
- 418 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
The Handbook of Rare Earth Elements focuses on the essential role of modern instrumental analytics in the recycling, purification and analysis of rare earth elements. Due to their numerous applications, e.g. in novel magnetic materials for computer hardware, mobile phones and displays, rare earth elements have become a strategic and valuable resource. The detailed knowledge of rare earth element contents at every step of their life cycle is of great importance.
This reference work was compiled with contribution from an international team of expert authors from Academia and Industry to presend a comprehensive discussion on the state-of-the-art of rare earth element analysis for industrial and scientific purposes, recycling processes and purification of REEs from various sources.
Written with Analytical Chemists, Inorganic Chemists, Spectroscopists as well as Industry Practitioners in mind, the Handbook of Rare Earth Elements is an indispensable reference for everyone working with rare earth elements.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
1Introduction
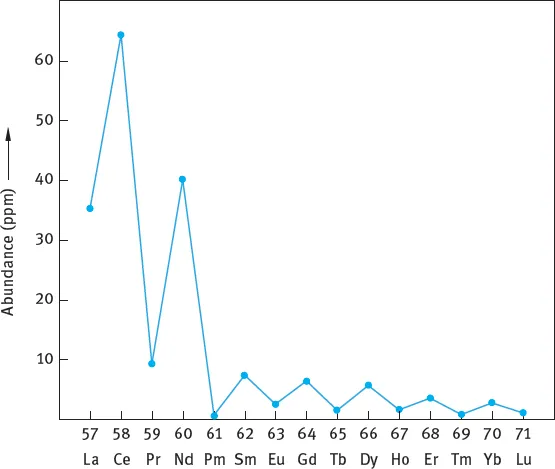
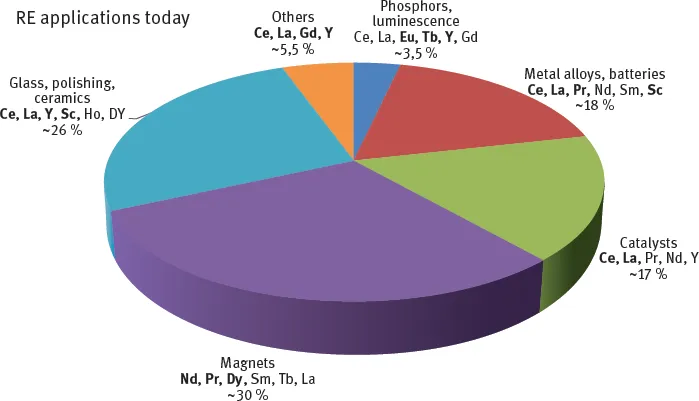

References
2Analytics of Rare Earth Elements – Basics and Methods
2.1Electronic configurations of RE elements and analytical properties
Lanthanum | 5d16s2 |
Gadolinium | 4f7 5d1 6s2 |
Lutetium | 4f14 5d1 6s2 |
Scandium | 3d1 4s2 |
Yttrium | 4d1 5s2 |
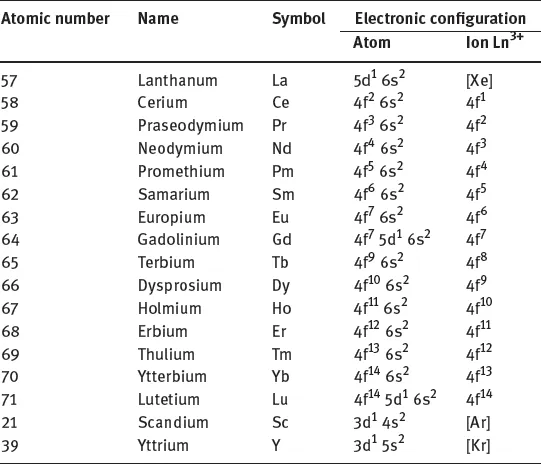
2.1.1Chemistry of Ln3+ ions
Table of contents
- Cover
- Titelseite
- Impressum
- Preface
- Contents
- List of Contributing Authors
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Analytics of Rare Earth Elements – Basics and Methods
- 3 Separation/Preconcentration Techniques for Rare Earth Elements Analysis
- 4 Chromatographic Techniques for Rare Earth Elements Analysis
- 5 Analysis and Speciation of Lanthanoides by ICP-MS
- 6 Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry for Rare Earth Elements Analysis
- 7 Application of Spark Atomic Emission Spectrometry for the Determination of Rare Earth Elements in Metals and Alloys
- 8 Use of X-ray Fluorescence Analysis for the Determination of Rare Earth Elements
- 9 Neutron Activation Analysis of the Rare Earth Elements (REE) – With Emphasis on Geological Materials
- 10 Automated Quantitative Rare Earth Elements Mineralogy by Scanning Electron Microscopy
- 11 Novel Applications of Lanthanoides as Analytical or Diagnostic Tools in the Life Sciences by ICP-MS-based Techniques
- 12 Lanthanoides in Glass and Glass Ceramics
- 13 Analysis of Rare Earth Elements in Rock and Mineral Samples by ICP-MS and LA-ICP-MS
- 14 Recycling of Rare Earth Elements
- Index