
Advanced Computational Techniques for Sustainable Computing
- 336 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Advanced Computational Techniques for Sustainable Computing
About this book
Advanced Computational Techniques for Sustainable Computing is considered multi-disciplinary field encompassing advanced computational techniques across several domain, including, Computer Science, Statistical Computation and Electronics Engineering. The core idea of sustainable computing is to deploy algorithms, models, policies and protocols to improve energy efficiency and management of resources, enhancing ecological balance, biological sustenance and other services on societal contexts.
The book offers a comprehensive coverage of some of the most essential topics:
- It provides an insight on building smart sustainable solutions.
- Includes details of applying mining, learning, IOT and sensor-based techniques for sustainable computing.
- Entails data extraction from various sources followed with pre-processing of data, and how to make effective use of extracted data for application-based research.
- Involves practical usage of data analytic language, including R, Python, etc. for improving sustainable services offered by multi-disciplinary domains.
- Encompasses comparison and analysis of recent technologies and trends.
- Includes development of smart models for information gain and effective decision making with visualization.
The readers would get acquainted with the utilization of massive data sets for intelligent mining and processing. It includes the integration of data mining techniques for effective decision-making in the social, economic, and global environmental domains to achieve sustainability. The implementation of computational frameworks can be accomplished using open-source software for the building of resource-efficient models. The content of the book demonstrates the usage of data science and the internet of things for the advent of smart and realistic solutions for attaining sustainability.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1 Sustainable Computing—An Overview
CONTENTS
- 1.1 What Is Sustainability?
- 1.2 Sustainable Development: Motivations and Obstacles
- 1.2.1 Present versus Future Generations
- 1.2.2 Economic versus Environmental Perspectives
- 1.3 Goals to Strive toward Sustainable Development
- 1.4 Sustainability and Computing
- 1.4.1 Product from Hardware Perspective
- 1.4.2 Product from Software Perspective
- 1.4.3 Production Processes from Hardware Perspective
- 1.4.4 Production Processes from Software Perspective
- 1.4.5 Consumption Processes from Hardware Perspective
- 1.4.6 Consumption Processes from Software Perspective
- 1.5 Computing Paradigms for Individual Sustainable Development Goals
- 1.5.1 No Poverty
- 1.5.2 Zero Hunger
- 1.5.3 Good Health and Well-Being
- 1.5.4 Quality Education
- 1.5.5 Gender Equality
- 1.5.6 Clean Water and Sanitation
- 1.5.7 Affordable/Clean Energy
- 1.5.8 Decent Work/Economic Growth
- 1.5.9 Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure
- 1.5.10 Reduced Inequalities
- 1.5.11 Sustainable Cities/Communities
- 1.5.12 Responsible Consumption/Production
- 1.5.13 Climate Action
- 1.5.14 Life below Water
- 1.5.15 Life on Land
- 1.5.16 Peace/Justice/Strong Institutions
- 1.5.17 Partnerships for the Goals
- 1.6 Conclusion and Future Scope of Research
- References
1.1 What Is Sustainability?
1.2 Sustainable Development: Motivations and Obstacles
1.2.1 Present versus Future Generations
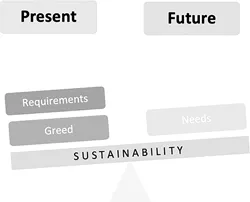
1.2.2 Economic versus Environmental Perspectives
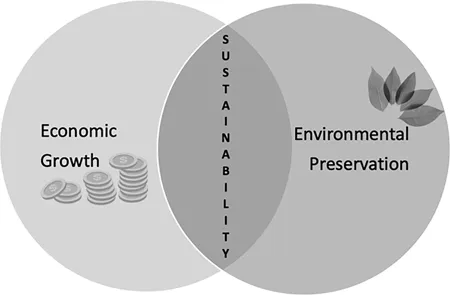
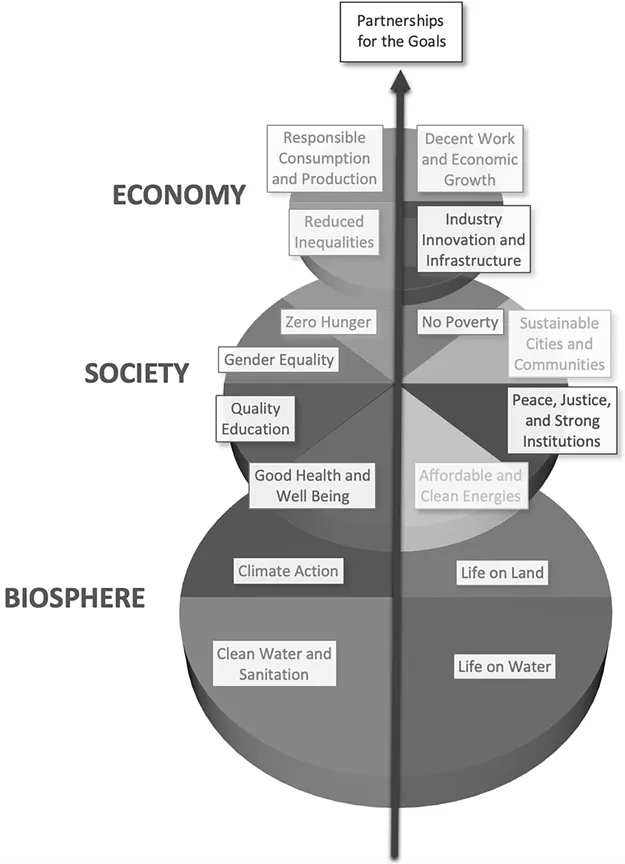
1.3 Goals to Strive toward Sustainable Development
- No Poverty—Eradicating poverty in all possible forms everywhere
- Zero Hunger—Eradicating hunger while promoting sustainable agriculture
- Good Health and Well-Being—Promoting well-being while ensuring healthy lives for all at all ages
- Quality Education—Ensuring quality education that is equitable and conclusive for all
- Gender Equality—Empowering all women and girls and achieving gender equality
- Clean Water and Sanitation—Managing sustainable water and sanitation for all
- Affordable and Clean Energy—Making available reliable, affordable, and modern energy for everyone
- Decent Work and Economic Growth—Ensuring productive employment for everyone by promoting both sustained and sustainable economic growth
- Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure—Building infrastructure that is resilient to promote sustainable industrialization to drive innovation
- Reduced Inequalities—Reducing inter- and intracountry inequalities
- Sustainable Cities and Communities—Making human settlements like cities safe, sustainable, and inclusive
- Responsible Consumption and Production—Ensuring patterns in consumption and production that are sustainable
- Climate Action—Acting to fight climate change urgently to reduce its long-term impacts
- Life below Water—Conserving the water bodies such as seas and oceans while sustainably using marine resources
- Life on Land—Restoring and promoting sustainable use of ecosystems that are terrestrial by combating desertification, and halting land degradation and biodiversity loss
- Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions—Providing easy access to justice for everyone by building accountable and effective institutions at all levels
- Partnerships for the Goals—Strengthening the ways to implement and revitalize the Global Partnerships to collaborate to achieve sustainable development (Figure 1.3)
1.4 Sustainability and Computing
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Table of Contents
- Preface
- Editors
- Contributors
- 1 Sustainable Computing—An Overview
- 2 Ambient Air Quality Analysis and Prediction Using Air Quality Index and Machine Learning Models—The Case Study of Delhi
- 3 Assessing Land Cover and Drought Prediction for Sustainable Agriculture
- 4 Electronic Health Record for Sustainable eHealth
- 5 Team Member Selection in Global Software Development—A Blockchain-Oriented Approach
- 6 Machine Learning in Sustainable Healthcare
- 7 Multimedia Audio Signal Analysis for Sustainable Education
- 8 Smart Health Analytics for Sustainable Energy Monitoring Using IoT Data Analytics
- 9 Customer Analytics for Purchasing Behavior Prediction
- 10 Discernment of Malaria-Infected Cells in the Blood Streak Images Using Advanced Learning Techniques
- 11 Handwritten Text Recognition with IoT Devices
- 12 Circadian Rhythm and Lifestyle Diseases
- 13 Deep Learning for Automated Disease Detection
- 14 Time Series Analysis and Trend Exploration of Stock Market
- 15 Medical Search Engine
- 16 Assessing Impact of Global Terrorism Using Time Series Analysis
- 17 Sustainable Statistics for Death Cognizance Analysis
- 18 Modeling the Immune Response of B-Cell Receptor Using Petri Net for Tuberculosis
- 19 Crop Prediction and the Sustainability of Farming
- 20 Personalized Heart Disease Framework for Health Sustainability
- 21 Sports Analytics for Classifying Player Actions in Basketball Games
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app