
Bayesian Reasoning and Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning Applications
- 133 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Bayesian Reasoning and Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning Applications
About this book
This book introduces Bayesian reasoning and Gaussian processes into machine learning applications. Bayesian methods are applied in many areas, such as game development, decision making, and drug discovery. It is very effective for machine learning algorithms in handling missing data and extracting information from small datasets. Bayesian Reasoning and Gaussian Processes for Machine Learning Applications uses a statistical background to understand continuous distributions and how learning can be viewed from a probabilistic framework. The chapters progress into such machine learning topics as belief network and Bayesian reinforcement learning, which is followed by Gaussian process introduction, classification, regression, covariance, and performance analysis of Gaussian processes with other models.
FEATURES
- Contains recent advancements in machine learning
- Highlights applications of machine learning algorithms
- Offers both quantitative and qualitative research
- Includes numerous case studies
This book is aimed at graduates, researchers, and professionals in the field of data science and machine learning.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Introduction to Naive Bayes and a Review on Its Subtypes with Applications
CONTENTS
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Intuition behind the Naive Bayes Algorithm and Its Subtypes with Applications
- 1.2.1 Why Is It Called Naive Bayes?
- 1.2.2 Bayes Theorem – Intuition behind the Classification
- 1.2.2.1 Bayes Theorem
- 1.2.2.2 Bayes Theorem in Machine Learning
- 1.2.3 Types of Naive Bayes Models
- 1.2.4 Gaussian Naive Bayes
- 1.2.5 Predictions Using Gaussian Naive Bayes Model
- 1.2.6 Bernoulli Classification
- 1.2.6.1 Bernoulli Statistics or Distribution
- 1.2.6.2 Rule for Bernoulli Naive Bayes Classifier
- 1.2.6.3 An Example for Bernoulli Naive Bayes
- 1.2.6.4 Advantages
- 1.2.6.5 Disadvantages
- 1.2.7 Multinomial Naive Bayes Classifier
- 1.2.8 Differences between Gaussian, Bernoulli, and Multinomial Distributions
- 1.2.9 Advantages of Naive Bayes
- 1.2.10 Disadvantages of Naive Bayes
- 1.3 Real-Time Application: Human Activity Recognition Using Naive Bayes Algorithm
- 1.3.1 Dataset Attributes
- 1.3.2 Naive Bayes Algorithm–Based Result
- 1.4 Conclusion
- References
1.1 Introduction
- Supervised learning algorithms
- Unsupervised learning algorithms
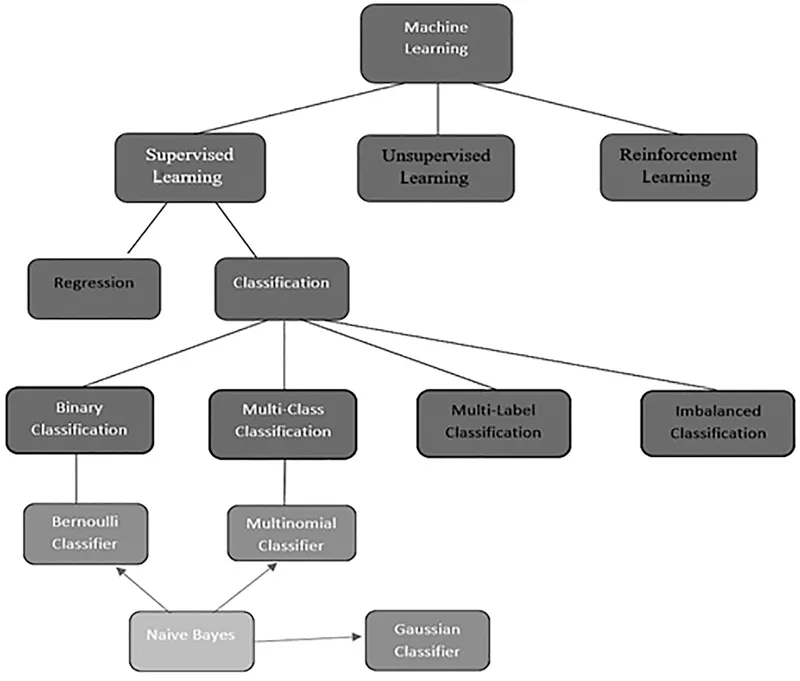
- Regression modeling
- Classification modeling
1.2 Intuition behind the Naive Bayes Algorithm and Its Subtypes with Applications
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- 1. Introduction to Naive Bayes and a Review on Its Subtypes with Applications
- 2. A Review on the Different Regression Analysis in Supervised Learning
- 3. Methods to Predict the Performance Analysis of Various Machine Learning Algorithms
- 4. A Viewpoint on Belief Networks and Their Applications
- 5. Reinforcement Learning Using Bayesian Algorithms with Applications
- 6. Alerting System for Gas Leakage in Pipelines
- 7. Two New Nonparametric Models for Biological Networks
- 8. Generating Various Types of Graphical Models via MARS
- 9. Financial Applications of Gaussian Processes and Bayesian Optimization
- 10. Bayesian Network Inference on Diabetes Risk Prediction Data
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app