
Reinvention of Health Applications with IoT
Challenges and Solutions
- 191 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Reinvention of Health Applications with IoT
Challenges and Solutions
About this book
This book discusses IoT in healthcare and how it enables interoperability, machine-to-machine communication, information exchange, and data movement. It also covers how healthcare service delivery automates patient care with the help of mobility solutions, new technologies, and next-gen healthcare facilities with challenges faced and suggested solutions prescribed.
Reinvention of Health Applications with IoT: Challenges and Solutions presents the latest applications of IoT in healthcare along with challenges and solutions. It looks at a comparison of advanced technologies such as Deep Learning, Machine Learning, and AI and explores the ways they can be applied to sensed data to improve prediction and decision-making in smart health services. It focuses on society 5.0 technologies and illustrates how they can improve society and the transformation of IoT in healthcare facilities to support patient independence. Case studies are included for applications such as smart eyewear, smart jackets, and smart beds. The book will also go into detail on wearable technologies and how they can communicate patient information to doctors in medical emergencies.
The target audiences for this edited volume is researchers, practitioners, students, as well as key stakeholders involved in and working on healthcare engineering solutions.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1Deep Machine Learning for Sensing, Analysis, and Interpretation in IoT Healthcare
CONTENTS
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 How IoT Works
- 1.2.1 Sensors
- 1.2.2 Connectivity
- 1.2.3 Data Processing
- 1.2.4 User Interface
- 1.3 Applications of IoT
- 1.3.1 Consumer Applications
- 1.3.2 Commercial Applications
- 1.3.3 Industrial Applications
- 1.3.4 Infrastructure Applications
- 1.4 IoT for Healthcare
- 1.4.1 Medical Diagnosis
- 1.4.2 Robotic Surgeries
- 1.4.3 Recuperation
- 1.4.4 Monitoring and Destroying Pathogens
- 1.4.5 Hospital Operations Management
- 1.5 Overview of Deep Machine Learning
- 1.6 Approaches to Deep Learning
- 1.6.1 Supervised Learning
- 1.6.1.1 Regression
- 1.6.1.2 Classification
- 1.6.2 Unsupervised Learning
- 1.6.2.1 Clustering
- 1.6.2.2 Association
- 1.6.2.3 Dimensionality Reduction
- 1.6.3 Semisupervised Learning
- 1.7 Deep Machine Learning Neural Network Architectures
- 1.7.1 Artificial Neural Networks
- 1.7.2 Deep Neural Networks
- 1.7.3 Generative Adversarial Networks
- 1.7.4 Recurrent Neural Networks
- 1.7.5 Deep Belief Networks
- 1.8 Application of Deep Learning in IoT Healthcare
- 1.8.1 Classifying Image Data for Disease Detection (Malaria)
- 1.8.2 Predicting Epidemic Outbreaks
- 1.8.3 Pattern Imaging Analytics
- References
1.1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 HOW IoT WORKS
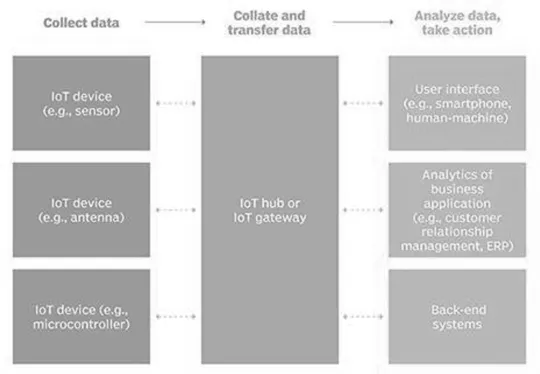
1.2.1 SENSORS
1.2.2 CONNECTIVITY
1.2.3 DATA PROCESSING
1.2.4 USER INTERFACE
1.3 APPLICATIONS OF IoT
1.3.1 CONSUMER APPLICATIONS
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Half-Title Page
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Preface
- About the Editors
- Chapter 1 Deep Machine Learning for Sensing, Analysis, and Interpretation in IoT Healthcare
- Chapter 2 IoT-Based Personalized Health and Fitness Monitoring System: The Next Big Thing
- Chapter 3 A Novel LC-DEH Algorithm to Enhance Efficiency and Security for Reliable Data Transmission in Blockchain with IoT-Based Healthcare Systems
- Chapter 4 Introduction to Blockchain Technology and Its Role in the Healthcare Sector
- Chapter 5 Emerging IoT Applications: Smart Dialysis Monitoring System
- Chapter 6 Role of Analytics in IoT: A Development of AAAS
- Chapter 7 IoT in M-Health Care
- Chapter 8 IoT-Based Anaesthesia Control and Monitoring System
- Chapter 9 Implantable Electronics: Real-Time Adaptive Image Security of Smart Visual Sensor Nod
- Chapter 10 Security Concerns with IoT-Based Health and Fitness Systems
- Chapter 11 Emerging eHealth IoT Applications: A Review on Kiosk-Based Systems
- Chapter 12 Early Identification of Medical Image Analysis for Normal and Abnormal Fetal Heart Rate: A Predictive Optimization Design