A widespread view is that the evoking cause of religion is fear. Humans, as the species capable—probably solely on Earth—of contemplating its own death, need religion to make that knowledge tolerable. In ancient Rome, the poet Lucretius 1 wrote in his philosophical poem De Rerum Natura that “fear created gods”. At present, the whole “Terror Management Theory ”, based on the hypothesis that human behavior is mostly motivated by the fear of mortality, develops with support of experimental existential psychology. Although, according to the theory, not only religion but laws and cultures also are motivated by the “existential fear”, and yet just religion—with its promise of life after death —seems to be the most natural and primitive remedy for this fear.
There are arguments, based on scientific discoveries—discussed in next sections—proving that “a sense of divine” has been instilled into humans as a result of species evolution. And the supposition considered here is that spirituality is a key actor in a “survival gear ”2 built-in purposely with the use of an evolutionary intelligent tool by the Creator, and religion is a virtual stake driven by Him to help in the growth of a tree of young civilization.
Quest After Spirit
Spirituality is an ambiguous idea treating either the supernatural element or the “high” regions of psyche—or both of them on the assumption that the high regions of psyche have supernatural stimulation. Anyway, searching for Spirit as a source of spirituality in our world has always been exercised.
The linguistic connection between “respiration” and “spirit” (after Latin respiratio—spiritus; similarly in Slavonic languages: Russian dyhanie—dusha, Polish oddychanie—duch) shows that at one time spirit was identified with breath. This has its expression in the Bible ’s statement that God “breathed the breath of life into clay to make Adam a living soul ”.3 The real essence of breathing, entirely natural, was described by Arab physician Ibn al-Nafis in the thirteenth century, and in Europe was confirmed by dissections made by English physician William Harvey in the seventeenth century.4
Emotions, primitive psychological phenomena that appear also in animals, have natural neurobiological mechanisms confirmed experimentally—triggered off by different external and internal factors but produced by hormones and neurotransmitters affecting the brain. One of recent research reports published by Hugo Lövheim of Umeå University, Sweden5, announces which combinations of three neurochemicals —serotonin, dopamine, and noradrenaline—are responsible for eight basic emotions: shame/humiliation, distress/anguish, fear/terror, anger/rage, contempt/disgust, surprise, enjoyment/joy, and interest/excitement. For example, according to Lövheim’s report, low levels of serotonin, high levels of dopamine, and low levels of noradrenaline are responsible for fear, as well as low serotonin, high dopamine, and high noradrenaline are responsible for anger.
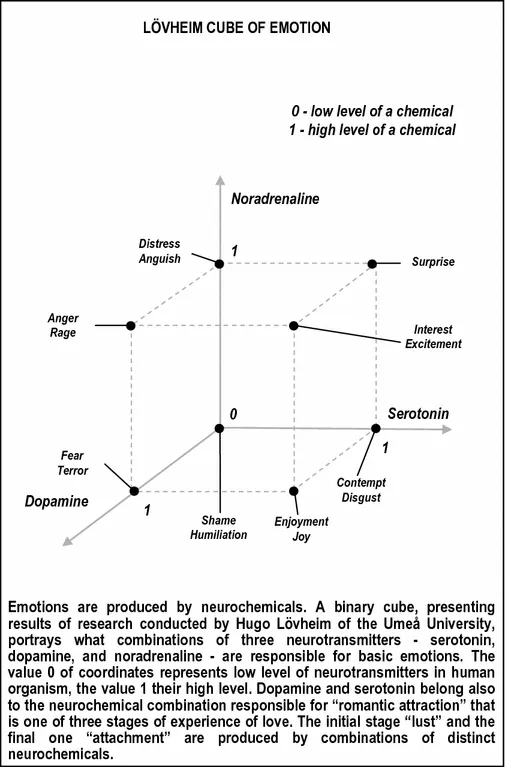
Love, essential for the matter of many religions, is a psychological phenomenon that appeared rather early in evolution of the human species, and is related to and composed of neuron paleocircuits of the brain that formed before the advent of circuits responsible for speech; there are opinions that animals feel love as well. Love is also produced by neurochemicals . Three stages of the experience of love are discerned: lust, attraction, and attachment. Lust is the initial passionate sexual desire, is temporary—lasts weeks—and is caused by testosterone and estrogen. The second temporary stage, lasting no more than a few years, is romantic attraction for which dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin (acting in a manner similar to amphetamines) are responsible. The third stage, attachment, is long lasting, can be all life long, and is of a more universal character, and includes feelings such as of motherhood6 also. Vasopressin and oxytocin are responsible for attachment.
Oxytocin significantly exceeds the love area. Paul J. Zak , originator of a new research branch that he named “neuroeconomics”, has presented in his book7 results of experimental research on oxytocin’s widened role. According to Zak’s results, oxytocin “modulates social behaviors”, makes people “more prosocial, more moral, more virtuous”, and makes them feel empathy. “So oxytocin is really the foundation for civilization”, states the author in conclusion.
An area close to neuroeconomics, named “biology of risk”, has been penetrated and presented in a book8 by a very competent researcher: neuroscientist and former Wall Street trader John M. Coates. Coates’ research had been related to the neurochemical basis of financial decision making. It was stated that testosterone dramatically lowers the fear of risk—in younger men especially—and cortisol lowers the appetite for risk (intense failure leads to cortisol’s level rise).
There are also neurochemicals that generally evoke euphoric states and smother feelings of tiredness and pain—endorphins, being “endogenous morphine” produced by the human body, called “hormones of happiness”. The long list of trigger factors evoking production of endorphins includes among others: laughing, orgasm, chocolate, oxygen deficiency, placebo effects.
Consciousness, maybe the highest region of the psyche, making people aware of themselves and of external world, is localized in the cerebral cortex. Here, attached to neocortex, the claustrum is located—a sheet of neurons with three of them stretched across both brain hemispheres, so having the potential to coordinate signals from different brain regions. It has been established experimentally—by stimulation and neuron activity observation—that loss of consciousness is related just to the claustrum state.9 Of course, for a long time the phenomenon of consciousness has been a subject of deliberations and investigations. Recently, a theory of consciousness focused on the information aspect, named IIT —Integrated Information Theory—, of consciousness arose and develops. The IIT is authored10 by a psychiatrist and neuroscientist Giulio Tononi of the University of Wisconsin–Madison , and examines consciousness just as integrated information.11 According to the theory, there are two factors involved in the existence of consciousness: in a single system-entity, there must be generated and recorded information being a repertoire of differentiated states of the system, and this information must be integrated because integration enables us to derive meaning from it. Tononi has proposed a measure of integrated information—of consciousness as a measurable entity12—expressed in bits. This measure, represented by the symbol Φ, is defined as “the amount of information generated by a complex of elements above and beyond the information generated by its parts”. In mathematical depiction of Φ, a quantity of information included in the repertoire of possible states is expressed probabilistically, with the use of entropy as a measure of states of unpredictability. A value of Φ can be calculated for any physical system with some capacity of information. The simplest on-off system, as, for example, photodiode that can detect the presence or absence of light, has Φ = 1 bit. Human brains are of course very high-Φ entities.13
Thus, one cannot perceive immediate involvement of Spirit in high regions of human psyche14; however, in neurobiological mechanisms producing spiritual effects one can find possible components of the built-in survival gear . And the quest of Spirit should be transferred to more fundamental regions of the Universe’s configuration.
Two aspects of Spirit’s manifestation on our side of the Big Bang , in our Universe, can be considered. One of them is a form of content revealing, the second is a manner (a way) of affecting by Spirit the material substance. The supposition, resulting from previous considerations, is that information constitutes the form of content revealing. And how does Spirit affect the substance of our Universe?
In the second chapter, the problem of the Creator’s interventions was discussed, and yet any particular way of affecting material substance wasn’t shown. However, the hypothesis that interventions into the human mind occur at the subatomic quantum level was presented. In any case, there is no doubt that only very subtle interaction could serve to trigger the processes of change in the world of matter—adjusting intelligent tools with their self-organization parts. The particular mechanism of such triggering remains unknown as the first sliver of a second after the Big Bang , and in just this initial period the key may be situated. Time goes by in one direction only by us, in our Universe, on our side of the Big Bang , but not necessarily for God the Creator. For Him in the eternity, time—if...
