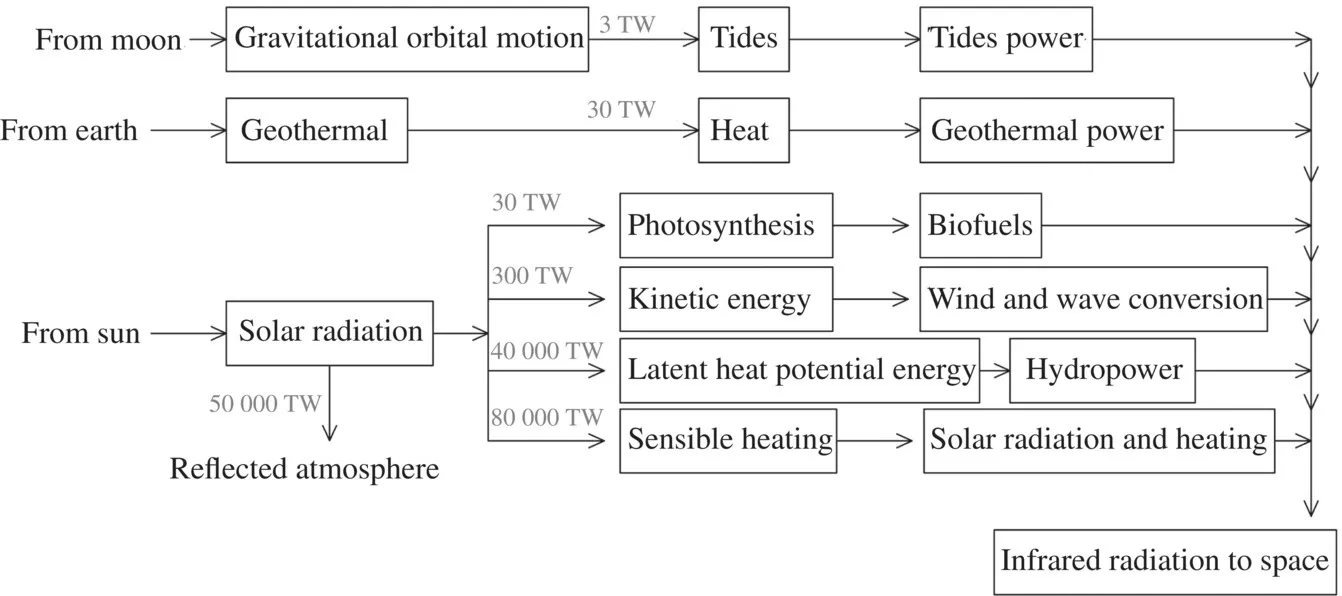
1.1 Solar Energy
1.2 Diverse Solar Energy Applications
1.2.1 Solar Thermal Power Plant
- Parabolic Plant The parabolic plant has a linear parabolic collector consisting of few rows of parabolic reflectors. The reflectors absorb the reflected rays of solar radiation and warm up the heat transfer fluid.
- Central Receiver Plant The central receiver plant consists of a set of mirrors, where each separately concentrates solar energy and transmits it to a central receiver tower.
- Parabolic Dish Plant In a parabolic dish plant, the sun's rays reflected on a parabolic surface are concentrated at a focal point. The thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy by a Stirling engine. An electric generator converts the mechanical energy into the electrical energy.
- Solar Chimney Plant In a solar chimney plant, a combination of solar air collectors and air conduction towers are used to produce induced air currents. The currents provide mechanical forces in order to rotate a pressure step turbine coupled to a generator to produce electricity.
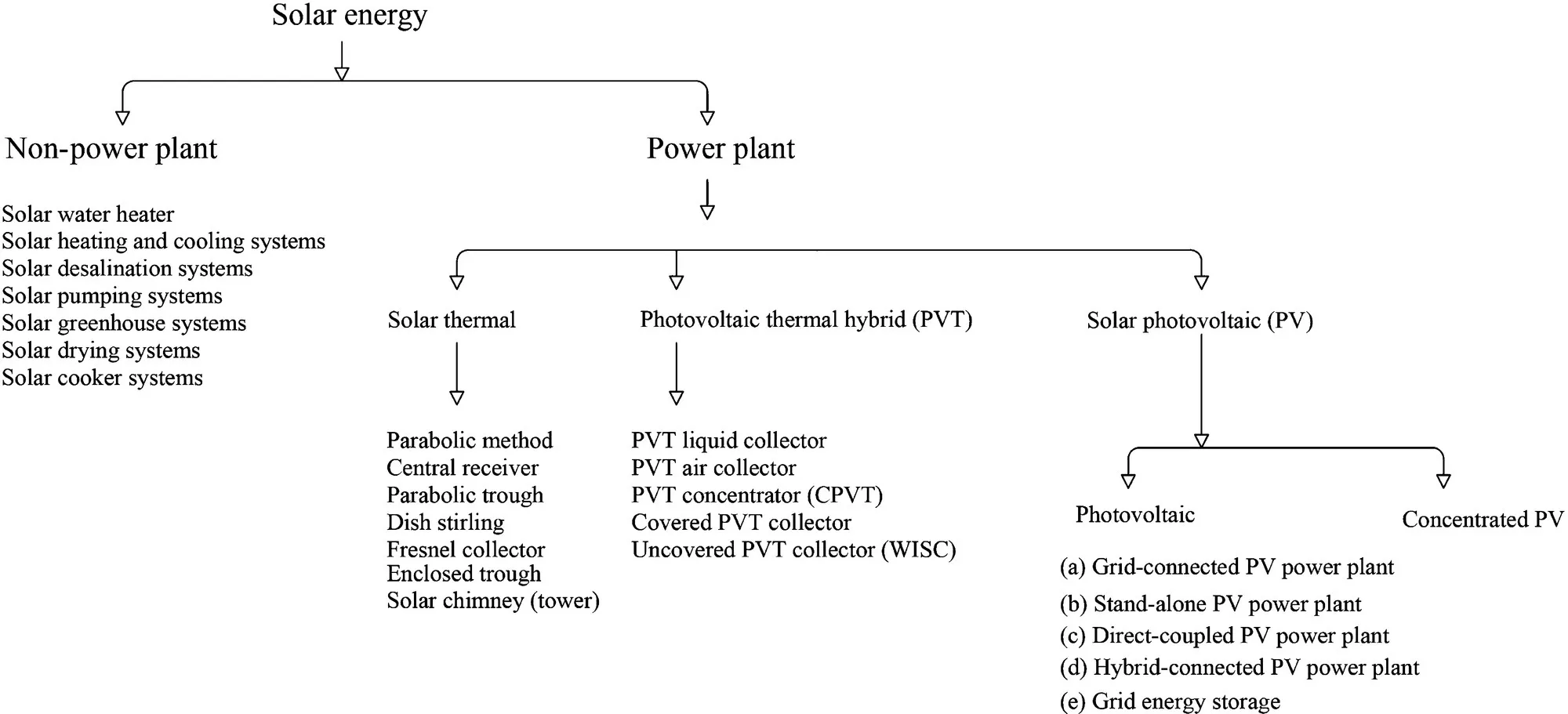 Figure 1.2 Various solar power plant categories.Source: Dincer and Abu‐Rayash [2].
Figure 1.2 Various solar power plant categories.Source: Dincer and Abu‐Rayash [2].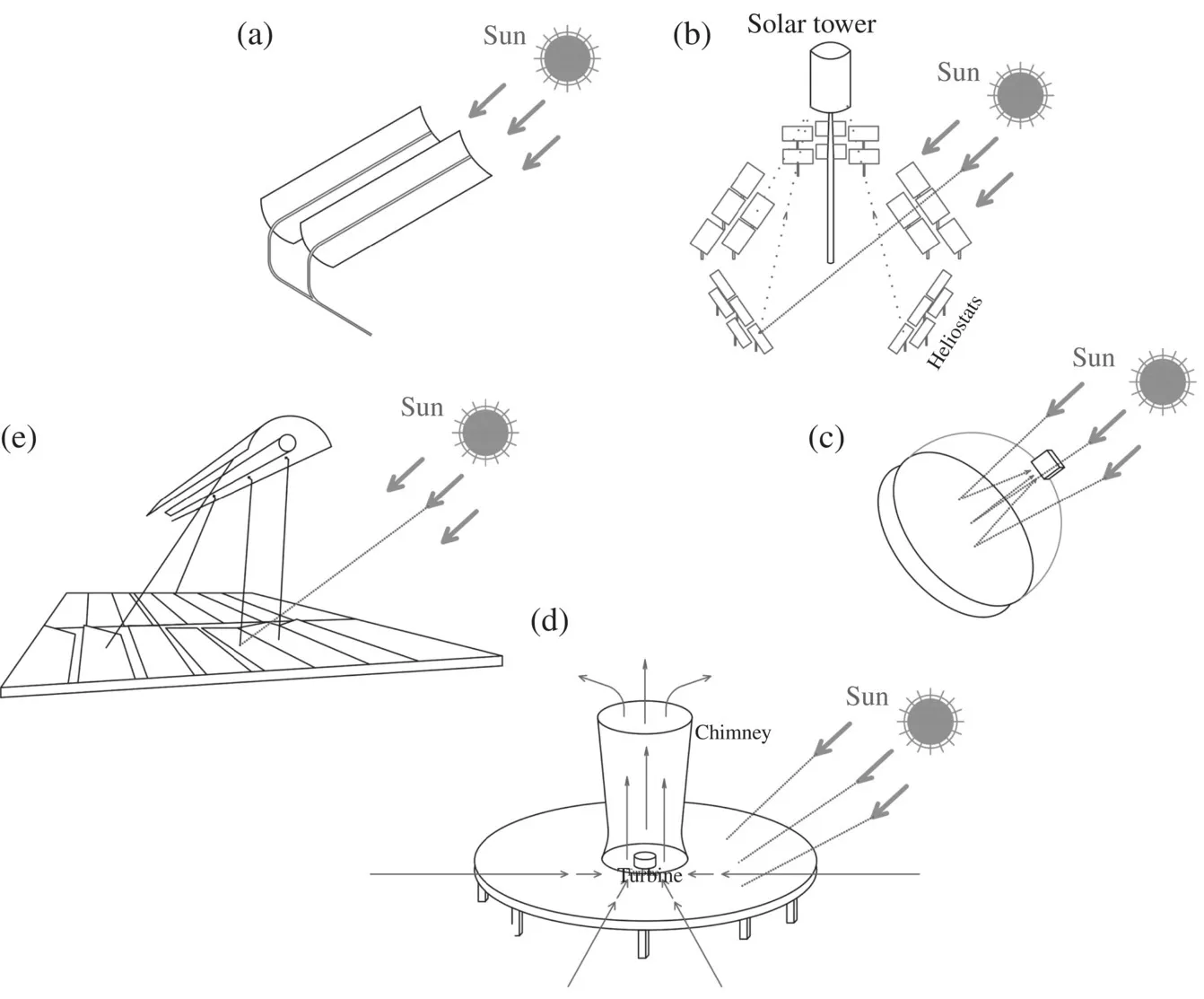 Figure 1.3 Various applications of solar thermal energy: (a) Parabolic plant, (b) Central receiver plant, (c) Parabolic dish plant, (d) Solar chimney plant, and (e) Fresnel collector plant.Source: Modified from González‐Roubaud et al. [3].
Figure 1.3 Various applications of solar thermal energy: (a) Parabolic plant, (b) Central receiver plant, (c) Parabolic dish plant, (d) Solar chimney plant, and (e) Fresnel collector plant.Source: Modified from González‐Roubaud et al. [3]. - Fresnel Collector Plant The Fresnel collector plant includes flat mirror collectors with low width and long length that collect the incoming sunlight on the concentrator and send it to a receiver tube. The receiver tube heats up the fluid inside the tube.
1.2.2 PV Thermal Hybrid Power Plant
1.2.3 PV Power Plant
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Preface
- Acknowledgment
- Acronyms
- Symbols
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Design Requirements
- 3 Feasibility Studies
- 4 Grid Connection Studies
- 5 Solar Resource and Irradiance
- 6 Large‐Scale PV Plant Design Overview
- 7 PV Power Plant DC Side Design
- 8 PV System Losses and Energy Yield
- Index
- End User License Agreement