
Apache Hadoop 3 Quick Start Guide
Learn about big data processing and analytics
- 220 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Apache Hadoop 3 Quick Start Guide
Learn about big data processing and analytics
About this book
A fast paced guide that will help you learn about Apache Hadoop 3 and its ecosystem
Key Features
- Set up, configure and get started with Hadoop to get useful insights from large data sets
- Work with the different components of Hadoop such as MapReduce, HDFS and YARN
- Learn about the new features introduced in Hadoop 3
Book Description
Apache Hadoop is a widely used distributed data platform. It enables large datasets to be efficiently processed instead of using one large computer to store and process the data. This book will get you started with the Hadoop ecosystem, and introduce you to the main technical topics, including MapReduce, YARN, and HDFS.
The book begins with an overview of big data and Apache Hadoop. Then, you will set up a pseudo Hadoop development environment and a multi-node enterprise Hadoop cluster. You will see how the parallel programming paradigm, such as MapReduce, can solve many complex data processing problems.
The book also covers the important aspects of the big data software development lifecycle, including quality assurance and control, performance, administration, and monitoring.
You will then learn about the Hadoop ecosystem, and tools such as Kafka, Sqoop, Flume, Pig, Hive, and HBase. Finally, you will look at advanced topics, including real time streaming using Apache Storm, and data analytics using Apache Spark.
By the end of the book, you will be well versed with different configurations of the Hadoop 3 cluster.
What you will learn
- Store and analyze data at scale using HDFS, MapReduce and YARN
- Install and configure Hadoop 3 in different modes
- Use Yarn effectively to run different applications on Hadoop based platform
- Understand and monitor how Hadoop cluster is managed
- Consume streaming data using Storm, and then analyze it using Spark
- Explore Apache Hadoop ecosystem components, such as Flume, Sqoop, HBase, Hive, and Kafka
Who this book is for
Aspiring Big Data professionals who want to learn the essentials of Hadoop 3 will find this book to be useful. Existing Hadoop users who want to get up to speed with the new features introduced in Hadoop 3 will also benefit from this book. Having knowledge of Java programming will be an added advantage.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Developing MapReduce Applications
- How MapReduce works
- Configuring a MapReduce environment
- Understanding Hadoop APIs and packages
- Setting up a MapReduce project
- Deep diving into MapReduce APIs
- Compiling and running MapReduce jobs
- Streaming in MapReduce programming
Technical requirements
How MapReduce works
What is MapReduce?
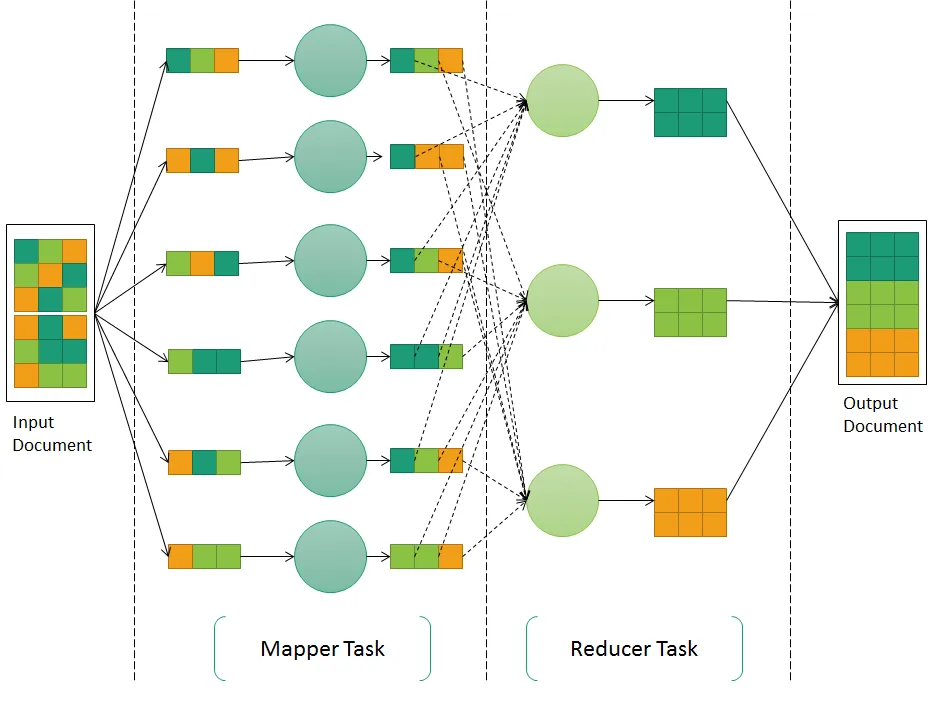
An example of MapReduce
- Problem: There is an e-commerce company that offers different products for purchase through online sale. The task is to find out the items that are sold in each of the cities. The following is the available information:
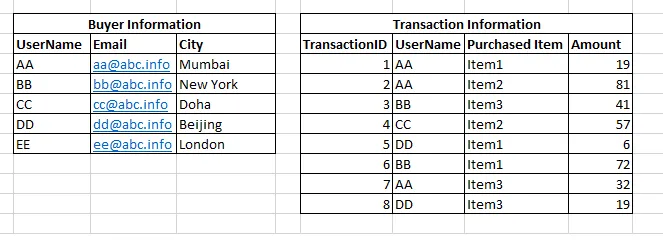
- Solution: As you can see, we need to perform the right outer join across these tables to get the city-wise item sale report. I am sure database experts who are reading this book can simply write a SQL query, to do this join using database. It works well in general. When we look at high-volume data processing, this can be alternatively performed using MapReduce and with massively parallel processing. The overall processing happens in two phases:
- Map phase: In this phase, the Mapper job is relatively simple—it cleanses all of the input and creates key-value pairs for further processing. User will supply the information pertaining to user in <key, value> form for the Map Task. So, a Map Task will only pick relevant attributes in this case, which would matter for further processing, such as UserName and City.
- Reduce phase: This is the second stage, where the processed <key, value> pair is reduced to a smaller set. The Reducer will receive information directly from Map Task. As you can see in the following screenshot, the reduce task performs the majority of operations; in this case, it reads the tuples and creates intermediate files process. Once the ...
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- Dedication
- Packt Upsell
- Contributors
- Preface
- Hadoop 3.0 - Background and Introduction
- Planning and Setting Up Hadoop Clusters
- Deep Dive into the Hadoop Distributed File System
- Developing MapReduce Applications
- Building Rich YARN Applications
- Monitoring and Administration of a Hadoop Cluster
- Demystifying Hadoop Ecosystem Components
- Advanced Topics in Apache Hadoop
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app