
Smart Electrical Grid System
Design Principle, Modernization, and Techniques
- 278 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Smart Electrical Grid System
Design Principle, Modernization, and Techniques
About this book
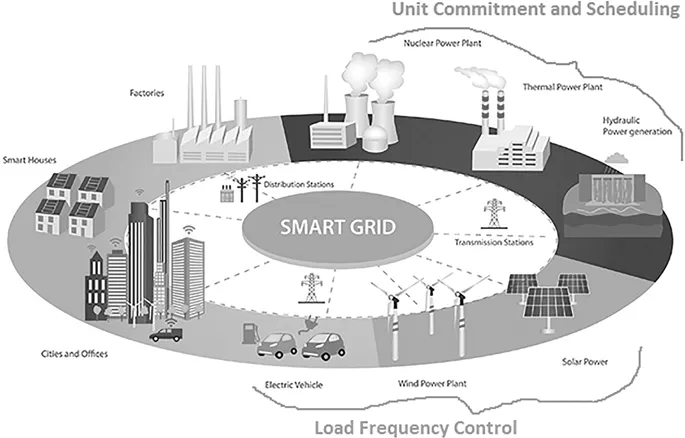
Smart technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, play a vital role in modeling, analysis, performance prediction, effective control, and utilization of smart energy systems. This book presents novel concepts in the development of smart cities and smart grids as well as discusses the technologies involved in producing efficient and economically feasible energy technologies around the world.
It comprehensively covers important topics, including optimization methods for smart grids, power converters, smart meters, load frequency control, automatic generation control, and power electronics for smart grids.
This book focuses mainly on three areas of electrical engineering: control systems, power electronics, and renewable resources, including artificial intelligence for the development of smart electrical grids.
Key Features
• Clarifies how the smart grid plays an important role in modern smart technologies
• Introduces the basic concepts of modernization of smart grid with the assumption of basic knowledge of mathematics and power systems
• Describes the structure of technologies based on Internet of Things (IoT), which acts like a bridge to cover the gap between the physical and virtual worlds required for the realization of the smart grid
• Includes practical examples of the smart grid and energy saving
• Illustrates the integration of renewable energy sources with worked examples
• Enables readers to engage with the immediate development of power systems by using smart approaches for future smart grids
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Internet of Things-Based Modernization of Smart Electrical Grid
CONTENTS
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Pros of Smart Electrical Grid (SEG)
- 1.3 Existing System
- 1.4 Research Gaps
- 1.5 Proposed System
- 1.6 Methodology
- 1.6.1 Framework
- 1.6.2 Component Requirement Analysis
- 1.7 Implementation
- 1.8 Functional Requirements
- 1.9 Results and Discussion
- 1.10 Conclusions
- References
1.1 Introduction
1.2 Pros of Smart Electrical Grid (SEG)
- Cost-Effective: The installation cost decreases due to the non-requirement of cables in contrast to the wired system where the cable, its material, and laying technology along with the need for experienced professionals add up to the cost.
- Easy Deployment, Installation, and Coverage: Remote devices or appliances can be easily accessed wirelessly along with easy deployment and installation.
- System Extension and Scalability: Transportation of a native structure is predominantly priceless when, due to novel or distorted prerequisites, augmentation of the scheme is essential. More than wired establishments, in which cabling extension is expensive and time-consuming [7], this makes remote systems an original essence.
- Amalgamation of Mobile Devices: With the advancement of the communication technology, wireless platform gives the automation an easier and possible solution, where devices or appliances can be remotely controlled or observed without any physical connections.
- Aesthetic Benefits: This not only covers a large area, but also beautifully manages the architecture and gives immense benefits to historical buildings and tourist spots.
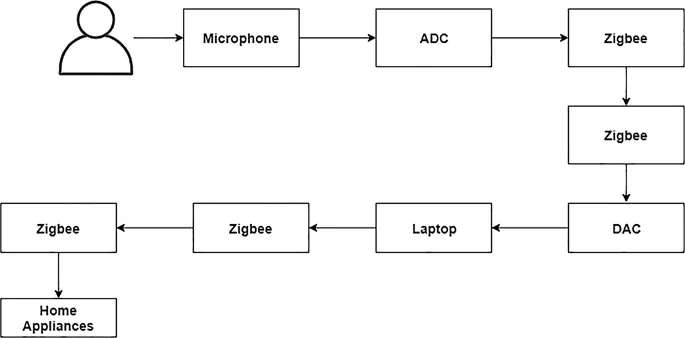
1.3 Existing System
| Methodologies | Communication Interface | Controller | User Interface | No. of Devices | Cost | Speed | Range | Energy Savings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth | Bluetooth and AT instructions | Arduino Uno | Android | Unlimited | Moderate | Low | 10 m | No |
| GSM | SMS messages | Arduino ADK | Mobile phone | Limited | Low | Very low | No | |
| Zigbee | Zigbee with instructions | Zigbee controller (ZC) | Smartphone | Unlimited | High | Low | 10 m | Yes |
| The proposed wireless design | Wi-Fi (NODEMCU) | Arduino SDK | Smartphone | Unlimited | Low | High | Unlimited | Yes |
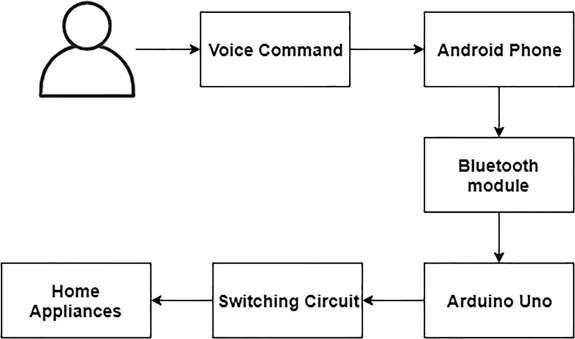
1.4 Research Gaps
- Dependency on Range: The SEG connects all the devices of the grid to the mobile app through...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Series Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- Chapter 1 Internet of Things Based Modernization of Smart Electrical Grid
- Chapter 2 Role of Non-Conventional Energy Resources in Today’s Environment
- Chapter 3 Flexible Load and Renewable Energy Integration with Impact on Voltage Profile of a Large Size Grid
- Chapter 4 Energy Storing Devices for Sustainable Environment
- Chapter 5 Clean and Green Energy Fundamentals
- Chapter 6 Evaluation of Sustainable Window for Energy Mitigation in an Electrical Grid Building
- Chapter 7 Filter Bank Multicarrier for Smart Grid Systems
- Chapter 8 Recent Trends in Economic Scheduling and Emission Dispatch of Distributed Generators in Microgrids
- Chapter 9 Forecasting of Tensile–Shear Strength of JSC 590RN Low-Carbon Steel Spot Welds Using Taguchi Technique Used in Electrical Grids
- Chapter 10 Experimental Analysis of Surface Integrity of Machined Stainless Steel (SS-304) by Taguchi Method Coupled with GRA Used in Electrical Grids
- Chapter 11 Energy Storage Devices Based on 2D Phosphorene as an Electrode Material
- Chapter 12 Application and Performance Analysis of Various Nature-Inspired Algorithm in AGC Synthesis
- Chapter 13 Unified Smith Predictor for MIMO Systems with Multiple Time Delays
- Chapter 14 Renewable Energy Sources and Small Hydro Power Scenario in Mountainous Regions of Himalayas
- Chapter 15 A Comprehensive Review on Energy Storage Systems
- Chapter 16 Cyber and Theft Attacks on Smart Electric Metering Systems: An Overview of Defenses
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app