Designing Weldments
About this book
Designing Weldments
An important tool for professionals wishing to enhance their understanding or those who are new to the subject, Designing Weldments bridges that gap between structural engineers and a deeper understanding of the welding engineering within the structures.
In modern-day construction, welding is the primary method to join various members of any structure. Welds are required to meet various types of load in tension, compression, torsion, and perform in static or cyclic loading conditions. The weld has to be at least as strong as the parent metal to meet the demands of various stress working on the structure. It should meet the structural requirement, add value to the integrity of the structure, and prevent failures.
However, many design engineers lack even a fundamental insight or a basic understanding of essential welding processes and design requirements. Simply copying a few joint configurations in a drawing will not suffice. All-embracing and readable, Designing Weldments delivers a deeper understanding of many design factors that play a critical role in the design. The book clarifies welding design principles and applications. With this reference in hand, designers will have expert knowledge to consider very early on in the project, the implications of the choice of what type of weld to use for joining structural members, and how the component is made. The author explains the many welding techniques developed over the years, as well as some of which are still evolving.
The reader will also find in this book:
- Rules of thumb for saving time and money in the design phase of a project.
- An insider's view for choosing the proper welding approach to ensure the overall strength of a structure.
- Offers structural engineers a deeper understanding of the weld within their structures.
- Clarifies welding design principles and applications, limiting the necessity to redesign the structure.
Audience
The intended market for this book is professionals working on the infrastructural projects in shipbuilding, construction of buildings, bridges, offshore platforms, wind towers for renewable energy, and other structures that join plates, pipes, and pipelines in power plants, manufacturing, and repair.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Properties and Strength of Material
1.1 Introduction
- (i) to provide the intended purpose of the structure and
- (ii) to be a reliable and safe structure.
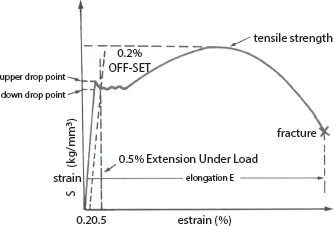
- 1. Casting and Forging process by which the original component is made of,
- 2. Welding and other joining processes,
- 3. Cutting and machining process,
- 4. Inspection and testing methods,
- 5. Fabrication activities and tools available for the task,
- 6. Properties of various materials,
- 7. Weldability of materials,
- 8. Effects of restrains on welds,
- 9. Distortion control,
- 10. Design for appropriate stiffness and or flexibility as desired of the structure,
- 11. Designing to address, required tension, compression and torsional load on the structure,
- 12. Weld and NDE symbols,
- 13. Knowledge of nondestructive inspection (NDE) methods, with their specific advantages and limitations.
- 14. Applicable codes, regulations and practices,
- 15. Selection of suitable weld design for welding.
2
Properties of Metals
2.1 Material Properties
- 1. Mechanical properties
- 2. Physical properties and
- 3. Corrosion properties.
| General group | Structure-insensitive properties | Structure–sensitive properties |
| Mechanical | Elastic moduli |
|
| Physical | Thermal Expansion, Thermal conductivity, Melting point, Specific heat, Emissivity, Thermal evaporation rate, Density, Vapor pressure, Electrical conductivity, Magnetic properties, Thermionic emission. | Ferromagnetic properties |
| Corrosion |
| Corrosion of metals does affect some of the mechanical properties leading to metals failures. |
| Optical |
| |
| Nuclear |
|
2.1.1 Structure Insensitive Properties
2.1.2 Structure Sensitive Prop...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Table of Contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Foreword
- Preface
- 1 Properties and Strength of Material
- 2 Properties of Metals
- 3 Design: Load Conditions
- 4 Design of Welds and Weldments
- 5 Introduction to Welding Processes
- 6 Welding Symbols
- 7 Structural Design and Welding Specifications, and Other Useful Information
- Index
- Also of Interest
- End User License Agreement
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
