
- 240 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
Murray C. Kemp is one of Australia's foremost economists. He has held positions across the world including London School of Economics, U.C. Berkeley, Columbia University, McGill University, MIT, and latterly Macquarie University. Kemp was a Member of Council for the Econometric Society and was a Distinguished Fellow of the Economics
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Part I
The classical theory of international trade
1
The Torrens-Ricardo Principle of Comparative Advantage
An extension
1.1 Introduction
Nearly two hundred years on, the Torrens-Ricardo Principle of Comparative Advantage is still widely admired within the profession, and appears prominently in many elementary textbooks and in most treatises on international trade. However, careful inspection of the Principle, either in the mildly disparate formulations of Torrens (1815:264–5) and Ricardo (1817:135) or in any later formulation, reveals that it relies on restrictive assumptions about preferences and technology in each trading country, assumptions that are always implicit, never explicit. Specifically, the Principle rests on the assumption that in autarkic equilibrium each country consumes all commodities, at least incipiently. Our purpose is to make good this claim and to reformulate the Principle in sufficient generality to accommodate alternative assumptions about preferences and technology. In our reformulation the emphasis is on marginal rates of substitution in consumption, not on the traditional ratios of marginal labour costs in production. Thus our restatement concerns not merely the proper display of the Torrens-Ricardo Principle but rather its essential content. It is shown in effect that, in existing formulations, the supply side is assigned a role that it cannot always sustain. That two classical economists overlooked this point can be understood, but the same indulgence cannot be extended to the authors of neo-classical textbooks.1
1.2 The standard formulation
In the usual textbook formulation, two countries, England and Portugal, produce, consume and trade two commodities, cloth and wine; there are no non-tradable commodities. Each commodity is produced by means of a single primary factor, homogeneous labour, under constant returns to scale. Within each country, but not necessarily across countries, all households are identical in all respects: size, age distribution, preferences, quality of labour and access to technical information.2
For England, the household and (by revision of quantity units) the economy-wide production possibility locus is represented in Figure 1.1(a) by the straight segment QEQ′E, the slope of which is (minus) the ratio of the two marginal labour costs of production. In the absence of market distortions, a unique autarkic equilibrium is represented by point CE, where a community indifference curve forms a tangent to the production possibility locus and where, for each commodity, (positive) consumption is equal to production. The equilibrium commodity price ratio is equal to the ratio of marginal labour costs. Similarly, the unique autarkic equilibrium of Portugal is represented in Figure 1.1(b) by point CP.
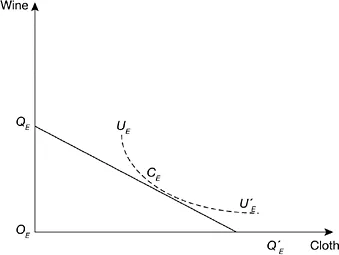
Figure 1.1a England’s autarkic equilibrium, with incomplete specialization
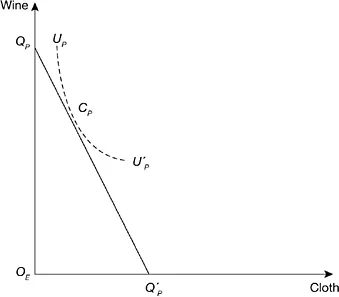
Figure 1.1b Portugal’s autarkic equilibrium, with incomplete specialization
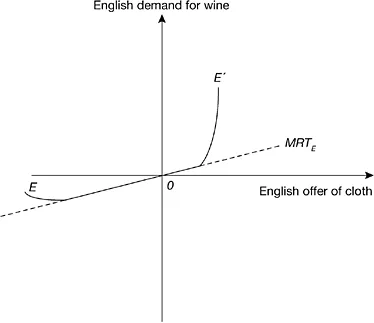
Figure 1.2a England’s offer curve, with incomplete autarkic specialization
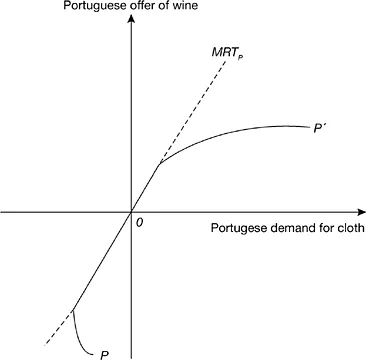
Figure 1.2b Portugal’s offer curve, with incomplete autarkic specialization
Abandoning the assumption of autarky, let us pass in review all conceivable world price ratios. Given any particular price ratio, we can determine the profit-maximizing pair of English outputs, uniquely except when the hypothetical price ratio is equal to the equilibrium autarkic price ratio, and we can determine uniquely the utility-maximizing English consumption pair. Transferring that information to Figure 1.2(a), we obtain the offer curve EOE′ for England, where the straight segm...
Table of contents
- Routledge Studies in International Business and the World Economy
- Contents
- Acknowledgements
- Introduction
- Part I The classical theory of international trade
- Part II The neo-classical theory of international trade
- Part III Normative trade theory
- Part IV Methodology
- Notes
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access International Trade Theory by Murray Kemp in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Business General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.