
eBook - ePub
A Different Day
African American Struggles for Justice in Rural Louisiana, 1900-1970
- 336 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Examining African Americans' struggles for freedom and justice in rural Louisiana during the Jim Crow and civil rights eras, Greta de Jong illuminates the connections between the informal strategies of resistance that black people pursued in the early twentieth century and the mass protests that emerged in the 1950s and 1960s. Using evidence drawn from oral histories and a wide range of other sources, she demonstrates that rural African Americans were politically aware and active long before civil rights organizers arrived in the region in the 1960s to encourage voter registration and demonstrations against segregation.
De Jong explores the numerous, often-subtle methods African Americans used to resist oppression within the confines of the Jim Crow system. Such everyday forms of resistance included developing strategies for educating black children, creating strong community institutions, and fighting back against white violence. In the wake of the economic changes that swept the South during and after World War II, these activities became more open and organized, culminating in voter registration drives and other protests conducted in cooperation with civil rights workers.
Deeply researched and accessibly written, A Different Day spotlights the ordinary heroes of the freedom struggle and offers a new perspective on black activism throughout the twentieth century.
De Jong explores the numerous, often-subtle methods African Americans used to resist oppression within the confines of the Jim Crow system. Such everyday forms of resistance included developing strategies for educating black children, creating strong community institutions, and fighting back against white violence. In the wake of the economic changes that swept the South during and after World War II, these activities became more open and organized, culminating in voter registration drives and other protests conducted in cooperation with civil rights workers.
Deeply researched and accessibly written, A Different Day spotlights the ordinary heroes of the freedom struggle and offers a new perspective on black activism throughout the twentieth century.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access A Different Day by Greta de Jong in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Social Sciences & North American History. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
1 And Did Not Pay Them a Cent:
Reconstruction and the Roots of the Twentieth-Century Freedom Struggle
Louisiana's geographic diversity and its unique history of colonization by the Spanish and French before the arrival of Anglo-Americans in some ways set it apart from the other Deep South states. Scholars have typically distinguished between French Catholic parishes and Anglo-Protestant parishes, between New Orleans and the rural areas, and between the different agricultural regions that developed along the rivers, on the southwestern prairies, and in the hill country of the north central and southeastern parts of the state. Attempts to classify parishes according to environmental, economic, and cultural characteristics have resulted in estimates ranging from two to thirteen distinct regions of Louisiana.1
For the purposes of this study, the rural parishes (which for much of the period covered meant the entire area outside New Orleans) can be divided into four main types. Along the southern stem of the Mississippi, the parishes from Pointe Coupee in the north to Terrebonne and Plaquemines in the south made up the Sugar Bowl area, characterized by large sugar plantations. This region retained many aspects of the language and culture of early French settlers. In contrast to other parts of the South, most residents of the sugar parishes were Catholic rather than Protestant. Relationships between white and black people also varied slightly from the rigid color lines that were drawn elsewhere. French colonists had accepted interracial marriages and partnerships to a greater extent than the Americans who arrived later on, giving rise to a significant population of native Louisianans with mixed ancestry. Lighter-skinned African Americans were not treated equally with white people yet enjoyed privileges that set them apart from most other black people in the South. Even after their incorporation into the United States, the French-speaking, Catholic parishes of southern Louisiana retained reputations for being more racially tolerant than those farther north.2
Stretching along the V-shape formed by the Red River and the northern Mississippi lay the cotton plantation parishes. Northern Louisiana was settled largely by Anglo-Americans who migrated to the region in the early nineteenth century. Many came from other southern states, seeking new territory in which to make their fortunes as landowners and slaveholders. These parishes closely resembled the rest of the Anglo-Saxon, Protestant South. More specifically, they were very much like the plantation regions of neighboring Mississippi and Arkansas. As in the sugar parishes, black people comprised the majority of the population, sometimes outnumbering white people by more than ten to one. White supremacy was strictly, often violently enforced. Researchers in the early twentieth century noticed an undercurrent of fear among the black population of the northern parishes that contrasted with the relatively relaxed atmosphere that prevailed in southern Louisiana.3
East of the Mississippi and on either side of the Red River, alluvial plains gradually merged into rolling hills that were unsuitable for plantation agriculture. In the parishes of this area white and black small farmers eked a living from less fertile plots of land, growing a mixture of subsistence and cash crops. As in the northern plantation regions, Anglo-Saxon, Protestant influences dominated here. Though most white people in the region had little need for black labor, competition for land, jobs, and resources often created strong racial tensions. Less likely than plantation workers to suffer violence at the hands of their employers, African Americans in these parishes still had to fear the random acts of aggression that endangered black lives throughout the South in the Jim Crow era.4
Below the Red River in the southwest were sparsely populated prairies and marshes, first settled by Cajun people who subsisted by growing rice, hunting, and raising cattle. After the Civil War, migrants from the Midwest introduced large-scale rice production and mechanized farming methods.
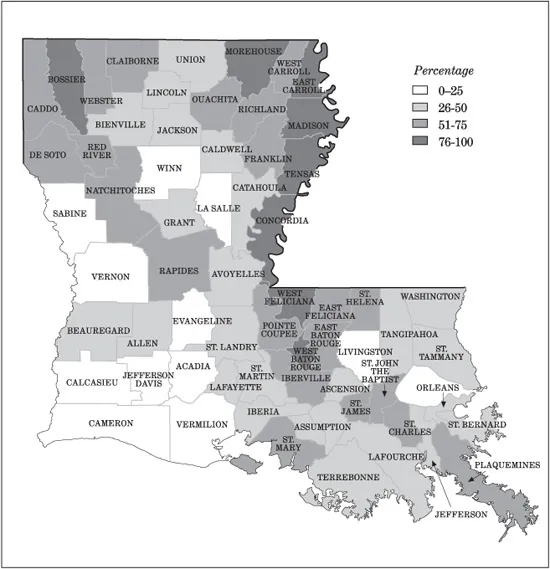
Map 1.1. African American Population as a Percentage of Total Population in Louisiana Parishes, 1900
Source: Bureau of the Census, Twelfth Census of the United States Taken in the Year 1900, Population, Part 2 (Washington, D.C.: GPO, 1902), 187.
Like the sugar parishes, the region retained much of its French Catholic heritage. There were some differences, however. Rice farmers preferred to hire white workers over black people because of the skill required to operate machinery, so African Americans usually represented only a small percentage of the population in these parishes. Less dependent than sugar growers on black labor and having no need to fear a large black majority, white people in the southwest could afford to be more racially tolerant than those in either of the plantation regions.5
Despite these regional variations, Louisiana was dominated politically and economically by a plantation- and business-owning elite whose behavior seemed influenced by its financial interests more than by its religious beliefs or cultural backgrounds. Whether French or Anglo, Louisiana's plantation parishes were among the most repressive areas in the nation, with reputations for the savage handling of black people dating back to the antebellum period.6 Even after slavery was abolished, neither the state's former slave-owners nor the northern investors who helped rebuild the plantation economy were willing to accord freed people the same rights to life, liberty, or property that they claimed for themselves. Successful cultivation of the state's staple crops depended on the availability of a reliable, cheap labor force that planters assumed would be provided by former slaves. When African Americans resisted that role, white Louisianans responded with intimidation, violence, and legislative measures designed to limit political participation and economic opportunities for black people.7
Planter priorities became apparent immediately after the Civil War, when state and local governments attempted to coerce freed people back onto the plantations by passing laws that restricted their mobility. In Opelousas, for example, ordinances prevented African Americans from buying property, limited the types of jobs they could hold, and prohibited black people who were not employed by white people from living in the town. In 1865 the state legislature discussed a series of measures to deny freed people any alternatives to plantation labor. At the end of the session, a new vagrancy law made unemployed or “idle” African Americans subject to arrest and hiring out to private employers if they were unable to pay the required bond, and legislation governing agricultural employment locked workers into year-long contracts with plantation owners. In addition, lawmakers set rules for laborers’ behavior that allowed employers to impose fines or deduct wages for infractions such as “feigning” sickness, disobeying orders, leaving without permission, impudence, and swearing.8
Planters also used physical violence to force black people to work for them. African Americans who deserted their employers, argued over working conditions, or attempted to rent or buy land of their own were harassed, beaten, and murdered. According to freedman Henry Adams, when two black men who had worked without pay for three months on a plantation near New Orleans complained to their employer, the white man “took his gun and shot at them, and did not pay them a cent.” Adams and other witnesses reported that landowners in Louisiana continued to whip black workers as they had done under slavery, and that hundreds of freed people who attempted to leave the plantations in 1865 had been killed.9
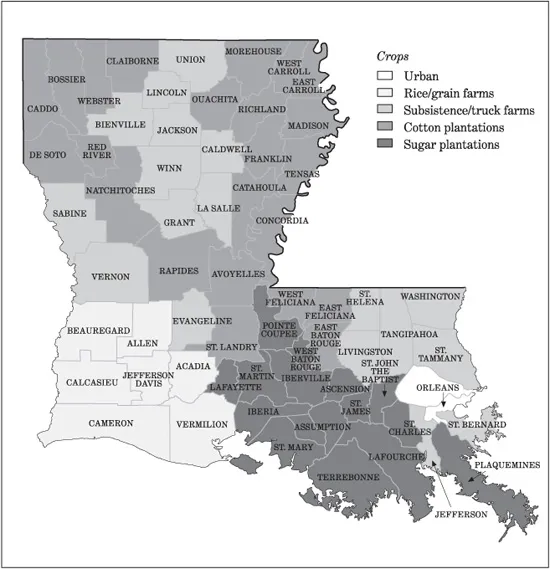
Map 1.2. Agricultural Regions of Louisiana, 1900–1930
Sources: Charles Robert Goins and John Michael Caldwell, Historical Atlas of Louisiana (Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1995), 4; Bureau of the Census, Thirteenth Census of the United States Taken in the Year 1910, Volume 6: Agriculture (Washington, D.C.: GPO, 1913), 690–95, and Fifteenth Census of the United States: 1930, Agriculture, Volume 2: Reports by States, Part 2: The Southern States (Washington, D.C.: GPO, 1932), 1265–71.
Congress responded to reports of violence against freed people by introducing harsher policies toward the South and weakening the plantation elite's political power. During Radical Reconstruction, many former Confederates were disfranchised while African Americans were allowed to vote and hold office. The result was massive and enthusiastic participation by black people in politics. Approximately 90 percent of black males of voting age were registered in Louisiana in 1867. Although not officially allowed to vote, black women influenced the political agenda by expressing their views at mass meetings and by encouraging men to vote for the candidates whom they believed would best protect their interests. African Americans’ voting strength and their active involvement in the Republican Party helped to elect a new state legislature in 1868 that was evenly divided between white and black representatives. African Americans also held the offices of lieutenant governor, state superintendent of education, and state treasurer. At the parish level, scores of black people served as sheriff, mayor, police juror, justice of the peace, tax collector, and in other administrative positions.10
Reconstruction legislators enacted laws to protect African Americans’ civil rights as well as social welfare provisions to help poor people.11 In response to demands from freed people, the Republican government introduced a system of universal education in Louisiana that was open to white and black children equally. African Americans expressed their desire for education in other ways as well. Black people of all ages flocked to classes organized by the Freedmen's Bureau and northern white missionaries to teach them to read and write. Many freed people also made access to education a condition of signing labor contracts with plantation owners.12
Most black families would have preferred to acquire land and work for themselves rather than continuing to labor for white people on the plantations. But the failure of the federal government to redistribute economic power as well as political power in the South after the Civil War left freed people dependent on their former masters for employment. Lacking the financial resources to strike out on their own, the majority of black people had few options apart from agricultural labor. Yet they resisted efforts by white employers to impose conditions resembling slavery. Freed people refused to work in gangs under the supervision of white overseers, forcing plantation owners to allow them to work as families on small plots of land in return for a portion of the crops that were raised. The sharecropping system thus initially emerged as a compromise between planters’ desire for a tightly controlled labor force and freed people's demands for land and autonomy. Though it caused much misery for African Americans in the twentieth century, sharecropping represented a small victory for freed people in their struggle for independence in the Reconstruction era.13
From the beginning, Radical Reconstruction faced strong opposition from many white Louisianans. Members of the planter aristocracy and newly arrived northern entrepreneurs resented the heavy taxes levied to pay for public services like schools, hospitals, and aid for unemployed people. They argued that prosperity could be regained only by keeping taxes and wages low to revive production of the state's staple crops and encourage investment. Although many poor white people benefited from and supported Republican economic policies, numerous others felt only the humiliation and bitterness of military defeat and occupation. In addition, for most white Louisianans, the loss of social superiority over black people was difficult to accept.14
Opponents of Reconstruction gravitated toward the state's reactionary Democratic Party, using violence, intimidation, and fraud to gain control of the state. Plantation owners and merchants denied land, credit, and supplies to people who supported the Republican Party, coercing many into voting for the Democrats instead. White supremacist groups like the Ku Klux Klan and the Knights of the White Camellia terrorized black communities to discourage African Americans from participating politically. Between 1866 and 1876 more than thirteen hundred black people were killed by white people in rural Louisiana, with political motivations underlying the vast majority of these murders.15
African Americans frequently fought back against these attacks, establishing a tradition of armed self-defense that continued into the twentieth century. During Reconstruction they commonly carried guns with them to political meetings, and some even armed themselves at work in the fields. Several “race riots” occurred in the spring of 1868 after black people shot back at white vigilantes in Bossier, St. Landry, St. Bernard, and Orleans Parishes. Black communities sometimes responded to threats of white violence by organizing into armed bands to protect themselves. Often, however, African Americans were outnumbered and faced opponents who had superior weaponry. In a shootout in the town of Colfax in 1873, black Republicans’ shotguns proved no match for a small cannon deployed by their Democratic adversaries. More than one hundred black people were killed, the worst massacre in the history of Reconstruction.16
By 1876 politics in many parts of the state had deteriorated into a virtual civil war. Political turmoil in Louisiana and elsewhere in the South disgusted northerners and convinced them to end the Reconstruction experiment. The federal government withdrew its forces from the region in 1877, leaving African Americans without the military and legal protections they needed to preserve the gains they had made. Fearing unrestrained violence and repression by white supremacists, thousands of black Louisianans left the state in 1879, joining similar numbers of “Exodusters” from other parts of the South who migrated to the Midwest after the end of Reconstruction.17 Those who remained behind experienced a steady deterioration in living and working conditions, along with the negation of their political rights.
With their opponents removed from office, conservative legislators passed measures that favored the state's wealthiest citizens. Funding for schools and other public services dropped off dramatically, while planters and businesspeople received hefty tax breaks. These actions plus successive economic crises in the late nineteenth century sparked a series of revolts by poorer people who demanded a government more responsive to their needs. In the 1880s and 1890s labor unions, farmers’ alliances, and the Populist movement gained widespread support from hard-pressed farmers and workers, both white and black. Plantation and business owners responded by employing the same violent methods they had used to overthrow Reconstruction. A strike by black sugar workers organized by the Knights of Labor in 1887 led to evictions and then to a massacre at Thibodaux that left over thirty people dead and hundreds more injured.18 Democrats punished supporters of the Populists with economic reprisals, social ostracism, beatings, and sometimes death. Conservatives did not even attempt to deny the deliberate miscounting of votes and other forms of corruption that became regular features of state and local elections. One northern Louisiana newspaper editorialized: “It is the religious duty of Democrats to rob Populists and Republicans of their votes whenever and wherever the opportunity presents itself and any failure to do so will be a violation of true Louisiana Democratic teaching. The Populists and Republicans are our legitimate political prey. Rob them! You bet! What are we here for?”19
By the late 1890s the state's prog...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- A Different Day
- Copyright Page
- Dedication
- Contents
- Illustrations, Tables, and Maps
- Acknowledgments
- Introduction
- 1 And Did Not Pay Them a Cent: Reconstruction and the Roots of the Twentieth-Century Freedom Struggle
- 2 Our Plight Here Is Bad: The Limits of Protest in a New South Plantation Economy
- 3 They Will Not Fight in the Open: Strategies of Resistance in the Jim Crow Era
- 4 We Feel You All Aut to Help Us: Struggles for Citizenship, 1914–1929
- 5 With the Aid of God and the F.S.A.: The Louisiana Farmers’ Union and the Freedom Struggle in the New Deal Era
- 6 I Am an American Born Negro: Black Empowerment and White Responses during World War II
- 7 The Social Order Have Changed: The Emergence of the Civil Rights Movement, 1945–1960
- 8 To Provide Leadership and an Example: The Congress of Racial Equality and Local People in the 1960s
- Epilogue
- Notes
- Bibliography
- Index