
Machine Learning with scikit-learn Quick Start Guide
Classification, regression, and clustering techniques in Python
- 172 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Machine Learning with scikit-learn Quick Start Guide
Classification, regression, and clustering techniques in Python
About this book
Deploy supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms using scikit-learn to perform classification, regression, and clustering.
Key Features
- Build your first machine learning model using scikit-learn
- Train supervised and unsupervised models using popular techniques such as classification, regression and clustering
- Understand how scikit-learn can be applied to different types of machine learning problems
Book Description
Scikit-learn is a robust machine learning library for the Python programming language. It provides a set of supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms. This book is the easiest way to learn how to deploy, optimize, and evaluate all of the important machine learning algorithms that scikit-learn provides.
This book teaches you how to use scikit-learn for machine learning. You will start by setting up and configuring your machine learning environment with scikit-learn. To put scikit-learn to use, you will learn how to implement various supervised and unsupervised machine learning models. You will learn classification, regression, and clustering techniques to work with different types of datasets and train your models.
Finally, you will learn about an effective pipeline to help you build a machine learning project from scratch. By the end of this book, you will be confident in building your own machine learning models for accurate predictions.
What you will learn
- Learn how to work with all scikit-learn's machine learning algorithms
- Install and set up scikit-learn to build your first machine learning model
- Employ Unsupervised Machine Learning Algorithms to cluster unlabelled data into groups
- Perform classification and regression machine learning
- Use an effective pipeline to build a machine learning project from scratch
Who this book is for
This book is for aspiring machine learning developers who want to get started with scikit-learn. Intermediate knowledge of Python programming and some fundamental knowledge of linear algebra and probability will help.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Classification and Regression with Trees
- Classification trees
- Regression trees
Technical requirements
https://github.com/PacktPublishing/Machine-Learning-with-scikit-learn-Quick-Start-Guide/blob/master/Chapter_06.ipynb.
Classification trees
- The decision tree classifier
- The random forest classifier
- The AdaBoost classifier
The decision tree classifier
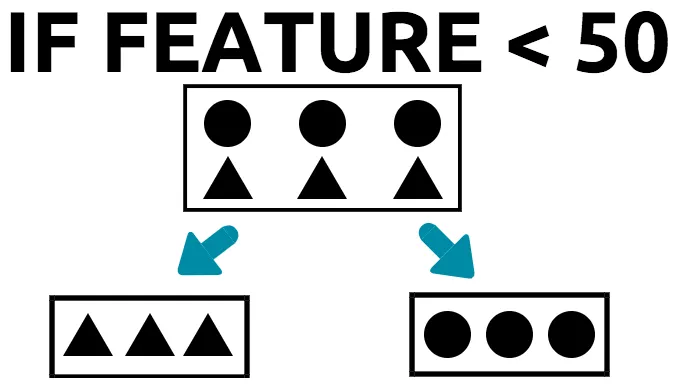
If (value of feature is less than 50); then (put the triangles in the left-hand box and put the circles in the right-hand box). Picking the best feature
- The tree splits the data from the root node into two distinct groups.
- In the left-hand group, we see that there are two triangles and one circle.
- In the right-hand group, we see that there are two circles and one triangle.
- Since the tree got the majority of each class into one group, we can say that the tree has done a good job when it comes to splitting the data into distinct groups.
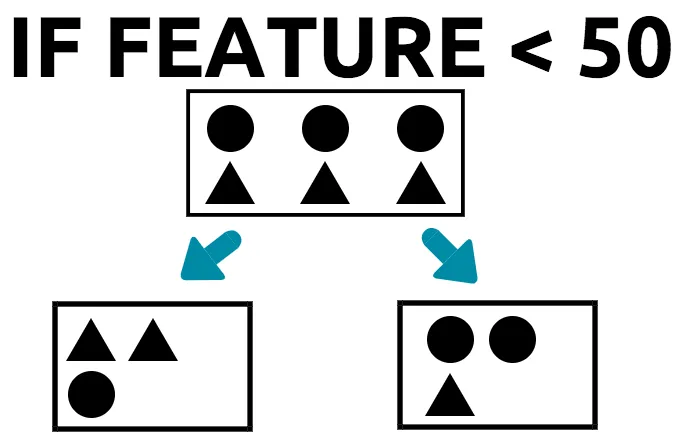
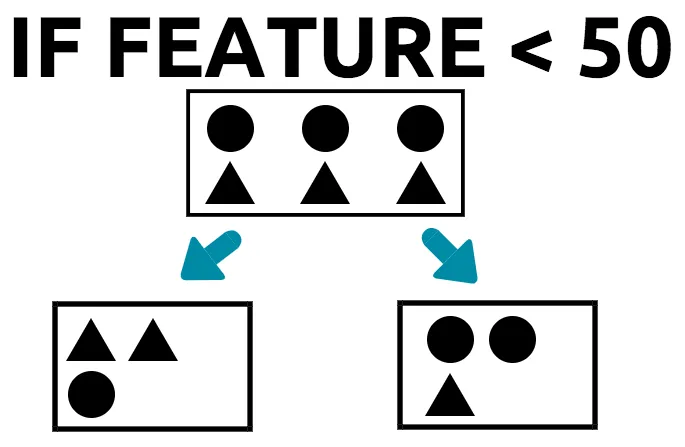
- The tree splits the data in the root node into four distinct groups. This is bad in itself, as it is clear that there are only two categories (circle and triangle).
- Furthermore, each group has one triangle and one circle.
- There is no majority class or category in any one of the four groups. Each group has 50% of one category; therefore, the tree cannot come to a conclusive decision, unless it relies on more features, which then increases the complexity of the tree.
The Gini coefficient
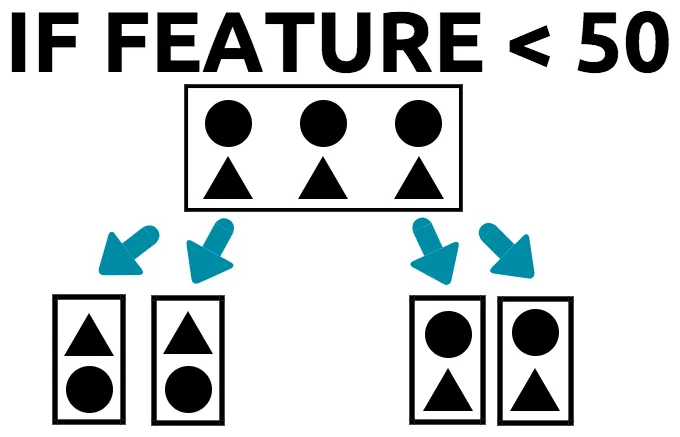
- The feature splits the data into two groups.
- In the left-hand group, we have two triangles and one circle.
- Therefore, the Gini for the left-hand group is (2 triangles/3 total data points)^2+ (1 circle/3 total data points)^2.
- To calculate this, do the following: 0.55.

- A value of 0.55 for the Gini coefficient indicates that the root of this tree splits the data in such a way that each group has a majority category.
- A perfect root feature would have a Gini coefficient of 1. This means that each group has only one class/category.
- A bad root feature would have a Gini coefficient of 0.5, which indicates that there is no distinct class/category in a group.
Implementing the decision tree classifier in scikit-learn
Table of contents
- Title Page
- Copyright and Credits
- Dedication
- About Packt
- Contributors
- Preface
- Introducing Machine Learning with scikit-learn
- Predicting Categories with K-Nearest Neighbors
- Predicting Categories with Logistic Regression
- Predicting Categories with Naive Bayes and SVMs
- Predicting Numeric Outcomes with Linear Regression
- Classification and Regression with Trees
- Clustering Data with Unsupervised Machine Learning
- Performance Evaluation Methods
- Other Books You May Enjoy
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app