
CCNA Security 210-260 Certification Guide
Build your knowledge of network security and pass your CCNA Security exam (210-260)
- 518 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
CCNA Security 210-260 Certification Guide
Build your knowledge of network security and pass your CCNA Security exam (210-260)
About this book
Become a Cisco security specialist by developing your skills in network security and explore advanced security technologies
Key Features
- Enhance your skills in network security by learning about Cisco's device configuration and installation
- Unlock the practical aspects of CCNA security to secure your devices
- Explore tips and tricks to help you achieve the CCNA Security 210-260 Certification
Book Description
With CCNA Security certification, a network professional can demonstrate the skills required to develop security infrastructure, recognize threats and vulnerabilities to networks, and mitigate security threats. The CCNA Security 210-260 Certification Guide will help you grasp the fundamentals of network security and prepare you for the Cisco CCNA Security Certification exam.
You'll begin by getting a grip on the fundamentals of network security and exploring the different tools available. Then, you'll see how to securely manage your network devices by implementing the AAA framework and configuring different management plane protocols.
Next, you'll learn about security on the data link layer by implementing various security toolkits. You'll be introduced to various firewall technologies and will understand how to configure a zone-based firewall on a Cisco IOS device. You'll configure a site-to-site VPN on a Cisco device and get familiar with different types of VPNs and configurations. Finally, you'll delve into the concepts of IPS and endpoint security to secure your organization's network infrastructure.
By the end of this book, you'll be ready to take the CCNA Security Exam (210-260).
What you will learn
- Grasp the fundamentals of network security
- Configure routing protocols to secure network devices
- Mitigate different styles of security attacks using Cisco devices
- Explore the different types of firewall technologies
- Discover the Cisco ASA functionality and gain insights into some advanced ASA configurations
- Implement IPS on a Cisco device and understand the concept of endpoint security
Who this book is for
CCNA Security 210-260 Certification Guide can help you become a network security engineer, a cyber security professional, or a security administrator. You should have valid CCENT or CCNA Routing and Switching certification before taking your CCNA Security exam.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Advanced ASA Configuration
- Routing on the ASA
- Device name, passwords, domain name
- Setting banners using the ASDM
- Configuring interfaces
- System time and Network Time Protocol (NTP)
- Access control list on the ASA
- Object groups
- Creating policies on ASA
- Advanced NAT configurations
Routing on the ASA
Static routing

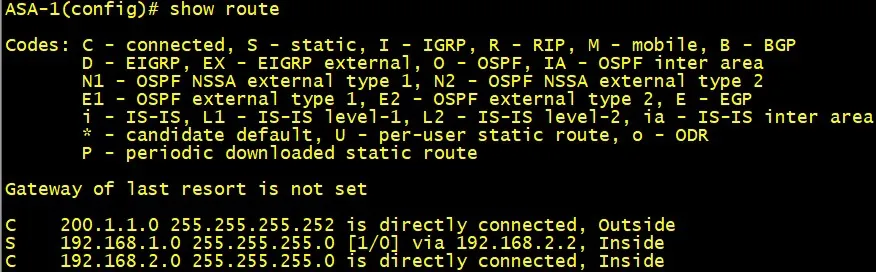



Configuring st...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- Packt Upsell
- Contributors
- Preface
- Exploring Security Threats
- Delving into Security Toolkits
- Understanding Security Policies
- Deep Diving into Cryptography
- Implementing the AAA Framework
- Securing the Control and Management Planes
- Protecting Layer 2 Protocols
- Protecting the Switch Infrastructure
- Exploring Firewall Technologies
- Cisco ASA
- Advanced ASA Configuration
- Configuring Zone-Based Firewalls
- IPSec – The Protocol that Drives VPN
- Configuring a Site-to-Site VPN
- Configuring a Remote-Access VPN
- Working with IPS
- Application and Endpoint Security
- Other Books You May Enjoy