eBook - ePub
Ancient Egypt
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
PART ONE
The land of the pharaohs
The emergence of civilization in Egypt depended heavily upon the region’s geographical features. Most important of these was the Nile, the longest river in the world, on the banks of which the first Egyptian settlements and cities evolved and developed.
THE VALLEY OF THE NILE
Little rain falls in the north-west corner of Africa where Egypt is located. Without the River Nile, Egypt would be little more than an uninhabitable hot sandy desert, and there would never have been an ancient Egyptian civilization, which sprang up along its banks.
Many thousands of years ago, Egypt was mainly swampland, but as the climate grew drier the Nile retreated, leaving a strip of fertile soil on both banks. This soil was refreshed each year by the floodwaters that covered the fields with rich black mud in which plants grew readily. The early settlers learned to farm this land and to construct canals and dykes to regulate the flow of water. Towns sprang up along the length of the Nile, the river providing the people with drinking water as well as water for crops.
THE BLACK LAND
The Egyptians called the fertile land on which they built their towns Kemet, meaning ‘black land’. The rest of the country was known as the Red Land. The deserts of the Red Land were very important because they protected the early Egyptians from attacks by neighbouring civilizations, as few armies were willing to cross such desolate waterless wastes.
Sacred river
The ancient Egyptians understood that their lives depended heavily upon the Nile. In their paintings, heaven was often depicted as fertile land surrounded by water.
The waterfalls and rapids of the Nile south of Egypt also hindered invasion from lower down the river. The Egyptians themselves transported their soldiers up or down the Nile to fight off any invaders. The Nile was also vital for trade, providing access to the waters of the Mediterranean Sea in the north and to central Africa in the south.
EGYPT AND THE WORLD
The geographical location of Egypt at the point where Africa meets the Middle East was to prove vital to its development into a great civilization. The natural resources of the region, which included minerals and building stone from the desert as well as crops from the fertile fields beside the Nile, could be transported either by river or across the desert to be traded with neighbouring peoples.
Access to the Mediterranean and to the Red Sea enabled Egyptian merchants sailing out of the Nile to take their goods anywhere in the known world.
EMPIRES OF THE PHARAOHS
With economic development came great wealth and political influence. The physical size of Egypt’s empire varied from age to age, sometimes extended by military conquest – at its greatest extent, it included large parts of northern Africa and Palestine among other neighbouring regions. The relatively close geographical links with the centres of Greek and Roman civilization were particularly important in the later history of ancient Egypt.
Centres of civilization
The most important centres of ancient Egyptian civilization were the traditional capitals of Memphis in the north (including the pyramids at Giza, near modern Cairo) and Thebes in the south (with such associated sites as Karnak, Luxor and the Valley of the Kings). The last capital of ancient Egypt, Alexandria (on the Nile delta in the far north of the country) was not built until the fourth century BC.
Aegyptus to Egypt
The word Egypt is derived from the Greek name for the country: Aegyptus. In Greek mythology, Aegyptus was a descendant of the heifer maiden lo and was the country’s first ruler.
Ancient Egypt
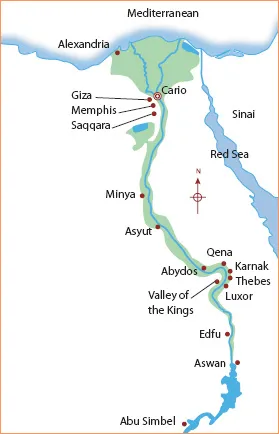

Egyptian civilization was concentrated on the banks of the Nile, from its delta extending 1000km (650 miles) south to Aswan.
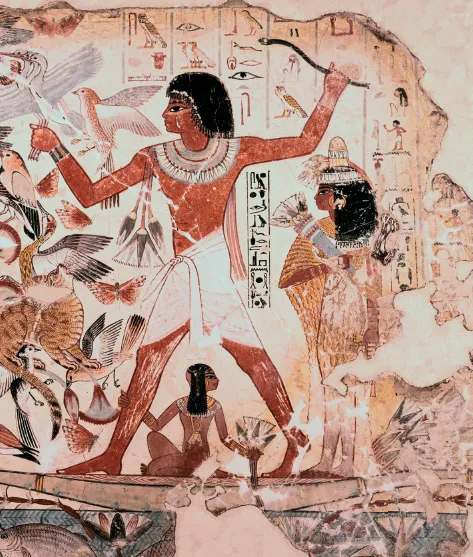

Egyptian life
A man and his family hunting wild birds on the River Nile, which was always at the heart of ancient Egyptian civilization.
A man and his family hunting wild birds on the River Nile, which was always at the heart of ancient Egyptian civilization.
PART TWO
The history of ancient Egypt
The civilization of ancient Egypt lasted some 3000 years, longer than any other civilization in world history. At its peak it was remarkable for its cultural, religious and economic achievements. Historians traditionally subdivide this era into a dozen or so periods covering 30 ruling dynasties, beginning around 3000 BC and ending with the Roman invasion in the first century AD.
PREDYNASTIC PERIOD
c. 8000 BC The drying-out of the Sahara caused by a change in the climate, and possibly over-grazing, forces the population to concentrate in the Nile Valley. Egyptian farmers become the first to herd domesticated cattle and other livestock.
c. 6000 BC The first simple single-sailed ships are built. Stone tools are replaced by tools made of metal. Trades include tanning and basket-weaving.
c. 5000 BC Two broadly similar civilizations develop, one in the south of the country (Upper Egypt) and one in the north (Lower Egypt).
c. 4000 BC The first large stone buildings are constructed. Advances are also made in the fields of alchemy, cosmetics, music, medicine and pottery. The building of underground tombs containing grave goods anticipates later burial practices.
c. 3500 BC The Egyptians invent senet, the world’s oldest known board game.
The first people came to Egypt from central Africa some time between 100,000 and 50,000 BC. Archaeological finds suggest that Egypt’s original hunter-gatherers learned to grow grain beside the Nile by 10,000 BC. It was on this prosperous agricultural economy that the country’s later greatness was to depend.
FLINT TOOLS
The first Egyptians belonged to wandering tribes who relied upon the use of flint tools. As the centuries passed they gradually settled in the Nile Valley, living by hunting animals and fishing.
CRAFTS AND TRADE
Around this time the Egyptians also developed skills in using stone, copper, clay, wood and leather and established thriving craft industries. The building of simple papyrus boats promoted links between communities and enabled traders to travel up and down the Nile. Villages and towns sprang up along the length of the river, from the delta in the north to what is now Aswan in the south, each with their own tribal chief, gods, burial customs and artistic styles.
UPPER AND LOWER EGYPT
Little is known about the history of these early kingdoms, though several rulers are known by name, among them Crocodile, Scorpion I, Scorpion II, Iryhor and Ka. The eventual merging of these two kingdoms, which shared a common language an...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Contents
- Introduction
- Part One: The Land of The Pharaohs
- Part Two: The History of Ancient Egypt
- Part Three: The Gods of Ancient Egypt
- Part Four: The Pharaohs
- Part Five: Life in Ancient Egypt
- Part Six: Working Life
- Part Seven: Learning in Ancient Egypt
- Part Eight: War in Ancient Egypt
- Part Nine: Death in Ancient Egypt
- Part Ten: Egypt Today
- Keep Reading
- Find Out More
- Glossary
- Copyright
- About the Publisher
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn how to download books offline
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 990+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn about our mission
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more about Read Aloud
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS and Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app
Yes, you can access Ancient Egypt by David Pickering in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in History & Egyptian Ancient History. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
