
- 284 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Banking and Finance Issues in Emerging Markets
About this book
The banking and finance sectors are relevant shares of modern economies and indeed drivers of growth in emerging economies. The majority of existing economic and finance textbooks focus on concepts and theories with briefly exposited real-world examples for illustration. This book, which collects chapters that are the contributions of the acknowledged experts in their fields, fills this gap by featuring in-depth analyses on prominent real-world topics in banking and finance. The book's applications of econometrics present insightful perspectives on the recent development of banking issues, stock market contagion, the impact of internet technology (IT) on stock markets, financial innovation and technology firms, and an international perspective on the loan puzzle and interest rate adjustment in emerging markets. In addition to exhaustive case studies on banking and finance in India, Hong Kong, Japan, and other Asian emerging markets, the authors coherently contribute an intellectual advancement of contemporary issues in banking and finance literature. The authors offer an essential reading and source of reference for postgraduate and advanced undergraduate courses in economics and finance.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Banking and Finance Issues in Emerging Markets by William A. Barnett,Bruno S. Sergi in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Finance. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
ASEAN-5 Economic and Exchange Rate Integration
a Faculty of Economics, Thammasat University, Bangkok, Thailand, e-mail: [email protected]
b College of Innovation Management, Rajamangala University of Technology Rattanakosin, Nakhonpathom, Thailand, e-mail: [email protected]
Abstract
For the past decades, issues concerning the impact of economic integration on financial integration, especially exchange rate integration, has been criticized among several regions such as ASEAN. This chapter intends to: (i) test for the exchange rate integration among the ASEAN-5, including Indonesia, Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand, using panel data techniques; and (ii) determine the impact of economic integration on the level of exchange rate integration among the ASEAN-5 countries. The purchasing power parity (PPP) is tested using panel unit root tests on monthly data. The results confirm the PPP among the ASEAN-5 countries due to lower transaction costs from ASEAN agreements. The chapter applies Multivariate GARCH (M-GARCH) models using daily data to determine the level of exchange rate integration among the ASEAN-3, including Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand. The results of panel cointegration tests using quarterly data of economic integration and exchange rate integration confirm the impact of international trade openness on exchange rate integration. With free trade agreements leading to lower trade barriers, lower transaction costs, and low transportation costs, the economic integration among ASEAN countries practically leads to a higher degree of exchange rate integration. The findings imply that trade liberalization has the strongest effect on the real exchange rate. As such, regulators of ASEAN countries should pay more attention to the exchange rate policies of each other because of the interdependence of their exchange rates.
Keywords: Economic integration; exchange rate integration; ASEAN-5; PPP; panel unit root test; panel cointegration test; M-GARCH
1. Introduction
For the past decades, economic integration among countries in the same region has been addressed and examined in many economic literatures. Controversies concerning advantages and disadvantages of the integration have long been studied and criticized, including the integration of the exchange rates of the countries in the same region or those of countries with the free trade agreement. Euro currency, as single currency among EU countries, can be used as an evidence of the exchange rate integration among the countries in Euro zone. For decades, economic integration among 10 Southeast Asia countries, ASEAN, including Brunei, Cambodia, Lao, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam, has resulted in the integration of these countries’ economies.
As the founder countries of ASEAN, Indonesia, Philippines, Malaysia, Singapore, and Thailand, also called as ASEAN-5, with the five decades agreement since 1967, invited their neighboring countries, including Brunei, Cambodia, Lao, Myanmar, and Vietnam, to join the free trade agreements among each other. With the goals of being regional single market and production base, ASEAN had set up agreement to continuously lower its tariff with the ultimate target of FTA at 0% tariffs rate. As a results, the tariff among ASEAN-5 have set to 0% since 2010. Petri, Plummer, and Zhai (2012) found that ASEAN market, especially ASEAN-5, had been integrated and converged in term of economic growth, both productivity and unemployment. Trade among ASEAN has increased from about 18% in 1985 to more than 30% in 2015.
According to the theory of purchasing power parity (PPP), with the lower transaction cost based on ASEAN agreements, law of one price of exchange rate among the five countries should hold. Figure 1 and Figure 2 reveal the comovement among the exchange rate indices of ASEAN-5 countries in US dollar and in real effective term during 2005–2017. However, Manzur (2018) claimed that exchange rate is always and everywhere controversial. Hence, question then arises whether the integration also covers exchange rate integration among the currency of these five countries.
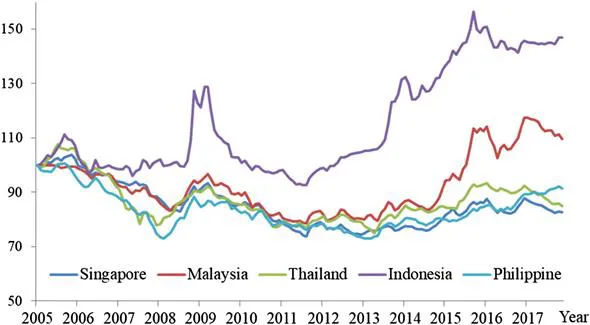
Figure 1: Exchange Rate Indices of ASEAN-5 (USD) 2005–2017.
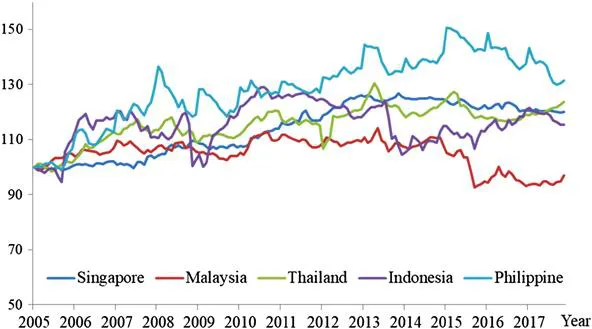
Figure 2: Real Effective Exchange Rates Index of ASEAN-5 2005–2017.
During 1980s, PPP were often tested by using time series analysis, such as unit root tests and cointegration test of the real exchange rate (i.e., Enders, 1988). These time series tests had later been criticized on the extreme low statistical power which led to unreliable testing results (Edison, Gagnon, & Melick, 1997; Koedijk, Schotman, & Van Dijk, 1998). To overcome the low power problem, the long-horizon ...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Introduction
- 1 ASEAN-5 Economic and Exchange Rate Integration
- 2 The Macroeconomic Effects of RMB Internationalization: The Perspective of Overseas Circulation
- 3 Dynamic Connectedness in Emerging Asian Equity Markets
- 4 Stock Market Contagion from a Spatial Perspective
- 5 Deposit Rate Asymmetry and Edgeworth Cycles after Hong Kong’s Interest Rate Deregulation
- 6 India’s Bad Loan Conundrum: Recurrent Concern for Banking System Stability and the Way Forward
- 7 An International Perspective on the Loan Puzzle in Emerging Markets☆
- 8 Is Japanese Regional Banks’ Overseas Business in Emerging Markets Hopeful?: An Observation through X-means Clustering
- 9 A Paradigm Shift in Banking: Unfolding Asia’s FinTech Adventures
- 10 Acceptance of Financial Technology in Thailand: Case Study of Algorithm Trading
- 11 Financial Innovation and Technology Firms: A Smart New World with Machines
- Index