
eBook - ePub
Industrial Internet of Things
Technologies, Design, and Applications
- 248 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Industrial Internet of Things
Technologies, Design, and Applications
About this book
Industrial Internet of Things: Technologies, Design, and Applications addresses the complete functional framework workflow in IoT technology. It explores basic and high-level concepts, thus serving as a manual for those in the industry while also helping beginners. The book incorporates the working methodology of Industrial IoT works, is based on the latest technologies, and will cover the major challenges, issues, and advances while exploring data-based intelligent and automated systems and their implications to the real world. The book discusses data acquisition, security, learning, intelligent data analysis, and case studies related to Industrial IoT-based applications.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Industrial Internet of Things by Sudan Jha, Usman Tariq, Gyanendra Prasad Joshi, Vijender Kumar Solanki, Sudan Jha,Usman Tariq,Gyanendra Prasad Joshi,Vijender Kumar Solanki in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Industrial Engineering. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 Introduction to Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
Hanan Ahmed
High Institute for Computers and Management Information System, New Cairo, Egypt
A.A. Ramadan and E.H. Elkordy
Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef, Egypt
Ahmed A. Elngar
Faculty of Computers and Artificial Intelligence Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef City, Egypt
DOI: 10.1201/9781003102267-1
Contents
- 1.1 Industrial Internet of Things
- 1.2 IoT, IIoT and Industry 4.0
- 1.3 IIoT Architectures and Frameworks
- 1.4 Challenges of IIoT
- 1.5 Conclusion
- References
1.1 Industrial Internet of Things
IIoT serves as a modern vision of IoT within the industrial sector by mechanizing smart objects for detecting, collecting, sensing, handling, and communicating the events of the real-time occasion in industrial systems. The main objective of IIoT is to achieve high operational productivity, expanded efficiency, and superior management of industrial resources and forms through item customization, brilliantly checking applications for generation floor shops and machine well-being, and predictive and preventive support of industrial hardware [3]. In [1], authors have defined the IIoT as follows: “Industrial IoT (IIoT) is the network of intelligent and highly connected industrial components that are deployed to achieve high production rate with reduced operational costs through real-time monitoring, efficient management and controlling of industrial processes, assets and operational time”.
IoT and IIoT have their particular focuses on concepts and viable application scenarios in spite of the fact that the IIoT is inferred from the IoT. The IoT broadly acknowledged by individuals is basically consumption-oriented and aims to improve people’s quality of life. The foremost normal application scenarios of IoT are keen domestic, well-being observing, and indoor localization. The IIoT is production-oriented and points to make strides in mechanical generation productivity. Ordinary application scenarios of IIoT incorporate perceptive coordination, inaccessible maintenance, and brilliantly production lines. The framework systems of diverse IoT application scenarios, by and large, have to be built from scratch, and the sending scale of sensors is generally little with low exactness requirements [4]. In any case, the framework systems of IIoT application scenarios are built based on the conventional mechanical framework, so the sending scale of sensors is exceptionally expansive with tall accuracy prerequisites. For the IoT, gadgets, for the most part, have solid portability, create medium information volume, and have a tall resilience for the delay; whereas for the IIoT, most of the gadgets are settled in position, produce an incredible sum of seen information, and have a too resistance for the delay [5]. The concept of IIoT is closely related to a few broadly acknowledged concepts, such as cyber-physical frameworks (CPSs), IoT, the Mechanical Web, and Industry 4.0. CPS, proposed by Helen Gill in 2006, emphasizes the profound integration of different data innovations, such as detecting innovation, implanted innovation, and program & equipment innovation, pointing to attain profoundly synergistic and independent informationization capabilities, real-time and adaptable criticism, and positive cycle between the physical and data universes. As a subset of CPS, IoT basically emphasizes the intuition between objects through the Internet based on one of a kind recognizable pieces of proof. The globalization, openness, interoperability, and socialization of the web give the premise for supporting the IoT concept [6]. The Industrial Internet, proposed by the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) propelled by the top five companies within the US, to be specific GE, AT&T, IBM, Intel, and Cisco, primarily centers on the development, application, and standardization of imaginative systems, the upgrade of information circulation, and the digital change of the full mechanical field. The subconcept of IIoT called Industry 4.0 propelled in Germany may be an all-inclusive arranged, manufactured intelligence-based data CPS, basically within the shrewd fabricating field. In rundown, CPS gives an outline for the relationship between the physical world and data world based on the interconnection of things, so CPS speaks to the broadest of the concepts specified over. IoT highlights the interconnects among objects through physical addresses, in any case of whether they are industry or civilian situated, whereas the Mechanical Web depicts the potential future patterns of businesses based on rising technologies [6, 7].
1.2 IoT, IIoT and Industry 4.0
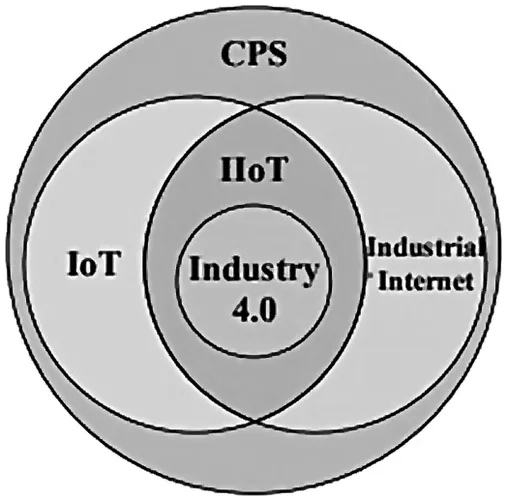
IoT, IIoT, and Industry 4.0 are closely related concepts but cannot be traded utilized. In this area, we offer a harsh classification of these terms. Concerning the IoT, a few definitions exist, each one attempting to capture one of its essential characteristics. It is frequently considered as a sort of web for the machines, highlighting the point of permitting things to trade information. Nonetheless, application areas so different from a few necessities (particularly those related to communication angles) can be exceptionally diverse, depending on the planning objectives and end-users, the basic commerce models, and the received mechanical arrangements [7]. What is usually addressed as IoT could be better named as consumer IoT, as opposed to IIoT. Customer IoT is human-centered; the “things” are savvy buyer electronic gadgets interconnected with each other in arrange to make strides human mindfulness of the encompassing environment, sparing time and cash. In common, customer IoT communications can be classified as machine-to-user and within the shape of client–server intelligence. On the other hand, within the industrial world, we are helping to the approach of the computerized and shrewd fabricating, which point at coordination Operational Innovation (OT) with Data Innovation (IT) spaces [8]. In exceptionally few words, the IIoT (the fundamental column of advanced fabricating) is almost interfacing all the mechanical resources, counting machines, and control frameworks, with the data frameworks and the commerce forms [8]. As a result, the huge amount of information collected can nourish analytics arrangements and lead to ideal mechanical operations. On the other hand, shrewd fabricating clearly centers on the fabricating arrange of (shrewd) items life cycle, with the objective of rapidly and powerfully react to request changes. Subsequently, the IIoT affects all the mechanical esteem chain and could be a necessity for savvy manufacturing. As underlined within the taking after, communication in IIoT is machine arranged and can extend over a huge assortment of distinctive showcase divisions and exercises. The IIoT scenarios incorporate bequest observing applications (e.g., handle checking in generation plants) and imaginative approaches for self-organizing frameworks (e.g., autonomic mechanical plant that requires small, in case any, human intervention) [9]. Whereas the foremost common communication prerequisites of IoT and IIoT are comparable, e.g., bolster for the web biological system utilizing low-cost, resource-constrained gadgets and organize versatility, numerous communication necessities are particular to each space and can be exceptionally distinctive, e.g., Quality of Benefit (QoS) (in terms of determinism, inactivity, throughput, etc.), the accessibility and unwavering quality, and the security and privacy [8, 9]. IoT centers more on the plan of modern communication benchmarks, which can interface novel gadgets into the web environment in an adaptable and user-friendly way. By differentiating, the current plan of IIoT emphasizes conceivable integration and interconnection of once disconnected plants and working islands or indeed machinery, thus advertising a more proficient generation and unused administrations [9]. For this reason, compared with IoT, IIoT can be considered more of an advancement instead of an insurgency. Table I gives a subjective comparison of these innovations. Regarding the network and criticality, IoT is more adaptable, permitting ad hoc and portable arrange structures and having less exacting timing and unwavering quality necessities (but for therapeutic applications) [10]. On the other hand, IIoT regularly utilizes settled and infrastructure-based organization that are well planned to coordinate communication and coexistence needs. In IIoT, communications are within the frame of machine-to-machine joins that got to fulfill rigid prerequisites in terms of convenience and unwavering quality. Taking prepare robotization as a case space where handle observing and control applications can be assembled into three subcategories: monitoring/supervision, closed circle control, and interlocking and control [11]. Whereas observing and supervision applications are less touchy to parcel misfortune and jitter and can endure transmission delay at moment level, closed circle control and interlocking and control applications require bounded delay at the millisecond level (10–100 ms) and a transmission unwavering quality of 99.99%. Comparing the information volume, the created information from IoT is intensely application subordinate, whereas IIoT right now targets analytics. The concept of Industry 4.0 (where 4.0 speaks to the fourth industrial revolution) emerges when the IoT worldview is blended with the CPSs thought [10]. Initially characterized in Germany, the Industry 4.0 concept has picked up a worldwide permeability and it is these days all around embraced for tending to the utilize of web innovations to move forward generation proficiency by implies of shrewd administrations in shrewd industrial facilities. CPSs amplify real-world, physical objects by interconnection them through and through and giving their computerized depictions. Such data, put away in models and information objects that can be upgraded in genuine time, speak to a moment personality of the question itself and constitutes a sort of “digital twin”. Thanks to the dynamic nature of these advanced twins, inventive administrations that were not conceivable in the past can be executed over the total item lifecycle, from inception to transfer of fabricated items [11]. IIoT could be a subset of IoT, which is particular to mechanical applications. The fabricating stage of the item lifecycle is where the IoT and Industry 4.0 meet, starting with the IIoT. Figure 1.1 shows convergences of IoT, CPS, IIoT, and Industry 4.0. It must be highlighted that the IIoT worldview isn’t intended for substituting conventional computerization applications, but points at expanding the information around the physical framework of intrigued.
As a result, the IIoT (at slightest nowadays) isn’t related to controlling applications at the field level, where bounded response time (i.e. determinism) must be guaranteed. On the opposite, as already expressed, IIoT applications counting supervision, optimization, and expectation exercises are ordinarily assembled into the so-called computerized or cloud fabricating (CM). The development intrigued by this subject is affirmed by the wide extend of writing. A study around CM is detailed in [10]. Within the past, the supervision exercises were ruled by man, but proficient machine-to-machine communications make human intercession pointless and expand the working run to a geological scale. For occasion, the accessibility of solid, brief idleness associations on such an expansive scale may increment the income [11]. The work in [12] highlights the significance of a real-time, large-scale approach for hardware upkeep applications. An IIoT-based energetic generation coordination engineering is displayed in [12] for real-time synchronization of inside and open generation coordination assets. In [13], the optimization of generation planning is based on IIoT decentralized vitality forecast calculations encouraged by the current state of the machines. Finally, the dynamic decrease of idleness and jitter of the Internet-based network will increment the extent of conceivable applications, as detailed in [14].
1.3 IIoT Architectures and Frameworks
A nonexclusive architecture of IIoT frameworks was talked about by the industrial web consortium [15] which is displayed in Figure 1.2 where IIoT gadgets and mechanical information sources create persistent information streams at Layer 1, whereas the edge servers and cloud computing frameworks enable IIoT applications at Layer 2 and Layer 3, separately. The endeavor applications are portrayed at Layer 4. Figure 1.2 appears the stream of information and data among diverse layers as well because it shows the organization stream for asset administration and operational flow for overseeing resources within the mechanical systems. In any case, diverse analysts unexpectedly see these designs considering plan varieties in terms of area mindfulness, communication standards, computational assignments, execution ideal models, asset administration plans, security, security, protection, accessibility, and versatility, to title some. Campobello et al. [16] have proposed an arrangement for IIoT named Remote Advancement for Computerization (WEVA) that’s based on open-source computer programs and communication conventions. Its design comprises sensors, actuator sheets, bits and working framework, conventions, get to portal, administrations, and applications. Besides, WEVA employs simple WSN as a graphical administration apparatus. The creators suggest that IPv6 may be a prerequisite for IIoT in terms of adaptability. In any case, consolidating these network advances isn’t a simple work in arrange to realize a high-performance IIoT in term...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Half Title Page
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Contents
- Foreword
- Editors
- Contributors
- 1 Introduction to Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- 2 Challenges in Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
- 3 IoT-Based Automated Healthcare System
- 4 Internet of Things (IoT)-Based Industrial Monitoring System
- 5 Internet Working of Vehicles and Relevant Issues in IoT Environment
- 6 Adoption of Industry 4.0 in Lean Manufacturing
- 7 Internet of Things-Based Economical Smart Home Automation System
- 8 Machine Vision Technology, Deep Learning, and IoT in Agricultural Industry
- 9 IIoT Edge Network and Spectrum Scarcity Issue
- 10 Review on Optical Character Recognition-Based Applications of Industrial IoT
- 11 Using Blockchain in Resolving the Challenges Faced by IIoT
- 12 Internet of Things-Based Arduino Controlled On-Load Tap Changer Distribution Transformer
- Index