![]()
2013 Jakarta Photo Club, Courtesy of Photoshare
1
Inclusive business can promote women’s economic empowerment
Inclusive business can contribute to women’s economic empowerment by creating economic opportunities for low-income women. And while the model bears considerable potential for promoting women’s empowerment and gender equity, not every inclusive business will inevitably empower women. Targeted action is required to bring about effective change.
1.1 Inclusive business includes low-income people in company value chains
Inclusive business includes low-income people in the value chain for mutual benefit.1 Inclusive business is defined as commercially viable private business activity that fosters systemic change in solving problems relevant to the lives of low-income people.2 Inclusive business models operate with the dual purpose of generating a reasonable profit and creating tangible effect on low-income people’s welfare. Within the model, low-income people are seen not as beneficiaries, but rather as business partners along the value chain: as clients and customers; producers and suppliers; employees and entrepreneurs.3 While the relevance of these roles is more pronounced in some sectors than in others, as Table 1 shows, all roles can be relevant for an inclusive business in any sector or across sectors. Manila Water Company, Inc. in the Philippines, for example, delivers water and wastewater services to low-income communities, employing community members for pipe maintenance. In addition, the company sources materials from local cooperatives it helped create through its foundation.
Table 1: Types of inclusion by role
Inclusive business approaches have emerged over the past 15 years in literature and in practice. In 2004, Stuart L. Hart and C.K. Prahalad first pointed to the potential “fortune at the bottom of the pyramid,” or “BoP.”4 The article sparked interest and activity within both the public and private sectors. In 2005, the World Business Council for Sustainable Development coined the term “inclusive business.”5 In 2007, IFC and the World Resources Institute (WRI) provided the first comprehensive estimate of the market volume at the BoP. The 4 billion people living on less than $3,000 per year, according to the WRI, have a combined total purchasing power of $5 trillion.6 In 2008, the UNDP provided the first comprehensive analysis of 50 inclusive business models in their publication “Creating Value for All.”7 Thereafter, IDB and IFC set up specific teams to promote inclusive business investments in their portfolio; ADB joined in 2013.
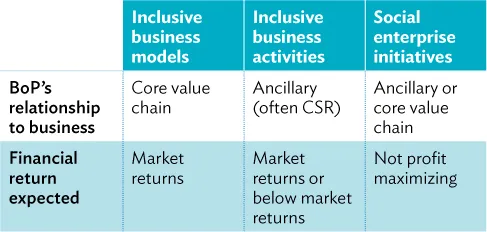
The G20 Inclusive Business Framework identifies three types of inclusive businesses: inclusive business models, inclusive business activities, and social enterprise initiatives (see Table 2).
Table 2: Inclusive business typology
Source: Adapted from G20 Framework of Inclusive Business.
Companies with an inclusive business model integrate low-income people into their core business operations. They are often large national companies operating in developing countries that seek to realize market returns. Inclusive business activities, by contrast, are not central to the commercial viability of the company, nor do low-income people make up a significant part of its value chain. Multinational companies often implement these activities as part of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) portfolio. Social enterprise initiatives seek to improve the well-being of low-income people and communities, and do not maximize profits. Social enterprises are often rather small, and not all of them are financially self-sustainable.8 Development finance institutions (DFI) concentrate their investments on inclusive business models with a minimum investment volume of $2 million. This report examines inclusive business models in particular.
Assessing quality: reach, quality, financial sustainability, and systemic impact and innovation. A textile company, for example, that employs many poor people would not be considered inclusive unless it pays them fair and stable wages. Women who receive fair and stable wages have greater capacity to influence their role in society. In this way, inclusive businesses can affect structural change in communities. The criteria used to assess how inclusive a business is are defined in Table 3.
Table 3: Criteria for evaluating inclusive business models
Criteria | Definition |
Reach: How many poor, vulnerable and low-income people does the business affect? | The business: deliberately targets low-income people as consumers, clients, suppliers, producers, entrepreneurs or employees involves a large number of poor people (1000+) affects large areas of a local economy or several countries |
Quality: What positive effect does the business achieve for low-income people? | A consumer and client-focused business: provides a product or service appropriate to the clients’ living conditions An employer or producer-focused business: provides increased and more stable income |
Financial sustainability: Is the business profitable? | The business: is profitable and based on a sizeable growth model |
Systemic impact and innovation: | The business: addresses a systemic issue or cause of poverty |
Source: ADB.
1.2 Increasing opportunities in market systems
Women’s economic empowerment is a prerequisite for sustainable development and pro-poor growth.9 When women are given equal access to education and economic decision-making, they are a key driving force against poverty. Access to paid work raises household incomes.10 The evidence shows that when women have greater control over resources, investment in children’s health, education and nutrition increases, which yields long-term benefits for future generations.11
There are many ways to define women’s economic empowerment, but overall, the concept encompasses not only women’s economic advancement but also enhancement of their rights and ability in markets.12 Golla et al. use two dimensions: ability to advance economically, and the power to make and act on economic decisions.13 The World Bank’s definition also focuses on economic terminology, which is about making markets work for women (at the policy level) and empowering women to compete in markets (at the agency level).14 OECD-DAC Network on Gender Equality adopts a broader definition of enhancing women’s “capacity to participate in, contribute to and benefit from growth processes in ways that recognize the value of their contributions, respect their dignity and make it possible to negotiate a fairer distribution of the benefits of growth”.15
Much has been done to narrow gender gaps and empower women. Over the past two decades, pregnancy and childbirth-related maternal deaths have dropped by 45% globally.16 Women have made gains in access to jobs and livelihoods, and more countries than ever guarantee equal rights in property and marriage.17 The gap in gender parity for primary education has closed in almost a...