
- 272 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Kafka in Action
About this book
Master the wicked-fast Apache Kafka streaming platform through hands-on examples and real-world projects. In Kafka in Action you will learn: Understanding Apache Kafka concepts
Setting up and executing basic ETL tasks using Kafka Connect
Using Kafka as part of a large data project team
Performing administrative tasks
Producing and consuming event streams
Working with Kafka from Java applications
Implementing Kafka as a message queue Kafka in Action is a fast-paced introduction to every aspect of working with Apache Kafka. Starting with an overview of Kafka's core concepts, you'll immediately learn how to set up and execute basic data movement tasks and how to produce and consume streams of events. Advancing quickly, you'll soon be ready to use Kafka in your day-to-day workflow, and start digging into even more advanced Kafka topics. About the technology
Think of Apache Kafka as a high performance software bus that facilitates event streaming, logging, analytics, and other data pipeline tasks. With Kafka, you can easily build features like operational data monitoring and large-scale event processing into both large and small-scale applications. About the book
Kafka in Action introduces the core features of Kafka, along with relevant examples of how to use it in real applications. In it, you'll explore the most common use cases such as logging and managing streaming data. When you're done, you'll be ready to handle both basic developer- and admin-based tasks in a Kafka-focused team. What's inside Kafka as an event streaming platform
Kafka producers and consumers from Java applications
Kafka as part of a large data projectAbout the reader
For intermediate Java developers or data engineers. No prior knowledge of Kafka required. About the author
Dylan Scott is a software developer in the insurance industry. Viktor Gamov is a Kafka-focused developer advocate. At Confluent, Dave Klein helps developers, teams, and enterprises harness the power of event streaming with Apache Kafka.Table of Contents
PART 1 GETTING STARTED
1 Introduction to Kafka
2 Getting to know Kafka
PART 2 APPLYING KAFK
3 Designing a Kafka project
4 Producers: Sourcing data
5 Consumers: Unlocking data
6 Brokers
7 Topics and partitions
8 Kafka storage
9 Management: Tools and logging
PART 3 GOING FURTHER
10 Protecting Kafka
11 Schema registry
12 Stream processing with Kafka Streams and ksqlDB
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part 1. Getting started
-
In chapter 1, we give a detailed description of why you would want to use Kafka, and we dispel some myths you might have heard about Kafka in relation to Hadoop.
-
In chapter 2, we focus on learning about the high-level architecture of Kafka as well as the various other parts that make up the Kafka ecosystem: Kafka Streams, Connect, and ksqlDB.
1 Introduction to Kafka
- Why you might want to use Kafka
- Common myths of big data and message systems
- Real-world use cases to help power messaging, streaming, and IoT data processing
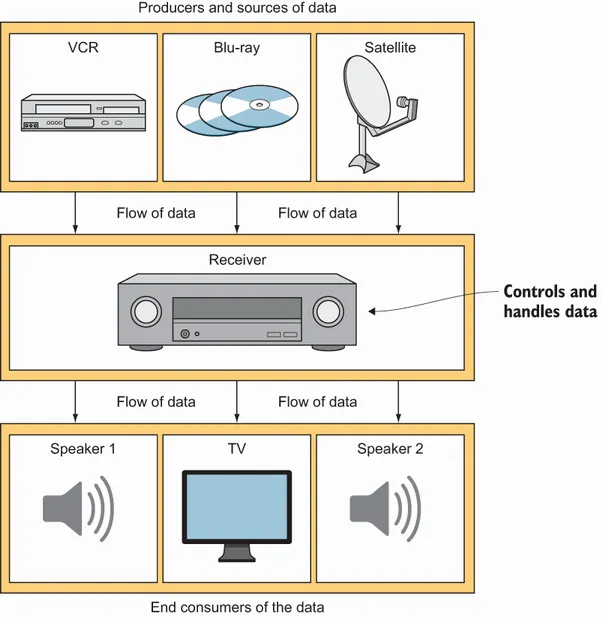
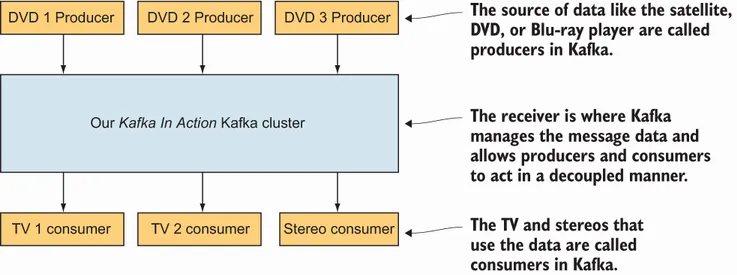
1.1 What is Kafka?
- Reading and writing records like a message queue
- Storing records with fault tolerance
- Processing streams as they occur [2]
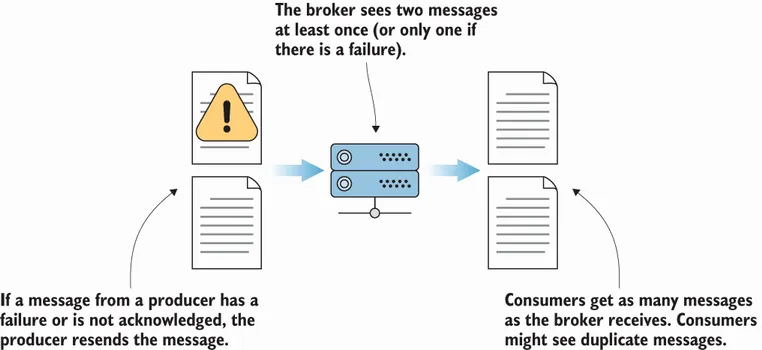
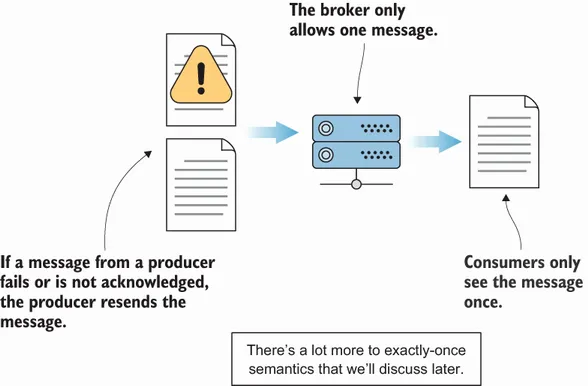
- At-least-once semantics—A message is sent as needed until it is acknowledged.
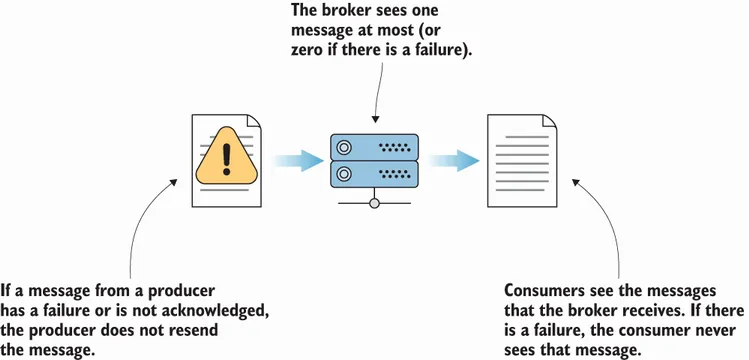
- At-most-once semantics—A message is only sent once and not resent on failure.
- Exactly-once semantics—A message is only seen once by the consumer of the message.
1.2 Kafka usage
Table of contents
- Kafka in Action
- Copyright
- Dedication
- Brief contents
- contents
- Front matter
- Part 1. Getting started
- 1 Introduction to Kafka
- 2 Getting to know Kafka
- Part 2. Applying Kafka
- 3 Designing a Kafka project
- 4 Producers: Sourcing data
- 5 Consumers: Unlocking data
- 6 Brokers
- 7 Topics and partitions
- 8 Kafka storage
- 9 Management: Tools and logging
- Part 3. Going further
- 10 Protecting Kafka
- 11 Schema registry
- 12 Stream processing with Kafka Streams and ksqlDB
- Appendix A. Installation
- Appendix B. Client example
- index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app