
Renewable Resources for Functional Polymers and Biomaterials
Polysaccharides, Proteins and Polyesters
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Renewable Resources for Functional Polymers and Biomaterials
Polysaccharides, Proteins and Polyesters
About this book
This book details polysaccharides and other important biomacromolecules covering their source, production, structures, properties, and current and potential application in the fields of biotechnology and medicine. It includes a systematic discussion on the general strategies of isolation, separation and characterization of polysaccharides and proteins. Subsequent chapters are devoted to polysaccharides obtained from various sources, including botanical, algal, animal and microbial.
In the area of botanical polysaccharides, separate chapters are devoted to the sources, structure, properties and medical applications of cellulose and its derivatives, starch and its derivatives, pectins, and exudate gums, notably gum arabic. Another chapter discusses the potential of hemicelluloses (xylans and xylan derivatives) as a new source of functional biopolymers for biomedical and industrial applications. The algal polysaccharide, alginate, has significant application in food, pharmaceuticals and the medical field, all of which are reviewed in a separate chapter. Polysaccharides of animal origin are included with separate chapters on the sources, production, biocompatibility, biodegradability and biomedical applications of chitin (chitosan) and hyaluronan. With the increasing knowledge and applications of genetic engineering there is also an introduction in the book to nucleic acid polymers, the genome research and genetic engineering.
Proteins and protein conjugates are covered, with one chapter providing a general review of structural glycoproteins, fibronectin and laminin, together with their role in the promotion of cell adhesion in vascular grafts, implants and tissue engineering. Another chapter discusses general aspects of a number of industrial proteins, including casein, caseinates, whey protein, gluten and soy proteins, with emphasis on their medical applications, and with reference to the potential of bacterial proteins. Another natural polymer resource, microbial polyesters, although small compared with polysaccharides and proteins, is also gaining increasing interest in biomedical technology and other industrial sectors. One chapter, therefore, is devoted to microbial polyesters, with comprehensive coverage of their biosynthesis, properties, enzymic degradation and applications.
By dealing with biopolymers at the molecular level, the book is aimed at the biomedical and wider materials science communities and provides an advanced overview of biopolymers at the graduate and postgraduate level. In addition it will appeal to both academic and industrial life scientists who are involved in research and development activities in the medical and biotechnology field.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
This chapter introduces the aim and scope of the book and presents an overview of the subject of natural polymers, mainly polysaccharides and proteins, but also microbial polyesters and nucleic acids. Details of the types, names and functions of individual polysaccharides and proteins are provided together with examples of their structural and physicochemical characteristics. It also highlights the main functional properties of these polymers including their rheological behavior, mechanisms of gelation, emulsification characteristics and film formation. The main applications of polysaccharides and proteins in medical and industrial sectors are also outlined with market size and trends.
1.1 Introduction to Biopolymers
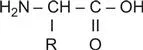
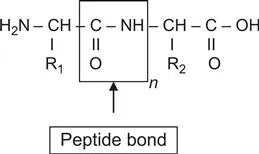
| Protein | Biological function |
| Collagen | Fibrous connective tissue (tendons, cartilage, bone) |
| Elastin | Elastic connective tissue (ligaments) |
| Keratin | Hair, skin, nails |
| Sclerotin | Exoskeletons of insects |
| Fibroin | Spiders web |
| Myosin | Thick filaments in microfibril |
| Actin | Thin fibrils in microfibril |
| Haemoglobin | Transports oxygen in blood |
| Myoglobin | Transports oxygen in muscle cells |
| Serum albumin | Transports fatty acids in blood |
| Ovalbumin | Egg-white protein |
| Casein | Milk protein |
| Ferritin | Stores iron in the spleen |
| Gliadin | Seed protein of wheat |
| Soy | Seed protein of soya bean |
| DNA polymerase (enzyme) | Replicates and repairs DNA |
| Galactosidase (enzyme) | Cleave galactose glycosidic bonds |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- Chapter 1 Natural Polymers: Introduction and Overview
- Chapter 2 Natural Polymer Resources: Isolation, Separation and Characterization
- Chapter 3 Cellulose and Its Derivatives in Medical Use
- Chapter 4 Xylan and Xylan Derivatives – Basis of Functional Polymers for the Future
- Chapter 5 Starch and its Derived Products: Biotechnological and Biomedical Applications
- Chapter 6 Gum Arabic and other Exudate Gums
- Chapter 7 Alginates: Existing and Potential Biotechnological and Medical Applications
- Chapter 8 Pectins: Production, Properties and Applications
- Chapter 9 Hyaluronan: a Simple Molecule with Complex Character
- Chapter 10 Chitin and Chitosan: Sources, Production and Medical Applications
- Chapter 11 β-Glucans
- Chapter 12 Microbial Polyesters: Biosynthesis, Properties, Biodegradation and Applications
- Chapter 13 Glycoproteins and Adhesion Ligands: Properties and Biomedical Applications
- Chapter 14 Nucleic Acid Polymers and Applications of Recombinant DNA Technology
- Subject Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app