
- 310 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Image Analysis
About this book
This graduate textbook presents fundamentals, applications and evaluation of image segregation, unit description, feature measurement and pattern recognition. Analysis on textile, shape and motion are discussed and mathematical tools are employed extensively. Rich in examples and excises, it prepares electrical engineering and computer science students with knowledge and skills for further studies on image understanding.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1Introduction to Image Analysis
This book is the second volume of the book set “Image Engineering” and focuses on image analysis.
Image analysis concerns with the extraction of information from an image, that is, it yields data out for an image in. It is based on the results of image processing and provides the foundation for image understanding. It thus establishes the linkage between image processing and image understanding.
The sections of this chapter are arranged as follows:
Section 1.1 reviews first some concepts and definitions of image and then provides an overview of image engineering—the new disciplines for the combination of various image technology for the entire image field of research and application.
Section 1.2 recapitulates the definition and research contents of image analysis, discusses the connection and difference between image analysis and image processing as well as image analysis and pattern recognition, and presents the functions and features of each working module in the framework of an image analysis system.
Section 1.3 introduces a series of digital concepts commonly used in image analysis, including discrete distances, connected components, digitization models, digital arcs, and digital chords.
Section 1.4 focuses on the distance transforms (DTs) used extensively in image analysis. First, the definition and properties of DT are given. Then, the principle of using local distance to calculate the global distance is introduced. Finally, serial implementation and parallel implementation of discrete distance transformation are discussed separately.
Section 1.5 overviews the main contents of each chapter in the book and indicates the characteristics of the preparation and some prerequisite knowledge for this book.
1.1Image and Image Engineering
First, a brief review on the basic concepts of image is introduced, and then, the main terms, definitions, and development of the three levels of image engineering, as well as the relationship between different disciplines, are summarized.
1.1.1Image Foundation
Images are obtained by observing the objective world in different forms and by various observing systems; they are entities that can be applied either directly or indirectly to the human eye to provide visual perception (Zhang, 1996a). Here, the concept of the image is more general, including photos, pictures, drawings, animation, video, and even documents. The image contains a rich description of the objects it expresses, which is our most important source of information.
The objective world is three dimensional (3-D) in space, and two-dimensional (2-D) images are obtained by projection, which is the main subject of this book. In the common observation scale, the objective world is continuous. In image acquisition, the requirements of computer processing are taken into account, and hence, both in the coordinate space and in the property space, the discretizations are needed. This book mainly discusses discreted digital images. In the case of no misunderstanding, the word “image” is simply used. An image can be represented by a 2-D array f(x, y), where x and y represent the positions of a discrete coordinate point in the 2-D space XY, and f represents the discrete value of the property F at the point position (x, y) of the image. For real images, x and y and f all have finite values.
From a computational point of view, a 2-D M × N matrix F, where M and N are the total number of rows and the total number of columns, respectively, is used to represent a 2-D image:
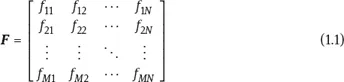
Equation (1.1) also provides a visual representation of a 2-D image as a spatial distribu...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- 1 Introduction to Image Analysis
- 2 Image Segmentation
- 3 Object Representation and Description
- 4 Feature Measurement and Error Analysis
- 5 Texture Analysis
- 6 Shape Analysis
- 7 Motion Analysis
- 8 Mathematical Morphology
- Answers to Selected Problems and Questions
- References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Image Analysis by Yujin Zhang, Tsinghua University Press in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Technology & Engineering & Data Mining. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.