
Essentials of Nursing Adults
- 792 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Essentials of Nursing Adults
About this book
Drawing together the best of text, video and interactive material for the definitive guide to adult nursing.
This one-stop-shop will enable students to understand the core aspects of care, learn the essential nursing skills and knowledge that underpin practice, deal with the complexities of the role and apply their learning to common conditions and patient groups. It has been developed in line with the 2018 NMC standards to provide a complete learning resource for adult nursing students.
Key features:
- Uses patient centered care and evidence-based practice as guiding principles throughout
- Clear and engaging features to help students understand the core theory and knowledge, apply it to nursing practice, revise for assessments and exams, and go further in their independent study.
- 12 months free access to an interactive eBook version, meaning you can access the book anytime.
The book is supported by online resources, including links to up to 100 instructional videos, case studies and accompanying questions, access to selected SAGE journal articles, weblinks, multiple-choice quizzes, and glossary flashcards.
Designed to make learning flexible and fun, leaving students better prepared for practice and ready to thrive in their future careers.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 The changing world of healthcare

This chapter covers
- The impact of a growing and ageing population and the increase in long-term conditions
- The impact of lifestyle choices and a shifting focus to prevention
- Changing expectations of healthcare
- New care models, increasing use of technology and changes in professional roles
- Nursing in a global context.
Nursing has changed significantly since I qualified in the 1980s, back then nurses did not even give IV drugs, now I work in a GP surgery running my own clinics and am a nurse prescriber.Ali, GP practice nurse
Introduction
The impact of a growing and ageing population
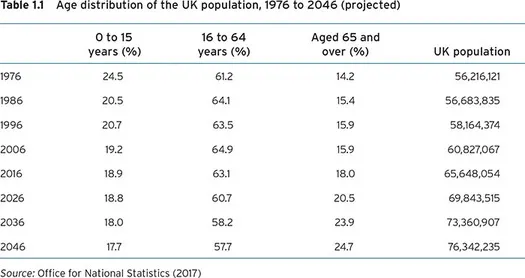
- Increased frailty, incidence of falls and subsequent neck of femur fractures
- Increased disability, including sight and hearing loss, resulting in reduced ability to carry out activities of daily living (ADL) independently
- Increased malnutrition
- Increased incontinence
- Increased incidence of mental health problems, such as depression and dementia
- Increased loneliness and social isolation
- Increased burden on unpaid family carers, many of whom are older adults themselves.



The impact of long-term conditions


The impact of lifestyle choices
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Publisher Note
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Foreword
- Guide to your book
- Notes on the editors and contributors
- Acknowledgments
- I Principles of Nursing Adults
- 1 The changing world of healthcare
- 2 Person-centred care
- 3 Professional values
- 4 Safeguarding adults at risk of harm
- 5 Patient safety
- 6 Research and evidence-based practice in nursing
- 7 Health promotion
- II Aspects of Nursing Adults
- 8 The fundamentals of care in nursing adults
- 9 Assessment of the adult with acute needs
- 10 Preparing adults for surgery, periand post-operative surgical care
- 11 Pain assessment and management
- 12 Clinical investigations
- 13 Medication management and administration
- 14 Infection prevention and control
- III Managing Nursing Care of Adults with Additional, Complex and High Dependency Needs
- 15 Care of the childbearing woman
- 16 Care of the highly dependent and critically ill adult
- 17 Care of the frail older adult
- 18 Care of the adult with long-term conditions
- 19 Care of the adult with mental health issues
- 20 Care of the adult with dementia
- 21 Care of the adult with a learning disability
- 22 Care of the adult with cancer
- 23 Care of the adult at the end of life
- IV Managing Nursing Care of Adults with Specific Conditions
- 24 Care of the adult with a respiratory condition
- 25 Care of the adult with a cardiac condition
- 26 Care of the adult with a vascular condition
- 27 Care of the adult with a neurological condition
- 28 Care of the adult with a urinary/renal condition
- 29 Care of the adult with an endocrine condition
- 30 Care of the adult with an immunological condition
- 31 Care of the adult with a musculoskeletal condition
- 32 Care of the adult with a haematological condition
- 33 Care of the adult with a dermatological condition
- 34 Care of the adult with a gastrointestinal condition
- 35 Care of the adult with a nutritional condition
- V Being a Professional Adult Nurse
- 36 Leadership and management in nursing adults
- 37 Decision-making
- 38 Lifelong learning and continuing professional development
- 39 The role of the nurse as teacher and educator
- Glossary
- Index