
- 428 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Advances In The Homotopy Analysis Method
About this book
Unlike other analytic techniques, the Homotopy Analysis Method (HAM) is independent of small/large physical parameters. Besides, it provides great freedom to choose equation type and solution expression of related linear high-order approximation equations. The HAM provides a simple way to guarantee the convergence of solution series. Such uniqueness differentiates the HAM from all other analytic approximation methods. In addition, the HAM can be applied to solve some challenging problems with high nonlinearity.This book, edited by the pioneer and founder of the HAM, describes the current advances of this powerful analytic approximation method for highly nonlinear problems. Coming from different countries and fields of research, the authors of each chapter are top experts in the HAM and its applications. Contents:
- Chance and Challenge: A Brief Review of Homotopy Analysis Method (S-J Liao)
- Predictor Homotopy Analysis Method (PHAM) (S Abbasbandy and E Shivanian)
- Spectral Homotopy Analysis Method for Nonlinear Boundary Value Problems (S Motsa and P Sibanda)
- Stability of Auxiliary Linear Operator and Convergence-Control Parameter (R A Van Gorder)
- A Convergence Condition of the Homotopy Analysis Method (M Turkyilmazoglu)
- Homotopy Analysis Method for Some Boundary Layer Flows of Nanofluids (T Hayat and M Mustafa)
- Homotopy Analysis Method for Fractional Swift–Hohenberg Equation (S Das and K Vishal)
- HAM-Based Package NOPH for Periodic Oscillations of Nonlinear Dynamic Systems (Y-P Liu)
- HAM-Based Mathematica Package BVPh 2.0 for Nonlinear Boundary Value Problems (Y-L Zhao and S-J Liao) Graduate students and researchers in applied mathematics, physics, nonlinear mechanics, engineering and finance. Key Features:
- The method described in the book can overcome almost all restrictions of other analytic approximation method for nonlinear problems
- This book is the first in homotopy analysis method, covering the newest advances, contributed by many top experts in different fields
Trusted by 375,005 students
Access to over 1 million titles for a fair monthly price.
Study more efficiently using our study tools.
Information
A Brief Review of Homotopy Analysis Method
[email protected]
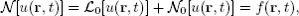
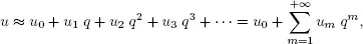
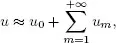
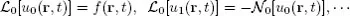
Table of contents
- Cover
- Half Title
- Title Page
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- Chapter 1. Chance and Challenge: A Brief Review of Homotopy Analysis Method
- Chapter 2. Predictor Homotopy Analysis Method (PHAM)
- Chapter 3. Spectral Homotopy Analysis Method for Nonlinear Boundary Value Problems
- Chapter 4. Stability of Auxiliary Linear Operator
- Chapter 5. A Convergence Condition of the Homotopy Analysis Method
- Chapter 6. Homotopy Analysis Method for Some Boundary Layer Flows of Nanofluids
- Chapter 7. Homotopy Analysis Method for Fractional Swift–Hohenberg Equation
- Chapter 8. HAM-Based Package NOPH for Periodic Oscillations of Nonlinear Dynamic Systems
- Chapter 9. HAM-Based Mathematica Package BVPh 2.0 for Nonlinear Boundary Value Problems
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app