
- 108 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Essential Angular
About this book
Essential Angular is a concise, complete overview of the key aspects of Angular, written by two Angular core contributors. The book covers the framework's mental model, its API, and the design principles behind it. It is fully up to date with the latest release of Angular.About This Book• Written by two Angular core contributors• A complete overview of the key aspects of Angular• Up to date with the latest Angular releaseWho This Book Is ForTo get the most from this book, you should already have a good understanding of Angular and general web development. The book dives quickly into the core Angular systems without stepping through the basics.What You Will Learn• Understand why and how to use JIT and AOT compilation in Angular• Bootstrap and inject NgModules• Learn about the component lifecycle• Understand the two phases of Change Detection• Visualize and parse the Injector tree• Understand advanced Lazy Loading• Integrate and run different testing strategies on your codeIn DetailEssential Angular is a concise, complete overview of the key aspects of Angular, written by two Angular core contributors. The book covers the framework's mental model, its API, and the design principles behind it. This book is fully up to date with the latest release of Angular.Essential Angular gives you a strong foundation in the core Angular technology. It will help you put all the concepts into the right places so you will have a good understanding of why the framework is the way it is. Read this book after you have toyed around with the framework, but before you embark on writing your first serious Angular application.This book covers concepts such as the differences between Just-In-Time (JIT) and Ahead-Of-Time (AOT) compilation in Angular, alongside NgModules, components and directives. It also goes into detail on Dependency Injection and Change Detection: essential skills for Angular developers to master. The book finishes with a look at testing, and how to integrate different testing methodologies in your Angular code.Style and approachEssential Angular is a complete overview of the key aspects of the latest release of Angular, written by two core Angular contributors. It goes far beyond a how-to-get-started guide and dives into the most important topics in modern Angular development at depth.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Forms
Two modules
High-level overview
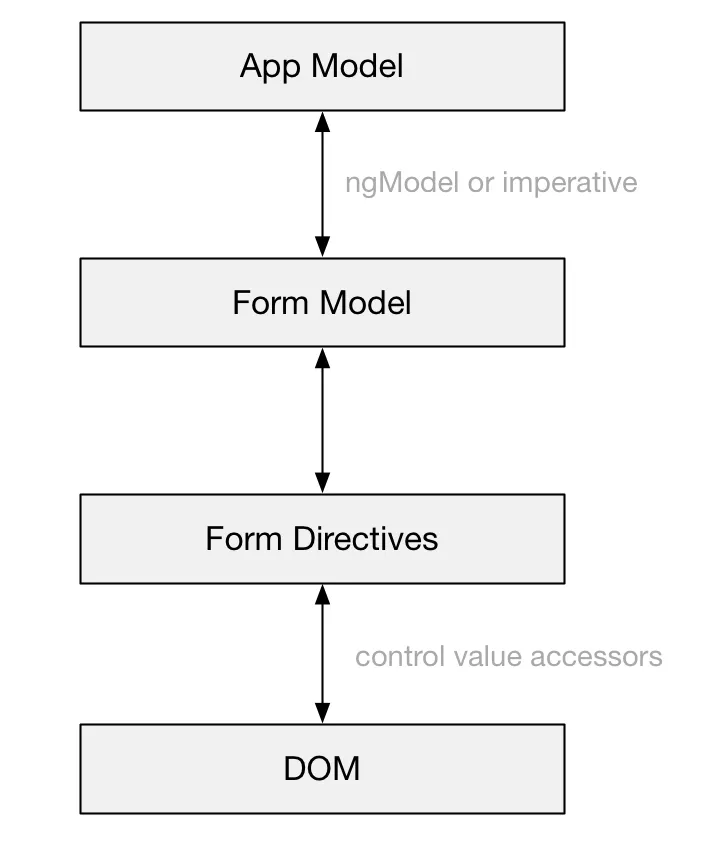
App model
Form model
Form directives
DOM
Form model
FormControl
const c = new FormControl('Init Value', Validators.required);
expect(c.value).toEqual('Init Value');
expect(c.errors).toEqual(null); //null means 'no errors'
expect(c.status).toEqual('VALID');
FormGroup
const c = new FormGroup({
login: new FormControl(''),
password: new FormControl('', Validators.required)
}); expect(c.value).toEqual({login: '', password: ''});
expect(c.errors).toEqual(null);
expect(c.status).toEqual('INVALID');
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Credits
- About the Authors
- www.PacktPub.com
- Customer Feedback
- Preface
- Example
- Compilation
- NgModules
- Components and Directives
- Templates
- Dependency Injection
- Change Detection
- Forms
- Testing
- Reactive Programming in Angular
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app