
- 340 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Principles and Fundamentals of Islamic Management
About this book
The traditional approach to business and public management
assumes that management decisions and outcomes will remain the same,
irrespective of the environment in which they are applied. However, the value
systems operating within a society can also influence the principles that
govern modern management within organizations.
Principles and
Fundamentals of Islamic Management examines the concept of business and
public management from the viewpoint of Islam, with close reference to the
Quran and other illuminating Islamic sources. Seyed Mohammad Moghimi provides
key insights from an Islamic perspective across a comprehensive range of
management topics, including planning,
decision making and policy making, organizing, human resources management,
directing and organizational control. The book concludes by analyzing the role
of a company director within an Islamic context. Through this in-depth
exploration of Islamic management principles and fundamentals, the author
creates a modern and practical framework suitable for use by international business
managers.
Providing a much-needed insight into the practicalities of
management operations in an Islamic context, this book is essential reading for
researchers, managers, and for students of Islamic management at both
undergraduate and graduate levels.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Principles and Fundamentals of Islamic Management by Seyed Mohammad Moghimi in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Business & Business Ethics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Section 1
Introduction of Islamic Management
Chapter 1
The Concept of Organization and Management from the Islam Point of View
Behavioral Objectives
At the end of this chapter, readers will be able to:
- Be familiar with the philosophy of organization from the Islam point of view and account its existential reasons;
- Review the nature of organization from the Islam viewpoint in regarded to the Quran concept and validity related to it;
- Analyze organization as a tool to conceptualize a goodly life;
- Be familiar with the typology of organization based on the specific tasks stated by Imam Ali (AS) and Islam thinkers and explain their functions;
- Account the organization elements based on Islam viewpoint and describe each of them;
- Know every kind of organization objectives and policies and explain the level of objectives;
- Be familiar with all sorts of Islamic management definitions and reach a comprehensive definition in this context;
- Explain the importance and necessity of management in Islam based on Islamic verses and traditions;
- Be familiar with the characteristics of leaders and managers according to the Quran and Infallibles narratives.
1.1 What Is Organization?
1.1.1 Existential Philosophy of Organization From the Islam Viewpoint
From Islam's point of view, human beings have been inherently created sociable and they need “organization”1 for their survival and evolution in order to reach intended purposes and adjust their social relationships through cooperation. The principle of being social is due to social nature that the Quran has announced in the best way. Some of the Quran verses that emphasize the necessity of organizing and human’s social nature are as below:
- Grouping community members in order to know properly. The Lord states in verse 13 of Surah Hujurat: “O mankind! We created you from a single [pair] of a male and a female, and made you into nations and tribes, that ye may know each other [not that ye may despise [each other]”; “Hey people, we create you from one man and woman, and divided you in different branches and species to know each other.”
- Utilizing from individuals’ services in the shape of forming human communities. The Lord states in verse 32 of Surah Zukhruf: “and we raise some of them above others in ranks, so that some may command work from others. But the Mercy of thy Lord is better than the [wealth] which they amass.”; “and some of them are superior to the others through their ranks (material and spiritual perfections) while some use the others (to obtain atoms system and rightly organizing human community) and your god’s mercy (prophecy and public and religion guardianship) is the best than what they gather.”
- The community members’ interdependence to each other to meet the needs and demands. It has been stated in verse 195 of Surah Al-i-Imran: “You are members, one of another”; “Each of you is related to the other.”
- Unorganized and controversial social relationships underlie disruption and fragmentation of human communities. God states in verse 19 of Surah Yunus: “Mankind was but one nation, but differed [later]. Had it not been for a word that went forth before from thy Lord, their differences would have been settled between them.”; “(and people for a long time in the early creation) were united nation (and without difference), then they became difference due to social links in affairs of the world, and after revelation of the book to solve their problems and disputes.”
- Leadership based on God’s law is the key factor in integrating and organizing human societies. According to verse 213 of Surah Baqara, prophets also came to solve their disputes and differences: “Mankind was one single nation, and Allah sent Messengers with glad tiding and warnings; and with them He sent the Book in truth, to judge between people in matters wherein they differed; but the People of the Book, after the clear Signs came to them, did not differ among themselves, except through selfish contumacy. Allah by His Grace guided the believers to the Truth, concerning that wherein they differed. For Allah guided whom He will to a path that is straight.”; “The whole people were one group (before choosing prophets having sharia (law) (that the live according to their thoughts and minds without any divine law, but gradually they had problems and disputes in their affair of world). Then god raised prophets as a bearer of glad tidings and warner (with religion and divine laws) and rightly sent the holy book with them (and the high and rational purpose) to judge among people who are different with each other.” According to verse 13 of Surah Shora, inviting to unity and community was started for the first time by Noah (AS2) (the oldest prophet who had book and sharia) and then Ibrahim (AS), Moses (AS), and Jesus (AS) were responsible to this invitation. Therefore inviting to community has independently and explicitly been started by prophets system and in the form of religion. The Holy Quran has stated this issue, and it can be confirmed by looking through history as well.
As we can see, each of above verses has discussed on human’s social ability in a special way.
The first verse reminds creating man and woman and then shaping the social groups in the family and tribe and recognizes making group the community member as a factor to well-know the human. The second verse notes using the people services in the form of humans’ capture and cooperation with each other. The third verse points to human interdependence by which all people belong to each other.
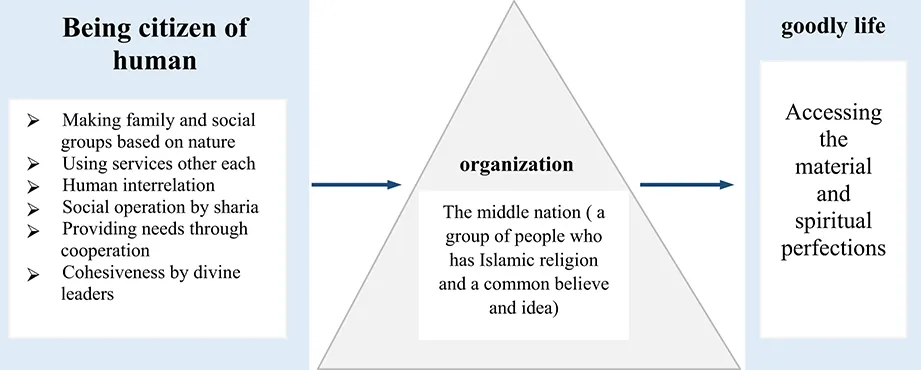
Fig. 1.1: The Process of Shaping an Organization Based on the Verses of the Quran.
According to the fourth verse, human beings have been suffering from conflicts and dispersion due to improper social relationships. In the verses 5 and 6, it is pointed out that prophets were raised as managers and leaders to solve the human conflicts. The Divinity has demanded all people to raise the religion (the verse 76 of Surah Nesa, the verse 159 of Surah Baqara, the verse 104 of Surah Al-I-Imran, the verse 25 of Surah Maida, the verse 13 of Surah Shura, and …). The Divinity states in the verse 200 of Surah Al-I-Imran: “O ye who believe! Persevere in patience and constancy; vie in such perseverance; strengthen each other; and fear Allah; that ye may prosper.”; “Oh, those who have believed, be patient and wait together and make relationships with each other and fear from God, perhaps be successful.”3 Patience in this verse includes patience in difficulties, patience in obedience, and patience in leaving the sin and emphasizing on mosabereh (being patient) means ordering each other to be patient that causes Islamic society members form a united and single force together and can bear harassments with each other. Morabeteh (having relationship) is more general than Mosabereh which means to be patient, and having patience means to unite forces against difficulties. Morabeteh, on the other hand, happens when all forces and affairs join the aspects of social and religious life either in joy or in severity. And the purpose of this relationship is that the society reach both the here and Hereafter bliss. In this verse, The Divinity has initially ordered the individual patience and then he has commanded to bear the difficulties collectively; that is to say, every individual's patience is dependent on the other individual's patience, as a result there will appear a strong mood in all the people that its effect will be multiplied. In this holy verse, it is commanded to the “communication,” it means that the community must make relationship in all aspects, whether in severity or in welfare. Allah has directly commanded on “sociability” in fighting for God (Jihad) that it is necessary to victory in defense and is a kind of social command. The other social order is the necessity of fasting ( not eating in a specific period of time) and Haj (Muslim pilgrimage to Mecca) for affordable people with no excuse, and the necessity of such canonization is that people gather to implement Hajj and fast; in particular, at the end of both worships, there is an Eid and also it is held as the pray of Eid. The Friday pray a week is necessary that it must hold collectively. In some cases, the lawgiver has enforced the congregational prayer; but in some other affairs sociability is not necessary (the congregational prayer is recommended, but traditionally people pray collectively because it is necessary that people implement the prophet’s tradition). Islam also respects sociability in all religious, trade, and political rules; it is sociable in its fundamental cognitions. Firstly, Islam has ordered the society to invite people to religion continuously; secondly, people are obliged to do enjoining good and forbidding wrong; and thirdly, Islam has commanded that Muslims keep away from people who have biased and dubious thoughts (the verse 104 of Surah, the verse 70 of Surah Anam) (Tabatabaei, 2012, pp. 126–132; Fig. 1.1).
According to Abouraihan Birouni, human sociability is based on some significant principles:
- The principle of homogeneity: Abouraihan approaches to the etymology of human through a principle derived from “familiarity and fondness,” meaning that the human life is completed by friendship and cooperation with others and the foundation of community is based on homogeneity and similarity. In addition to homogeneity, he emphasizes on the other concepts of the philosophy of human sociability such as “homomorphism, feeling the compassion and mutual understanding.”
- The principle of contradiction: this principle is related to the differences of various purposes and demands that cause to create social conflicts itself. In other words, the human body is formed by different and even opposite elements which cause differences among tastes and natures, and in the next step, impacts on individuals' relationships and intents in such a way that conflict against conflict is always wrath and usurpation and is against oneself. Therefore, while the opposite natures fend each other, for some reasons they also intend to attraction and cooperate.
- Human’s requirements: human beings need a social life to meet their life's needs and these are the needs which lead to human careers and different kinds of science and education. (Moghimi, 2011, pp. 73–75).
According to Khaje Nasirodin Toosi’s view, the origin of collective life is in human’s tendency to provide primary requirements, and meeting such needs is related to individuals’ cooperation and assistance, so somebody gives more than what it is needed to the others and others give what they have provided to him and they meet their requirements fairly. The existence of humankind can't be defined without their being helpful to each other, and this is impossible without society; thus humans need society, and such a community with all its own tools is called a “civilization.” Therefore, collective life is suitable for entities which provide for human’s collective needs, and with such entities, “civilization” is formed and determines a status and role for everyone and individuals play their roles according to their crafts originated from different interests, tastes, and motivations; therefore divine wisdom is based on efforts and opinions in order to find a job. Khaje Nasirodin Toosi believes that: “and the place where includes the community of different individuals with various opinions, thoughts, crafts and careers in itself that provide each other’s lives facilities through cooperation is called ‘utopia’ (Madine). This is the meaning of the philosophers’ words that ‘human is naturally civil.’ It means that human inherently needs what is called ‘civilization’” (Yousefi Rad, 2001, pp. 100–102). Sadrodin believes that human instead of his status as divine caliph is a “civil creature.” Human is naturally civil and its meaning is not realized in this world, except by accepting civilization and cooperation and social life with others (Mohajernia, 2008, pp. 236–237). Therefore, one the most important aims of sending prophets and holy books was to improve human beings' lives and their welfare, since divine knowledge and the origin of the spiritual journey are provided in this world. Mulla Sadra reach the necessity of government (organization) from the necessity of social life. Accessing the ultimate perfection, greater good and happiness are not possible except in the shadow of government (organization) in the triple shape of “city, nation, and world mission” (Mohajernia, 2008, pp. 236–240).
Farabi (829–929) believes: “so every city that the purpose of gathering in it really is cooperation will cause the people reach happiness; that city is ‘utopia’ and society where cooperation is implemented to reach happiness through it is utopian community and the nation that its all purposes is to reach the real happiness together cooperate and help with each other; that is utopian nation and that is why missioner or agent (utopian world community) and it will be realized when all nations cooperate to reach the real happiness.” In the other word, the citizen of utopia has dynamics and mobility and the right of participation in public affairs and has tasks according to his individual abilities to respond to the needs that are stated in a community. From Farabi’s point of view, the ultimate purpose of utopia is to reach human virtue, goodness, happiness, and perfection (PourAhmad, Habibi, & Jafari Mehrabadi, 2012, p. 17). Utopia is a political society where utopian policies are implemented by ruler and a set of organizations, structures, and special relationships (Yousefi Rad, 2001, pp. 74–75).
Khaje Nasirodin Toosi considers the tendencies inside the human as the origin of collective life so individuals gather to meet their necessary and primary needs, and such tendencies are always in any situation and position for the human and his fellow men. On the one hand, different crafts and career that people gain in the community is necessary to adjust and classify in order to meet their requirement, and on the other hand, the tempers of aggressiveness, jealousy, and greed to the property of others in any human cause to gather and attract much benefit for himself, and the other people are deprived. A manager must rule on this community to organize relationships and justice in people’s rights. Therefore, human community is established if they pursue a goal and there is a skillful manager on the top to manage their affairs. Thus, the societies of those individuals ready to cooperate is purposeful and away from disparities as well as conflict of interests and violating the rights of each other and a community with special relationships; so each one has a special role and position in technology and the world durability and human life system are realized by individuals’ important task (Yousefi Rad, 2001, pp. 146–148). According to Ibn Roshd, a human, by nature, is a civil creature who not only needs the government (organization) to reach his perfection and ultimate but also in all objects necessary for his life, he requires cooperation with others. Therefore, from Ibn Roshd’s view, not only the government (organization) causes to defect human, but also it is never possible that it provides human’s necessary needs (Majidi & Shafiei Ghahfarhi, 2012, p. 149).
According to Khaje Nasirodin Toosi, a complete human society includes people with different motivations. These motivations will result in creating various careers and crafts, and these different crafts and careers and their roles shape various institutions and organizations, each of which has a special position and status and provides a part of social human needs and their relations with their fellow men; the greatest decision-making institute that is on the top of all institutions whose leadership is the most superior is “the government.” Khaje Toosi believes that people's communication is the origin of creating a government that has a political community to meet its requirement together, and the case of such a collection and union is that the people leave their different tastes and desires to someone as an authority to control and direct them in a way that can meet the individuals' requirements and needs. Civil community respected Khaje Nasir Toosi is divided two kinds of system (utopia and non-utopia) through its validity of purpose and its people’s aim (Yousefi Rad, 2001, pp. 213–217). Alamme Davani knows the individual’s perfection by his attendance in the society and making relationships and cooperation in order to meet the others’ needs and implementing justice on relationships and cooperation. In the other word, the first and the last of human perfection and development is to find “a collective entity,” and if one goes away from this entity in each level, he has less perfection and development and if he tries to improve his collective entity in each level, he has more much perfection (Yousefi Rad, 2001, p. 112). From Khaje Nasirodin’s point of view, due to their extension and complexity, human societies need some factors which stabilize their base and form them to survive. Therefore, the factors of survival and durability of social organization and entity institutions are as follows: love, honesty, justice, policy (management), and law. Each of these factors plays an important role in stabilization of collective life. Justice makes balance in structures, and love causes convergence among individuals and social community, so promoting honesty among people leads to convergence and policy (management) and law leads to survival and co...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title
- Copyright
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- About the Author
- Preface
- Section 1: Introduction of Islamic Management
- Section 2: Management Functions In Islamic Management
- References
- Index