
Using ANSYS for Finite Element Analysis, Volume I
- 208 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Using ANSYS for Finite Element Analysis, Volume I
About this book
Over the past two decades, the use of finite element method as a design tool has grown rapidly. Easy to use commercial software, such as ANSYS, have become common tools in the hands of students as well as practicing engineers. The objective of this book is to demonstrate the use of one of the most commonly used Finite Element Analysis software, ANSYS, for linear static, dynamic, and thermal analysis through a series of tutorials and examples. Some of the topics covered in these tutorials include development of beam, frames, and Grid Equations; 2-D elasticity problems; dynamic analysis; composites, and heat transfer problems. These simple, yet, fundamental tutorials are expected to assist the users with the better understanding of finite element modeling, how to control modeling errors, and the use of the FEM in designing complex load bearing components and structures. These tutorials would supplement a course in basic finite element or can be used by practicing engineers who may not have the advanced training in finite element analysis.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
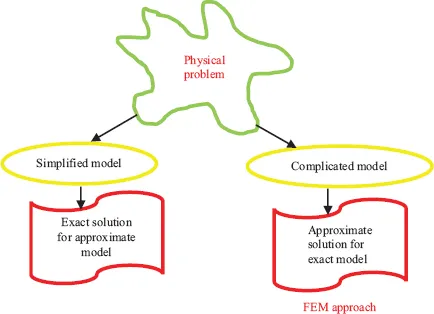
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half-title Page
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Contents
- List of Figures
- Preface
- 1 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis
- 2 Static Analysis Using Ansys
- 3 Geometric Modeling
- 4 Static Analysis Using Line Elements
- 5 Static Analysis Using Area Elements
- 6 Static Analysis Using Volume Elements
- 7 Thermal Stress Analysis
- Summary
- Bibliography
- Index
- Backcover
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app