
Kubernetes Design Patterns and Extensions
Enhance your container-cluster management skills and efficiently develop and deploy applications
- 106 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Kubernetes Design Patterns and Extensions
Enhance your container-cluster management skills and efficiently develop and deploy applications
About this book
Master the art of container management with Kubernetes and study robust container orchestration to ensure that your container-based applications sail into production without hiccups
Key Features
- Implement best practices in cloud-native applications using Kubernetes
- Explore the usage of client libraries and programmatic access to Kubernetes
- Use your domain expertise to code
Book Description
Before plunging into how Kubernetes works, this book introduces you to the world of container orchestration and describes the recent changes in application development. You'll understand problems that Kubernetes solves and get to grips with using Kubernetes resources to deploy applications. In addition to this, you'll learn to apply the security model of Kubernetes clusters.
Kubernetes Design Patterns and Extensions describes how services running in Kubernetes can leverage the platform's security features. Once you've grasped all this, you'll explore how to troubleshoot Kubernetes clusters and debug Kubernetes applications. You also discover how to analyze the networking model and its alternatives in Kubernetes, and apply best practices with design patterns.
By the end of this book, you'll have studied all about using the power of Kubernetes for managing your containers.
What you will learn
- Understand and classify software designs as per the cloud-native paradigm
- Apply best practices in Kubernetes with design patterns
- Set up Kubernetes clusters in managed and unmanaged environments
- Explore Kubernetes extension points
- Extend Kubernetes with custom resources and controllers
- Integrate dynamic admission controllers
- Develop and run custom schedulers in Kubernetes
- Analyze networking models in Kubernetes
Who this book is for
Kubernetes Design Patterns and Extensions is for you if you are interested in configuring and troubleshooting Kubernetes clusters and developing microservices-based applications on Kubernetes clusters. DevOps engineers with basic knowledge of Docker will also find this book useful. It is assumed that you are comfortable using command-line tools and programming concepts and languages.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
Kubernetes Extensions
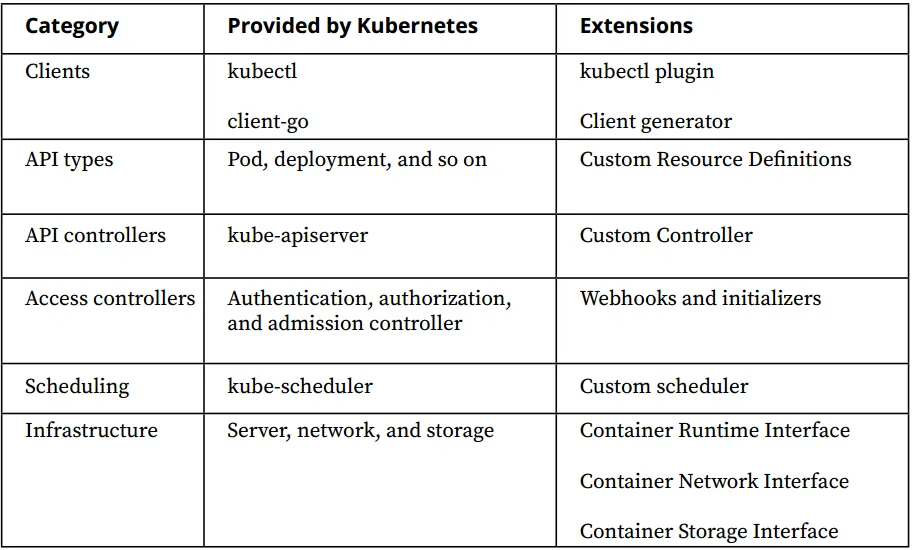
Kubernetes Extension Points
- Kubernetes clients: It is possible to extend client applications such as kubectl by writing kubectl plugins. These extensions will help you use kubectl with less human interaction, such as choosing a Kubernetes cluster context automatically. Likewise, generated clients with the OpenAPI specifications can extend client libraries such as client-go. With these generated clients, you can programmatically use the Kubernetes API in custom applications.
- Kubernetes API types: Kubernetes API resources such as pods, deployments, and many more are highly configurable, but it is also possible to add new resources called custom resources.
- Kubernetes API controllers: The control plane of Kubernetes, which includes the Kubernetes API server, handles all operations, such as automatic scaling or self-healing; however, it is also possible to develop custom controllers.
- Access controllers: The access control mechanism that handles authentication, authorization, and admission controllers can be extended by connecting to webhook servers or intervening with initializers.
- Scheduling: kube-scheduler already handles the scheduling of pods to the nodes; however, it is also possible to create custom schedulers and deploy them to the clusters.
- Infrastructure: The infrastructure part of Kubernetes is standardized, regarding the server, network, and storage with the Container Runtime Interface (CRI), Container Network Interface (CNI), and Container Storage Interface (CSI). The implementation, of these interfaces provide ways of extending the infrastructure of the underlying Kubernetes clusters.
Extending Kubernetes Clients
- It switches the Kubernetes cluster context automatically
- It calculates and displays the uptime information of pods
- It connects via SSH into a container with a specific user
Extending the Kubernetes API
- RESTful API: New resources are directly included in the RESTful API so that they are accessible with their special endpoints.
- Authentication and authorization: All requests for new resources go through the steps of authentication and authorization, like native requests.
- OpenAPI discovery: New resources can be discovered and integrated into OpenAPI specifications.
- Client libraries: Client libraries such as kubectl or client-go can be used to interact with new resources.
- Create a new Kubernetes resource to introduce the new API types
- Control and automate operations to implement custom logic as an additional API controller
Custom Resource Definitions
Table of contents
- Title
- Copyright and Credits
- Contributor
- Packt Upsell
- Preface
- Kubernetes Design Patterns
- Kubernetes Client Libraries
- Kubernetes Extensions
- Solutions
- Other Books You May Enjoy