
Mastering Numerical Computing with NumPy
Master scientific computing and perform complex operations with ease
- 248 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Mastering Numerical Computing with NumPy
Master scientific computing and perform complex operations with ease
About this book
Enhance the power of NumPy and start boosting your scientific computing capabilitiesAbout This Book• Grasp all aspects of numerical computing and understand NumPy• Explore examples to learn exploratory data analysis (EDA), regression, and clustering• Access NumPy libraries and use performance benchmarking to select the right toolWho This Book Is ForMastering Numerical Computing with NumPy is for you if you are a Python programmer, data analyst, data engineer, or a data science enthusiast, who wants to master the intricacies of NumPy and build solutions for your numeric and scientific computational problems. You are expected to have familiarity with mathematics to get the most out of this book.What You Will Learn• Perform vector and matrix operations using NumPy• Perform exploratory data analysis (EDA) on US housing data• Develop a predictive model using simple and multiple linear regression• Understand unsupervised learning and clustering algorithms with practical use cases• Write better NumPy code and implement the algorithms from scratch• Perform benchmark tests to choose the best configuration for your systemIn DetailNumPy is one of the most important scientific computing libraries available for Python. Mastering Numerical Computing with NumPy teaches you how to achieve expert level competency to perform complex operations, with in-depth coverage of advanced concepts.Beginning with NumPy's arrays and functions, you will familiarize yourself with linear algebra concepts to perform vector and matrix math operations. You will thoroughly understand and practice data processing, exploratory data analysis (EDA), and predictive modeling. You will then move on to working on practical examples which will teach you how to use NumPy statistics in order to explore US housing data and develop a predictive model using simple and multiple linear regression techniques. Once you have got to grips with the basics, you will explore unsupervised learning and clustering algorithms, followed by understanding how to write better NumPy code while keeping advanced considerations in mind. The book also demonstrates the use of different high-performance numerical computing libraries and their relationship with NumPy. You will study how to benchmark the performance of different configurations and choose the best for your system.By the end of this book, you will have become an expert in handling and performing complex data manipulations.Style and approachThis mastering guide will help you master your skills required to perform a complex numerical computation. The book contains the right mixture of theory and practical examples that will help you in dealing with the advanced NumPy and build solutions for your numeric and scientific computational problems
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Linear Algebra with NumPy
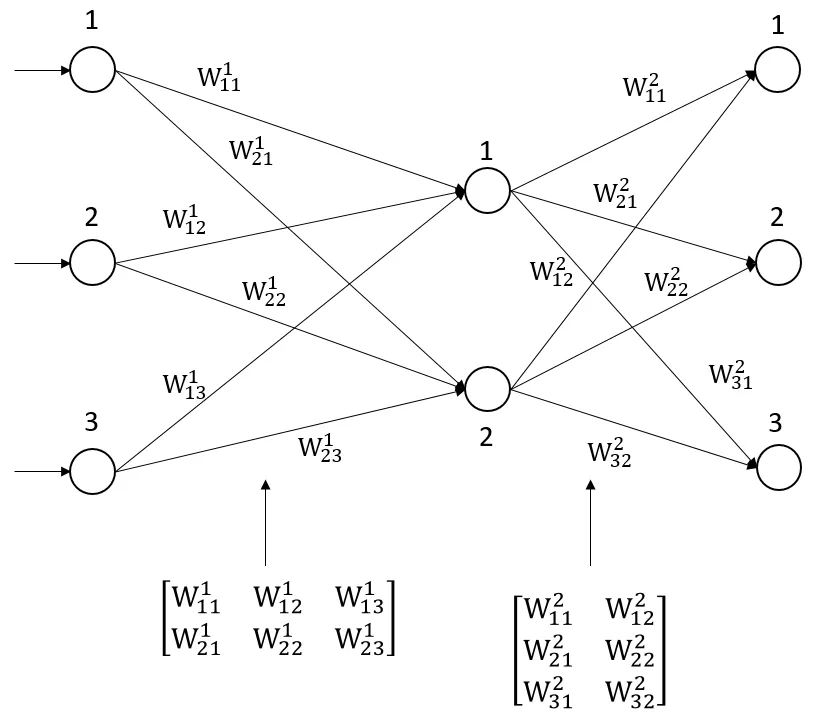
- Vector and matrix mathematics
- What's an eigenvalue and how do we compute it?
- Computing the norm and determinant
- Solving linear equations
- Computing gradient
Vector and matrix mathematics
In [1]: import numpy as np
a = np.arange(12).reshape(3,2)
b = np.arange(15).reshape(2,5)
print(a)
print(b)
Out[1]:
[[ 0 1]
[ 2 3]
[ 4 5]]
[[ 0 1 2 3 4]
[ 5 6 7 8 9]
In [2]: np.dot(a,b)
Out[2]: array([[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[15, 20, 25, 30, 35],
[25, 34, 43, 52, 61]])
In [3]: np.matmul(a,b)
Out[3]: array([[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[15, 20, 25, 30, 35],
[25, 34, 43, 52, 61]])
In [4]: a@b
Out[4]: array([[ 5, 6...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- Packt Upsell
- Contributors
- Preface
- Working with NumPy Arrays
- Linear Algebra with NumPy
- Exploratory Data Analysis of Boston Housing Data with NumPy Statistics
- Predicting Housing Prices Using Linear Regression
- Clustering Clients of a Wholesale Distributor Using NumPy
- NumPy, SciPy, Pandas, and Scikit-Learn
- Advanced Numpy
- Overview of High-Performance Numerical Computing Libraries
- Performance Benchmarks
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app