![]()
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
This book discusses and explores 10 emerging technology trends and their impact on the Financial Services industry.
The structure of the book can be split into four main parts:
Part One—Background and Context Setting
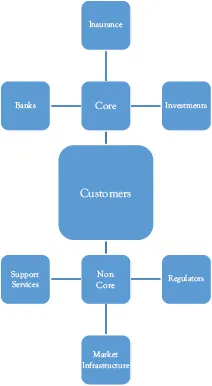
The first part starts (in Chapter 2) with a short overview of the Financial Services industry covering the main players which are summarized in Figure 1.1 below. This chapter is not meant to provide an in-depth overview but to provide sufficient context for the rest of the book.
Figure 1.1 High-level summary of the industry
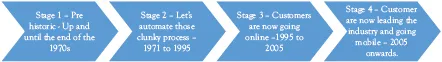
This is followed by (in Chapter 3) a history of the Financial Services industry and how technology has helped or hindered the growth of the industry. Again this chapter is not meant to provide a detailed chronological history with in-depth discussion, but it is to provide a sufficient context to explain how the industry has evolved with a particular nod to technology. This history is summarized in Figure 1.2 below.
Figure 1.2 The four stages of the financial services technology evolution
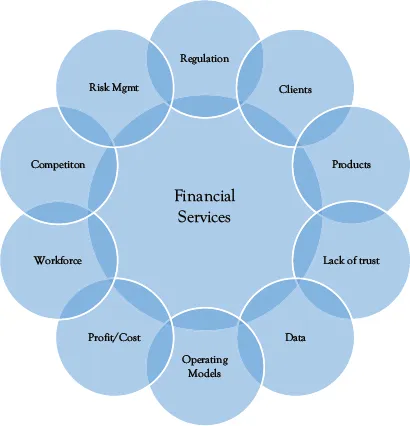
This first part then concludes (in Chapter 4) with a summary of the key challenges that the Financial Services industry is currently facing. These are summarized in Figure 1.3 below.
Figure 1.3 Summary of the challenges of impacting the financial services industry
Part Two—Exploring the Impact of the 10 Emerging Technology Trends
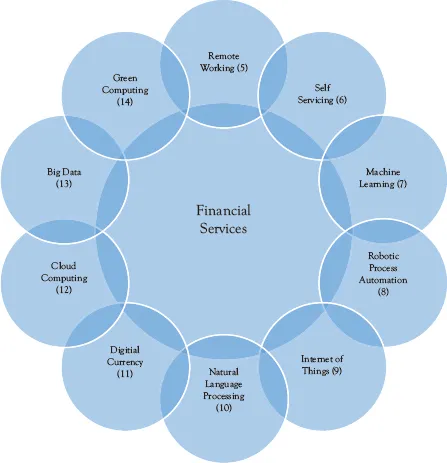
The second part is the main part of this book. It contains 10 chapters (from Chapters 5 to 14) with each chapter discussing an individual technology trend and its impact on the Financial Services industry. The 10 trends are summarized in Figure 1.4 below.
Figure 1.4 Summary of the 10 technology trends
The structure of each chapter is similar. Initially, an overview of the technology is given with the benefits it can provide at a general level. Then each chapter will discuss how the technology is currently being used within the Financial Services industry followed by a discussion on the pragmatic challenges of implementing and using the technology. This leads to how the technology either helps with or hinders the key industry challenges listed in Chapter 4. Each chapter then ends with a case study followed by a small summary of the key points to aid understanding.
Part Three—Wrap Up and Looking to the Future
The third and final part is a summary of the book outlining the key themes and challenges going forward.
![]()
CHAPTER 2
Overview of the Financial Services Industry
This chapter provides a summary of the Financial Services industry. It is not meant to provide an in-depth overview but to provide sufficient context for the rest of the book.
A Simple Definition
The Financial Services industry is a wide and complex area (which this chapter will hopefully demonstrate) which means providing a precise definition can be challenging. Therefore for this book, it will be defined as follows:
The Financial Industry consists of many Financial Services Organizations providing financial services products/services to their customers and consumers.
The Financial Services Organizations that provide these services cover many firms such as banks, credit card providers, investment managers plus others.
The products/services provided cover offerings such as bank accounts, investment products, credit cards, investment advice, capital funding plus others.
These customers and consumers who receive these products/ services will cover everything from individual retail customers to large multinational organizations, local/national governments and pension funds.
Why Is Financial Services Critical?
It is safe to say that the Financial Services industry is critical to the dayto-day operations of the global economy.
The movement of money must happen and if it does not happen then there will be material issues. For example, imagine the situation if invoices, salaries, or pensions were not being paid? There would be uproar, possible rioting, and a general breakdown of society.
Likewise, many activities legally need insurance in place to allow them to happen. For example, a pilot and airline need insurance to fly a plane, people need insurance to drive a car, and people often need to take out insurance before going on holiday.
How Big Is the Financial Services Industry?
Unfortunately, obtaining accurate statistics on the size of the Financial Services industry (or any industry for that matter) is challenging. This is because most assessments are performed using different measurements, using different methodologies, using differing timescales, using different assumptions, and are often performed for different purposes.
However, some high-level statistics can be quoted to demonstrate the size of the global Financial Services industry.
• Forbes in 2019 created a “list of world’s largest public firms in revenue generation” which showed Banking as the third biggest industry by sales globally (at USD 4.424 trillion) and Insurance as the sixth biggest industry by sales globally (at USD 2.611 trillion). The top industry was Oil and Gas (at USD 4.797 trillion) with Technology (also a topic of this book) coming in second at USD 4.726 trillion. Therefore, if Banking and Insurance were combined under the umbrella of Financial Services then it would be the largest industry by sales globally.
• The same study also assessed profitability by industry and Banking was top of the list at USD 773 million with Technology second (at USD 548 billion) and Oil and Gas third (at USD 292 billion). Insurance, in this case, was much further down the list with a profitability of USD 148 billion.
This means it is safe to say that Financial Services (and Technology for that matter) is one of the world’s largest industries in terms of revenue and profitability.
The Structure of the Financial Services Industry
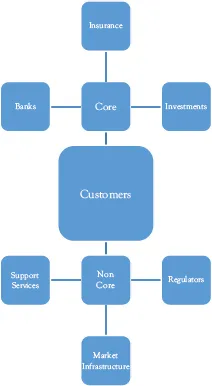
Figure 2.1 provides a high-level summary of the main areas of the industry.
At the center of the industry is (or should always be) the customer because ultimately they are the people which the industry is trying to service. Without customers, the industry would not exist. This area is discussed in more detail further below.
Figure 2.1 High-level summary of the industry
Around the customers, there are a variety of industry players which can be split into “core” players and “non-core” players namely:
• “Core” players are the organizations that provide actual financial products and services to customers. These organizations are Banks, Insurance (and Pension) Companies, and Investors. These are discussed in more detail below.
• “Non-core” players are other key industry members but these provide support services to the industry and do not provide actual services or products to the customers or consumers. These cover organizations such as Technology firms, Legal firms, Infrastructure, and Regulators. These are discussed in more depth below.
Customers
A customer can be any person or organization that can exist globally. For example, these could be individual people, partnerships, charities, organizations, and government bodies. Customers are the group who the industry is supposed to serve but (as this book will demonstrate) this is much more challenging than it sounds. This is because firms are often diverted away from serving their customers due to regulatory challenges, operating model complexities, the challenges of “going green,” the need to make a return for their shareholders plus many others....