
- 112 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant
About this book
Length Tension Testing Book 2, Upper Quadrant provides clear and comprehensive descriptions and illustrations for assessing flexibility and length tension in the muscles of the upper quadrant. It includes techniques for the cervical spine, temporomandibular joint, thoracic spine, shoulder, elbow, and wrist and hand.
Each technique listing includes concise, standardized descriptions of the actions and positions involved, high-quality colour photos and alternative positions to accommodate patient variability and comfort. Most of these tests can be adapted into treatment techniques. This resource will help physiotherapists, kinesiologists, chiropractors, and massage therapists improve patient care, and it will be an invaluable reference for students at the college and university level.
Also available: Length Tension Testing Book 1, Lower Quadrant.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
The Cervical Spine
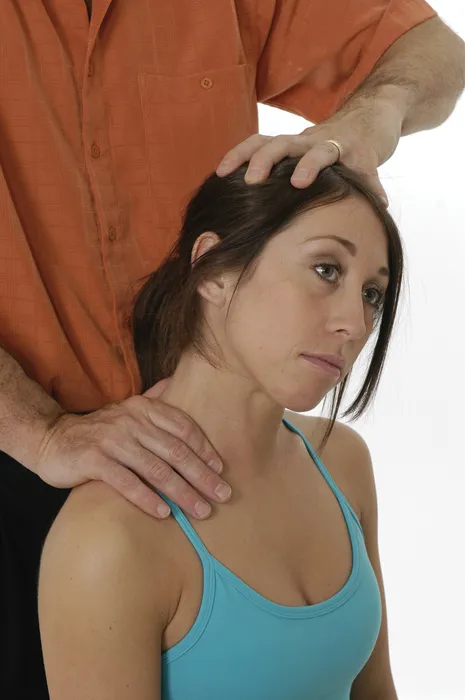

Trapezius—Upper Fibers
Technique 1
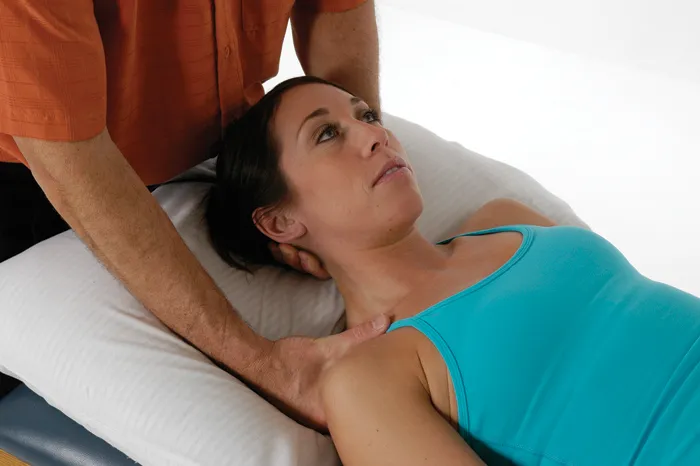

Trapezius—Upper Fibers
Technique 2
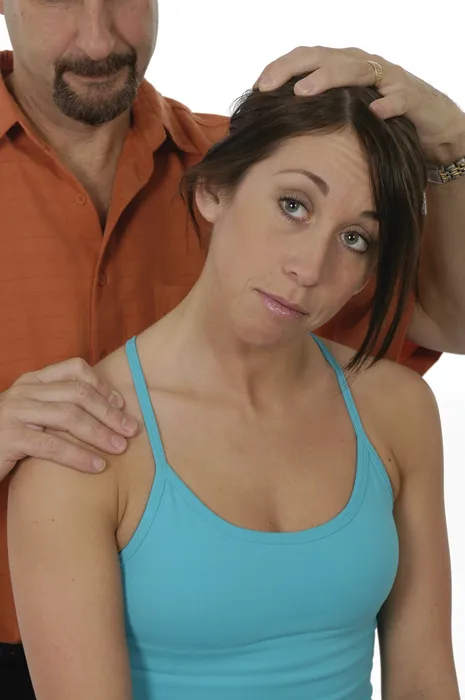

Trapezius—Middle Fibers
Technique 1
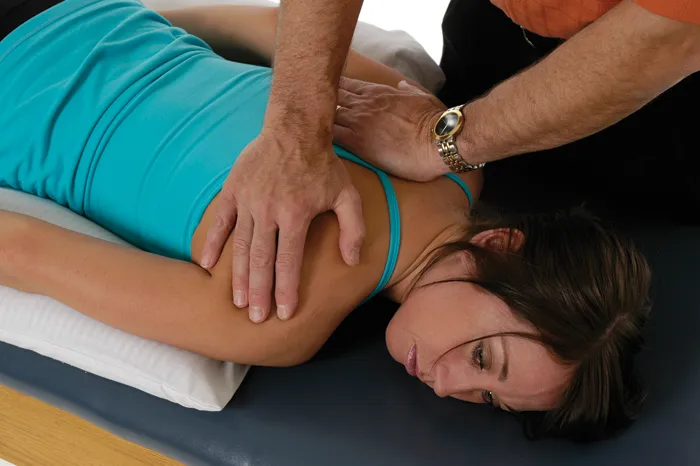
Trapezius—Middle Fibers
Technique 2
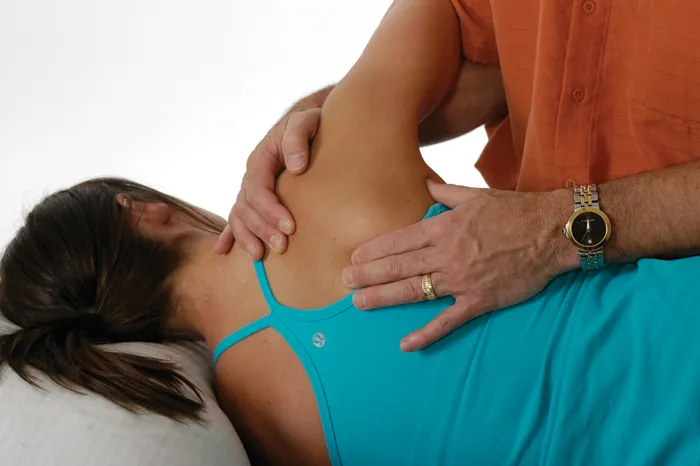
Trapezius—Lower Fibers
Technique 1
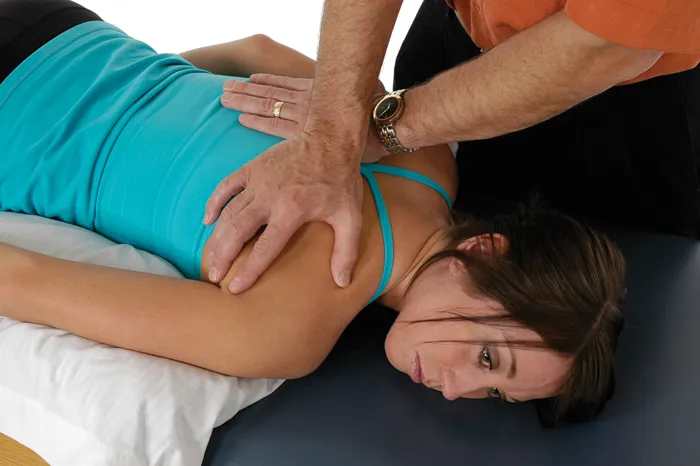

Trapezius—Lower Fibers
Technique 2
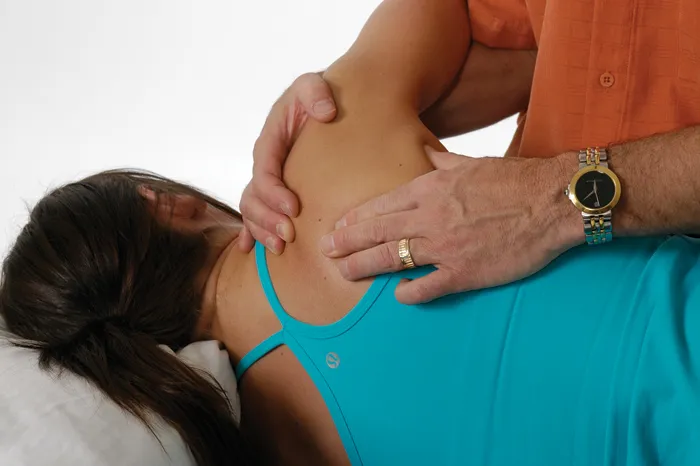
Rectus Capitis Posterior Major
Technique 1
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Acknowledgements
- Contents
- Introduction
- The Cervical Spine
- The Temporomandibular Joint
- The Thoracic Spine
- The Shoulder
- The Elbow
- The Wrist and Hand
- References
- About the Authors
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app