
Nutritional and Integrative Strategies in Cardiovascular Medicine
- 414 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Nutritional and Integrative Strategies in Cardiovascular Medicine
About this book
Despite decades of aggressive pharmaceutical and surgical interventions, coronary artery disease (CAD) remains the number one killer of both men and women in the Western world. The most important aspect in the treatment of CAD is to focus on prevention. Indeed, prevention is easier than cure and when CAD does present itself, a combination of conventional and alternative methodologies can truly make a difference in people's lives. Building upon its predecessor, Nutritional and Integrative Strategies in Cardiovascular Medicine, Second Edition, provides scientific and clinical insight from leaders in the field of cardiovascular medicine who explore an integrative approach to treating and curing cardiovascular diseases through conventional and non-allopathic methodologies.
Nutritional interventions with both appropriate non-inflammatory diets and targeted nutraceutical supports are simple and basic strategies to prevent as well as help manage CAD and congestive heart failure (CHF). In fact, nutritional strategies in the treatment of CHF have not only afforded patients a better quality of life but increased survival as well. This evidence-based book describes how to integrate nutrition, supplements, lifestyle changes, and medications for improved outcomes in hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, infectious myocarditis and much more.
Topics include:
- Covid-19: An evidence-based integrative approach to supporting the myocardium
- Metabolic cardiology: An exciting new way to manage heart failure
- Contains information on hypertension and dyslipidemia
- Naturopathic approaches
- Mediterranean diet as the longevity diet of the world
- Value of omega-3s and other fats
- Role of botanicals in the treatment of cardiovascular disease
- Integrative care of the patient in extending quality of life
- Gender-specific medicine – Perhaps a new evolving cardiovascular sub-specialty
- Role of dental disease inflammation and cardiovascular disease
- Environmental toxins and the heart
- Earthing and grounding as an energetic nutrition in healing the heart
- Autophagy and mTOR – the "new medicine" of the future
Nutritional medicine is vitally important in the integrative care of the patient. This book will assist established health professionals as well as students preparing for advanced degrees in healthcare and offer cutting-edge and new information in cardiovascular medicine. It offers simple nutritional supports that can make the difference between not only easing human suffering, but also life and death.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1 Nutrition, the Mediterranean Diet and Selected Supplements for the Prevention and Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
Contents
- Introduction
- Revolutionizing the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease and Interrupting the Finite Pathways
- Atherosclerosis, Endothelial Dysfunction and Arterial Stiffness
- Nutrition and CHD
- Specific Diets and Coronary Heart Disease
- Mediterranean Diet (TMD: Traditional Mediterranean Diet) (PREDIMED Diet)
- Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diets (DASH 1 and 2)
- Dietary Fats
- Omega 3 Fatty Acids (PUFA)
- Monounsaturated Fats
- Saturated Fatty Acids
- Conclusions and Summary on SFA [14,28,31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56]
- Trans Fatty Acids
- Coconut Oil
- Milk, Milk Products and Peptides
- Whey Protein
- Eggs
- Refined Carbohydrates, Sugars and Sugar Substitutes
- Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
- Protein
- Vegetarian Diets and Plant-Based Nutrition
- Animal Protein Diets
- Soy Protein
- Fish
- Dietary Acid Load and Protein
- Specific Dietary and Nutritional Components and Caloric Restriction
- Caffeine
- Caloric Restriction
- Alcohol
- Gluten
- Nuts
- Dietary Sodium, Potassium and Magnesium
- Summary and Conclusions
- References
Introduction
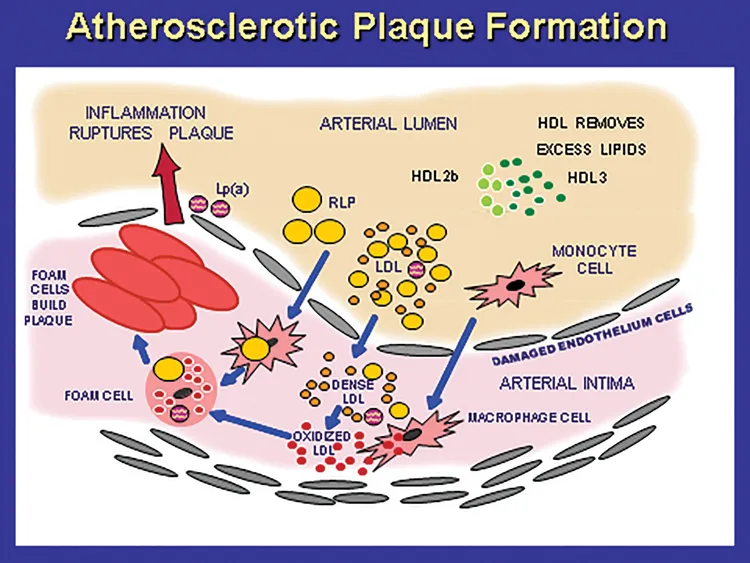
Revolutionizing the Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease and Interrupting the Finite Pathways
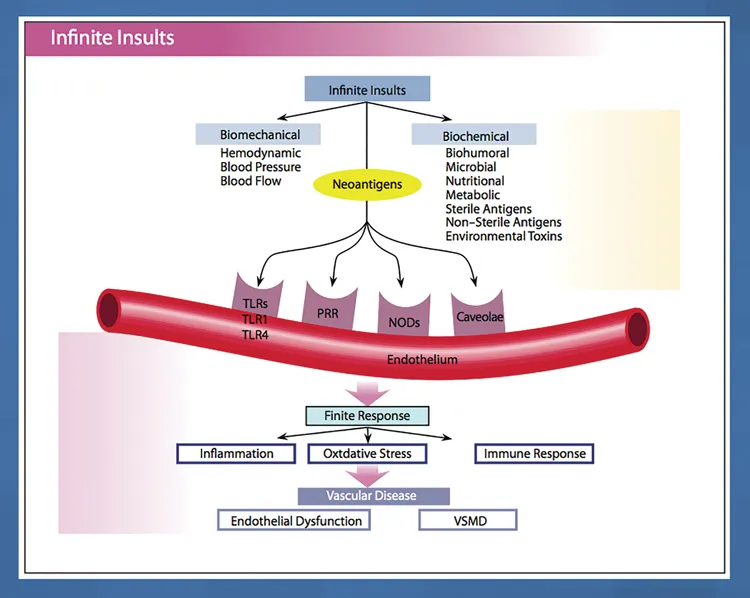
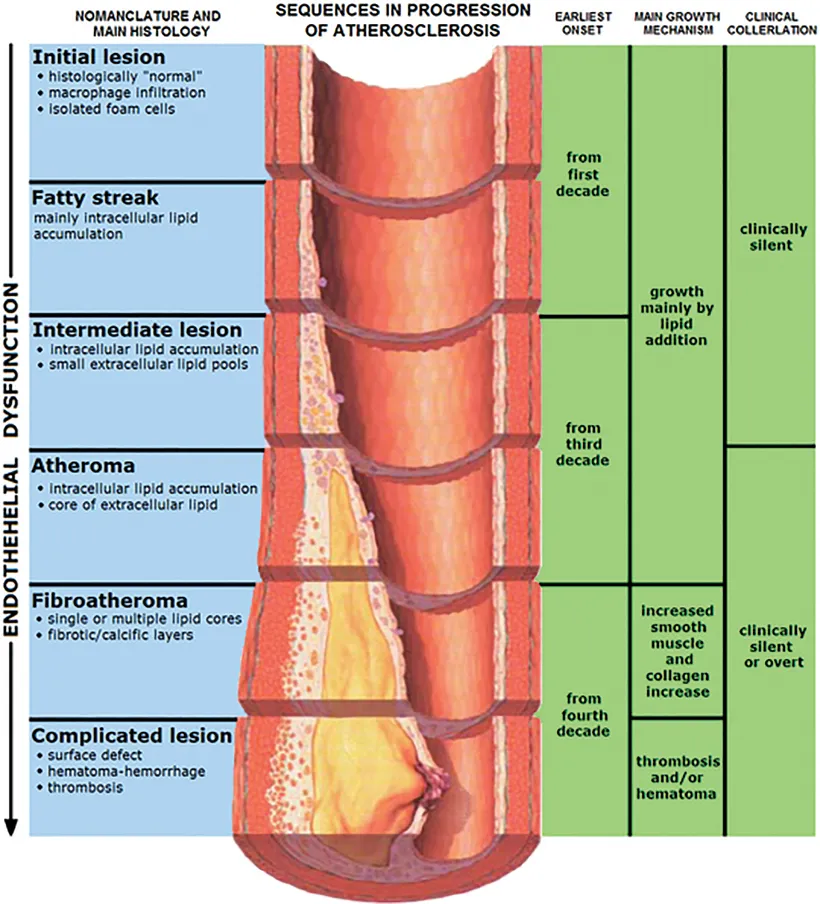
Atherosclerosis, Endothelial Dysfunction and Arterial Stiffness
Nutrition and CHD
| Nutrient | Daily Intake |
|---|---|
| Diets that benefit cardiovascular health | |
| Mediterranean diet and MD + ALA | |
| DASH 1 and 2 | |
Vegetarian diet
| |
| Paleolithic diet | |
| Caloric restriction and intermittent fasting | |
| Low ages | |
Alkaline diet
| |
| Fats | Less than 35% total caloric intake |
SFA
| <7%–9% of total diet Replace with PUFA or MUFA |
Coconut oil
| |
| Trans fat | Avoid trans fat |
| PUFA Omega 3 fatty acids
| Omega 3 to omega 6 ratio at 4:1 >1g of EPA + DHA per day 1.1 g/day for women 1.6 g/day for men ~2% total daily calories |
| MUFA [165]: Extra-virgin olive oil | 50 g/day |
| Diet elements | |
Animal protein
| |
Fish
| 1–2 servings/week 20 g/day |
| Nuts | >5 servings/week; 28 g/day |
Vegetables and fruits
| 200 g–800 g/day |
Milk and milk products
| |
Eggs
Special recommendation for diabetics | 6–12 eggs per week as part of a healthy cardiovascular diet |
| Refined carbs, sugar and sugar substitutes | Reduce or eliminate from diet |
| Alcohol | 1–2 drinks/day for women 2–4 drinks/day for men |
| Isolated nutrients and nutraceutical supplements | |
| Curcumin | |
| Cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon) | |
| Sulforaphane (broccoli) | |
| Resveratrol | |
| Luteolin | |
| Quercetin | |
Caffeine
| Caffeinated coffee for slow metabolizers 59 and younger <2–3 cups Older than 59 < 1 cup |
| Soy protein | 15–30 g/day |
| Whey protein | 20 g/day |
Gluten
| |
| Sodium | Low sodium–potassium ratio |
| Potassium | 4.7 g/day, preferably f... |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Editors
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 Nutrition, the Mediterranean Diet and Selected Supplements for the Prevention and Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
- Chapter 2 Coronary Artery Disease: The Impact of the Mediterranean Cuisine, Targeted Nutritional Supplements and Their Relationship to Autophagy/mTOR
- Chapter 3 Naturopathic Medicine and the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 4 Marine-Derived Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 5 Nutrition and Nutritional Supplements in the Management of Dyslipidemia and Dyslipidemia-Induced Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 6 The Role of Nitric Oxide Supplements and Foods in Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 7 The Treatment of Hypertension with Nutrition, Nutritional Supplements, Lifestyle and Pharmacologic Therapies
- Chapter 8 Metabolic Cardiology: Management of Congestive Heart Failure
- Chapter 9 Cardiovascular Disease in Women
- Chapter 10 Hormones and Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 11 The Heartbreak of Wheat-Related Disorders: Wheat, Gluten and Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 12 The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 13 Environmental Toxins and Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 14 Dental Disease, Inflammation, Cardiovascular Disease, Nutrition and Nutritional Supplements
- Chapter 15 COVID-19: An Evidence-Based Integrative Approach to Disease Management
- Chapter 16 Lymphstasis, Inflammation and Atherogenesis – Connecting the Dots
- Chapter 17 Vitamin G. Grounding as Energetic Nutrition and Its Role in Oxidative Defense and Cardiovascular Disease
- Chapter 18 The Role of Botanicals in Cardiovascular Health
- Chapter 19 Depression, Anxiety, Stress, and Spirituality in Cardiovascular Disease
- Index