
- 473 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Modern Communications Technology
About this book
The book explains in a comprehensive way the basic terms of communication engineering, giving a proper amount of the needed mathematical background and explanations of the physical nature of the problems. The theory of communication sciences is explained by using knowledge and examples from real-world applications. The information is presented in a way that is understandable also for those who are not directly involved in communication sciences, but would like to learn more about them.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Edition
1Subtopic
Signals & Signal Processing1Signals and Systems
1.1Communication System
Signals are electrical equivalents of data to be transmitted through a communication system. A complete communication system consists of two stations, each equipped with a transmitter and a receiver, or combined into a single device called transceiver (Fig. 1.1). The medium of signal transmission can be wired (see Chapter 7) or wireless (see Chapter 8).
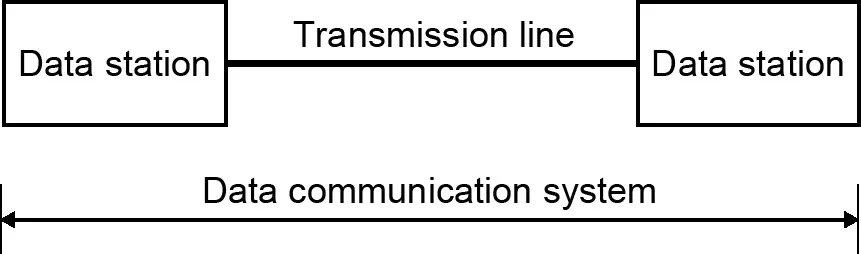
Fig. 1.1: Elements of communication system.
A data station consists of a Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and a Data Circuit Terminating Equipment (DCE). DTE converts user data into signals or reconverts received signals into user data. DCE is intermediate equipment between DTE and a data transmission circuit (Fig. 1.2).
The boundary between DTE and DCE is called interface and is defined according to the properties of transmission lines and exchanged signals between DTE and DCE. Intermediate devices (e.g. error control device, synchronization devices etc.) can be added into interfaces. Generally, an interface is also a boundary for performance and achievement of a network provider, his ownership and responsibility. Interfaces are internationally standardized, e.g. by ITU-T:
| – | V: | Data Communication over the telephone network (e.g. V.24/V.28, V.10, V.11) |
| – | X: | Data networks, open system communications and security (e.g. X.20, X.21, X.25, X.26, X.27) |
| – | I: | Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) |
| – | G: | Transmission systems in media, digital systems and networks |
| – | H: | Audiovisual and multimedia systems |
| – | T: | Terminals for telematic services |
| – | Z: | Languages and general software aspects for telecommunication systems |
| – | etc. |

Fig. 1.2: Elements of data station.
A DTE is a functional unit serving as a data source or a data sink and providing control function for data communication accordingly to the link protocol. A DTE can be a user himself or a device interacting with user, e.g. through a human-machine interface. DTE consists of:
–Data source or data sink in a form of data producers (input devices), data processing devices and data consumers (output devices).
–Controller with data preparation device, parallel-serial converter and serial-parallel converter, error control device, address recognizer end device, synchronizer device, sending or receiving part, management and data transmission control.
Examples of DTEs are terminals, memories, keyboards, printers, data concentrators and computers.
A DCE (also called Data Communication Equipment and Data Carrier Equipment) performs functions such as: line clocking, conversion of signals from DTE in corresponding form for transmission (line coding and modulation, see Chapter 5) and, the opposite, conversion of transmitted si...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Special Thanks
- Foreword
- Contents
- 1 Signals and Systems
- 2 Typical Communications Signals
- 3 Random Processes
- 4 Information Theory and Coding
- 5 Digital Transmission
- 6 Multiplexing
- 7 Wired Transmission Media
- 8 Wireless Channel
- 9 Cryptography
- References
- List of Acronyms
- Index
- Endnotes
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Modern Communications Technology by Natasa Zivic in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Signals & Signal Processing. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.