Bioremediation of Hydrocarbons and Xenobiotic Compound
Suman Singh1, Sucheta Singh2, Ramesh Kumar Kushwaha3, * 1 Department of Botany, University of Lucknow-226007, India
2 Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Division, CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow-226001, India
3 Department of Biochemistry, REVA University, Bangalore-560064, India
Abstract
In the last few decades, the increase in population, the industrial revolution, and modernization have produced numerous problems in the form of hazardous pollutants in the ecosystem rapidly. These hazardous pollutants such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), heavy metals, manmade pesticides (xenobiotics), radioactive materials, toxic chemicals, and dyes created an imbalance in the ecosystem and increased risks to human, plants, and animal’s health. Furthermore, the use of chemical fertilisers, pesticides, and sewage releases toxicants into the soil and potable water, where they enter the food chain and endanger food security. Many strategies and practices have been used to prevent harmful effects of these pollutants up to a certain extent. Various physical and chemical methods have been implemented to remove these contaminants, but due to some limitations, it has not been applied successfully. Despite this, appropriate biological methods are currently applied to decrease pollutants’ concentrations from the soil, water, and the environment. The use of biological methods for bioremediation should be cost-effective, eco-friendly, and biodegradable, decreasing the danger to the ecosystem and living beings. Microbe-assisted remediation technology has been developed to degrade xenobiotic compounds through various biosynthetic mechanisms. The objective of this chapter is to discuss different methods of bioremediation, their process, and mechanisms, employing potential plants and microbes in the remediation of pollutants from the environment. In addition, the present chapter highlighted the significance of recent biotechnological methods in improving the capability of microbial remediation methods. These methods successfully degrade pollutants, emphasizing current advances in microbe-assisted remediation along with phytoremediation as well as related challenges, future outlooks, and limitations.
Keywords: Bioremediation, Chemical Fertilizers, Ecosystem, Heavy Metals, Microbial Remediation, Pesticides.
* Corresponding author Ramesh Kumar Kushwaha: Department of Biochemistry, REVA University, Bangalore-560064, India; Tel:+918004425060; E-mails: [email protected], [email protected] 1. INTRODUCTION
The global population has exploded and calls attention towards excess production of grains, fibers, and herbal medicines. This leads to tremendous pressure on the environment in order to feed the ever-increasing population. So, the demand for food exceeded the population on earth. To obtain higher productivity and yields, we are compelled to use man-made chemical fertilizers and protectors, which show damaging effects on the environment and human health. Moreover, agricultural, domestic and industrial processes haphazardly introduced several contaminants into the environment, such as polyaromatic hydrocarbons, heavy metals, polychlorinated biphenyls, chlorinated phenols, radioactive, fertilizers, biocides, dyes, and plastics [1, 2]. Since the past decade, a mixture of contaminants, such as hydrocarbons, greenhouse gases, heavy metals, plastics, micropollutants, etc., have caused a severe threat to the functioning of the earth’s homeostasis globally. These contaminants cause soil, air, and water pollution, ensuing severe infections in life form, or impacting biodiversity completely [3, 4]. In developing countries, agricultural workers/farmers are prone to use a high content of agricultural chemicals, including pesticides, due to a lack of awareness about the application of biofertilizers or biopesticides and related information [5]. These contaminants’ exposure is highly susceptible for farmers, followed by production workers, food processors, and loaders. Besides, environmental contamination leads to a polluted ecosystem entirely, which causes deaths and chronic diseases due to contaminants poisoning concentrations to approximately one million per year globally [6, 7]. These contaminants are recalcitrant, therefore, degrade gradually.
To eliminate their lethal and toxic effect on living beings, special measures are required to remove these contaminants from the environment. Since ancient times, various physicochemical methods and their combinations have been employed to solve the problem to a certain extent. But these methods have some limitations and are, therefore, not very successful. Conventional waste disposal processes such as landfilling and incineration are highly expensive to clean up polluted areas in various countries [8]. Since ancient times, waste disposal has been done by throwing it into the river directly or burning it in the field and through incineration methods. At present, human beings have applied remediation practices such as bioremediation for removing these contaminants [9].
Among the biological techniques, bioremediation strategies have evolved as the most promising one because it is cost-effective, fast, efficient, safe, and has a permanent solution to clean up xenobiotic contaminants [10]. Bioremediation is described as the manipulation of biological systems to diminish the toxicity of hazardous wastes from contaminated areas [11]. It is also known as the use of living systems to fetch preferred chemical and physical changes in a limited environment [12]. It is a technology that utilizes biological activity to decrease the concentration of pollutants. It usually applies methods through which microorganisms transform or degrade toxic chemicals in the environment [13]. Bioremediation is a multidisciplinary organic approach to neutralize or remove something detrimental from the atmosphere by the application of biological agents such as microbes and plants [14].
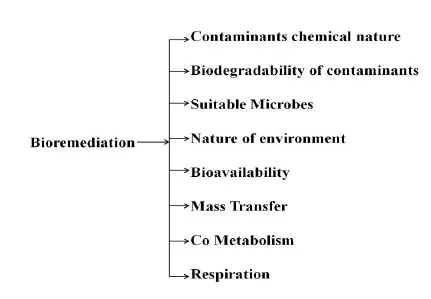
Bioremediation methods are preferred over other methods because of eco-friendly, risk-free, less expensive, and acceptable methods. The limitation of bioremediation techniques is that it is applied only to biodegradable substances [15]. A variety of factors such as type of organisms, nature, and concentration of contaminants, chemical and geological situation at the polluted place, the end product of the procedure, and the environmental policies affect the completion of bioremediation (Fig. 1) [16].
Fig. (1)) Factors affecting the bioremediation process.
2. Types of Bioremediation
Bioremediation has been categorized into ex-situ and in situ based on the location of waste materials treatment [17, 18]. In situ bioremediation helps in the treatment of waste material at the site of its origin. Ex-situ bioremediation facilitates the elimination of waste material from the site ...