
Handbook Of Instrumentation And Techniques For Semiconductor Nanostructure Characterization (In 2 Volumes)
(In 2 Volumes)
- 348 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Handbook Of Instrumentation And Techniques For Semiconductor Nanostructure Characterization (In 2 Volumes)
(In 2 Volumes)
About this book
"... These volumes provide the very latest in this critical technology and are an invaluable resource for scientists in both academia and industry concerned with the semiconductor future and all of science." Foreword by Leonard C Feldman
(Director Institute for Advanced Materials, Devices and Nanotechnology, Rutgers University, USA)
Highlights
-->
- First comprehensive handbook on instrumentation and techniques for semiconductor nanostructure characterization
- More than 900 references providing up-to-date information
- With over 260 illustrations
-->
As we delve more deeply into the physics and chemistry of functional materials and processes, we are inexorably driven to the nanoscale. And nowhere is the development of instrumentation and associated techniques more important to scientific progress than in the area of nanoscience. The dramatic expansion of efforts to peer into nanoscale materials and processes has made it critical to capture and summarize the cutting-edge instrumentation and techniques that have become indispensable for scientific investigation in this arena. This Handbook is a key resource developed for scientists, engineers and advanced graduate students in which eminent scientists present the forefront of instrumentation and techniques for the study of structural, optical and electronic properties of semiconductor nanostructures.
Foreword
Foreword (47k)
Sample Chapter(s)
Introduction (47k)
Contents:
- Volume 1:
- Electron Microscopies:
- Characterization of Semiconductor Nanostructures by Scanning Electron Microscopy (Lynne M Gignac & Oliver C Wells)
- Transmission Electron Microscopy and Ultra-high Vacuum Transmission Electron Microscopy of Semiconductor Nanostructures (Suneel Kodambaka & Frances M Ross)
- Aberration Corrected Electron Microscopy (Philip E Batson)
- Low-Energy Electron Microscopy for Nanoscale Characterization (James B Hannon & Rudolf M Tromp)
- Ultrafast Microscopy of Plasmon Dynamics in Nanostructured Metal Surfaces (Hrvoje Petek & Atsushi Kubo)
- X-Ray Diffraction Methods for Studying Strain and Composition in Epitaxial Nanostructured Systems (Angelo Malachias, Raul Freitas, Sérgio L Morelhão, Rogério Magalhães-Paniago, Stefan Kycia & Gilberto Medeiros-Ribeiro)
- Stress Determination in Semiconductor Nanostructures Using X-Ray Diffraction (Conal E Murry & I Cevdet Noyan)
- Electron Microscopies:
- Volume 2:
- Scanning Probes:
- An Introduction to Scanning Probe Microscopy of Semiconductors with Case Studies Concerning Gallium Nitride and Related Materials (Rachel Oliver)
- STM of Self Assembled III-V Nanostructures (Vaishno D Dasika & Rachel S Goldman)
- Atom and Optical Probes:
- Atom Probe Tomography for Microelectronics (David J Larson, Ty J Prosa, Dan Lawrence, Brian P Geiser, Clive M Jones & Thomas F Kelly)
- Raman Spectroscopy of Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Materials and Devices (Marcus Freitag & James C Tsang)
- Single Nanowire Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Carlos Aguilar & Richard Haight)
- Time-Domain Thermoreflectance Measurements for Thermal Property Characterization of Nanostructures (Scott Huxtable)
- Scanning Probes:
Readership: Advanced graduate students and professionals in physics, chemistry, materials science and nanoscience.
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
IBM T. J. Watson Research Center
Yorktown Heights, NY 10598, USA
__________
3-D | = three-dimensional |
α | = aperture or convergence angle |
β | = beam brightness = beam current per unit area per solid angle |
κ | = dielectric constant |
λ | = electron wave length |
θ | = collection scattering angle |
B | = incident electron beam |
BD | = beam deceleration |
BF | = bright field |
BSE | = backscattered electron |
Cc | = chromatic aberration coefficient |
CFE | = cold field emission |
CNT | = carbon nanotube |
Cs | = spherical aberration coefficient |
d1 | = electron beam size or diameter at Wehnelt cylinder |
dg | = demagnified electron beam size |
do | = electron beam size or diameter on sample surface |
DB-FIB | = dual beam focused ion beam |
DF | = dark field |
DoF | = depth of field |
Eo | = incident electron beam energy |
ΔEo | = electron beam energy spread |
EBSP | = electron backscatter patterning |
EDS | = energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy |
ETD | = Everhart-Thornley detector |
FE | = field emission |
FIB | = focused ion beam |
HAADF | = high angle annular dark field |
i | = beam current |
k | = immersion ratio = Eo/LE |
LE | = landing energy |
LEEM | = low energy electron microscope |
MFP | = mean free path |
PM | = photomultiplier |
SB | = sample bias |
SB-FIB | = single beam focused ion beam |
SE | = secondary electrons |
SEM | = scanning electron microscope |
SE-I | = secondary electrons produced from the incident electron beam |
SE-II | = secondary electrons produced from backscattered electrons |
SE-III | = secondary electrons produced from backscattered electrons hitting components in the microscope (chamber walls, pole piece, etc) |
SFE | = Schottky field emission |
s-MC | = source monochromator |
STEM | = scanning transmission electron microscope |
TEM | = transmission electron microscope |
TTL | = through the lens |
TTLD | = through the lens detector |
Z | = atomic number |
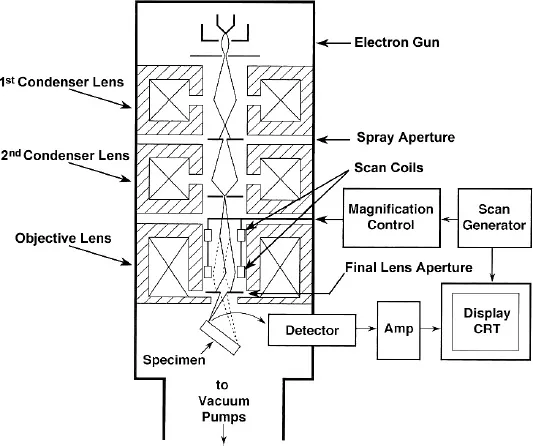
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half title
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- Foreword
- Introduction
- Volume 1
- Volume 2
- Atom and Optical Probes
- Index