
eBook - ePub
Econometric Methods And Their Applications In Finance, Macro And Related Fields
- 616 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
Econometric Methods And Their Applications In Finance, Macro And Related Fields
About this book
The volume aims at providing an outlet for some of the best papers presented at the 15th Annual Conference of the African Econometric Society, which is one of the “chapters” of the International Econometric Society. Many of these papers represent the state of the art in financial econometrics and applied econometric modeling, and some also provide useful simulations that shed light on the models' ability to generate meaningful scenarios for forecasting and policy analysis.
Contents:
- Financial Econometrics and International Finance:
- Modeling Interest Rates Using Reducible Stochastic Differential Equations: A Copula-Based Multivariate Approach (Ruijun Bu, Ludovic Giet, Kaddour Hadri and Michel Lubrano)
- Financial Risk Management Using Asymmetric Heavy-Tailed Distributions and Nonlinear Dependence Structures of Asset Returns Under Discontinuous Dynamics (Alaa El-Shazly)
- Time-Varying Dependence in the Term Structure of Interest Rates: A Copula-Based Approach (Diaa Noureldin)
- Nonlinear Filtering and Market Implied Rating for a Jump-Diffusion Structural Model of Credit Risk (Alaa El-Shazly)
- Time-Varying Optimal Weights for International Asset Allocation in African and South Asian Markets (Dalia El-Edel)
- Econometric Theory and Methods:
- Econometric Methods for Ordered Responses: Some Recent Developments (Franco Peracchi)
- Which Quantile is the Most Informative? Maximum Likelihood, Maximum Entropy and Quantile Regression (Anil K Bera, Antonio F Galvao Jr, Gabriel V Montes-Rojas and Sung Y Park)
- The Experimetrics of Fairness (Anna Conte and Peter G Moffatt)
- Uniform in Bandwidth Tests of Specification for Conditional Moment Restrictions Models (Pascal Lavergne and Pierre E Nguimkeu)
- Joint LM Test for Homoscedasticity in a Two-Way Error Components Model (Eugene Kouassi, Joel Sango, J M Bosson Brou and Kern O Kymn)
- An Approximation to the Distribution of the Pooled Estimator When the Time Series Equation is One of a Complete System (William M Mikhail and Ghazal A Ghazal)
- Monetary, Labor and Environmental Applications:
- Monetary Policy and the Role of the Exchange Rate in Egypt (Tarek A Moursi and Mai El-Mossallamy)
- International Migration, Remittances and Household Poverty Status in Egypt (Rania Roushdy, Ragui Assaad and Ali Rashed)
- Determinants of Job Quality and Wages of the Working Poor: Evidence From 1998–2006 Egypt Labor Market Panel Survey (Mona Said)
- A Contract-Theoretic Model of Conservation Agreements (Heidi Gjertsen, Theodore Groves, David A Miller, Eduard Niesten, Dale Squires and Joel Watson)
- Household Environment and Child Health in Egypt (Mahmoud Hailat and Franco Peracchi)
- Modeling the Relationship between Natural Resource Abundance, Economic Growth, and the Environment: A Cross-Country Study (Hala Abou-Ali and Yasmine M Abdelfattah)
- Global Cement Industry: Competitive and Institutional Frameworks (Tarek H Selim and Ahmed S Salem)
- On the Occurrence of Ponzi Schemes in Presence of Credit Restrictions Penalizing Default (A Seghir)
- Is Targeted Advertising Always Beneficial? (Nada Ben Elhadj-Ben Brahim, Rim Lahmandi-Ayed and Didier Laussel)
Readership: Graduate students and researchers in the fields of econometrics, economic theory, applied econometrics.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Econometric Methods And Their Applications In Finance, Macro And Related Fields by Kaddour Hadri, William Mikhail in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Biological Sciences & Science General. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Part I
Financial Econometrics and International Finance
The financial econometrics section in this book includes five chapters that cover topics in interest rate modeling, portfolio allocation, risk management and credit risk. The first two chapters deal with modeling multivariate interest-rate processes using time-varying copula functions that allow for dynamic and complex dependence among financial series. The third chapter studies intertemporal portfolio allocation under a time-varying covariance matrix of stock returns using a dynamic conditional correlation model. The fourth chapter is on portfolio risk management using a copula-based model that accounts for the distributional characteristics and tail dependence of stock returns. The fifth chapter focuses on credit risk analysis using an option-based approach and nonlinear filtering techniques that allow for jump-diffusions in the underlying asset price. These analytical methods are applied to data from both developed and emerging financial markets.
In their chapter entitled “Modeling Interest Rates Using Reducible Stochastic Differential Equations: A Copula-base Multivariate Approach,” Ruijun Bu, Ludovic Giet, Kaddour Hadri and Michel Lubrano consider a class of nonlinear stochastic differential equations for modeling the marginal processes of interest rates that are reducible to generalized versions of a mean-reversion process with time-varying volatility. This approach can account for nonlinear features observed in short-term interest-rate series and lead to exact discretization and closed-form likelihood functions. Results from an application to the UK and US interest-rate data suggest that the proposed generalized models outperform existing parametric models with closed-from likelihood functions. The authors also study the dynamic co-movements between the two rates using the conditional symmetrized Joe–Clayton copula and find that the time-varying effects as well as the asymmetry in the tail dependence implied by the copula are significant. There is evidence that the level of dependence is positively related to the level of the two rates.
In the chapter entitled “Time-varying Dependence in the Term Structure of Interest Rates: A Copula-based Approach,” Diaa Noureldin investigates the dependence structure of the level, slope and curvature factors for the US yield curve. The author extends the dynamic version of the Nelson–Siegel model for estimating these three latent factors that drive yields at different maturities by allowing for time-varying dependence among them. The analysis of the correlated factor dynamics using conditional elliptical copulas indicates that there is evidence of time-varying dependence structure among the factors. The time variation in factor dynamics is largely explained by past shocks and characterized by low persistence. Also, simulation results indicate that an invalid assumption of constant dependence among the yield curve factors leads to serious errors in risk assessment for bond portfolios.
In the chapter entitled “Time-varying Optimal Weights for International Asset Allocation in African, and South Asian Markets,” Dalia El-Edel presents an intertemporal analysis of asset allocation for internationally diversified portfolios from the perspective of domestic investors in selected emerging markets. The time-varying optimal portfolio weights are computed from a dynamic conditional correlation model. Estimation results of the model indicate that the share of domestic equities is generally small in the optimal portfolios. Also, there is increasing correlation between stock indices of emerging markets during crisis times.
In the chapter entitled “Financial Risk Management Using Asymmetric Heavy-tailed Distributions and Nonlinear Dependence Structures of Asset Returns under Discontinuous Dynamics,” Alaa El-Shazly studies a copula-based model for portfolio risk management when asset price dynamics are driven by non-Gaussian Levy processes. The model uses the Normal Inverse Gaussian distribution and the t-copula function to account for the distributional characteristics and tail dependence of asset returns. The modeling scheme allows measuring the strength of nonlinear relationships among the portfolio components under both normal and extreme market conditions. Application to data from developed and emerging stock markets suggests that the model yields useful information on dependence structure of the return distributions for devising portfolio and risk management strategies with a reasonably good predictive power based on conditional value-at-risk estimation.
In the chapter entitled “Nonlinear Filtering and Market Implied Rating for a Jump-diffusion Structural Model of Credit Risk,” Alaa El-Shazly puts forward an asset-based model for credit risk analysis in the context of a nonlinear and non-Gaussian state-space system to compute default probability and related metrics under realistic market conditions. The model draws on option pricing theory and allows for jump-diffusions in the underlying asset value. The author uses particle filtering for online estimation of latent state and parameters to assess credit risk and imply rating from market data as they arrive. Results from a simulation study show good performance of the information filtering method.
Chapter 1
Modeling Interest Rates Using Reducible Stochastic Differential Equations: A Copula-based Multivariate Approach
University of Liverpool, UK
GREQAM (Groupe de Recherche en economie quantitative d’aix Marseille), France
Queen’s University Belfast, UK
GREQAM (Groupe de Recherche en economie quantitative d’aix Marseille) and CNRS (Centre National de la Recherche scientifique)
1. Introduction
Continuous-time models have proved to be enormously useful in modeling financial and more generally economic variables. They are widely used to study issues that include the decision to optimally consume, save and invest, portfolio choice under a variety of constraints, contingent claim pricing, capital accumulation, resource extraction, game theory, and recently contract theory. The short-term risk-free interest rate is one of the key variables in economics and finance. More models have been put forward to explain its behavior than for any other issue in finance (Chan et al., 1992). Although many refinements and extensions are possible, the basic continuous-time dynamic model for an interest rate process {rt, t ≥ 0} is described by a stochastic differential equation (SDE):
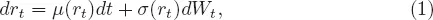
where {Wt, t ≥ 0} is a standard Brownian motion. Both parametric and non-parametric methods of estimation have been developed in the literature. Parametric approaches assume that the drift and diffusion are known functions except for an unknown parameter vector. Examples include Merton (1973), Cox (1975), Vasicek (1977), Cox et al. (1980, 1985), Courtadon (1982), Constantinid...
Table of contents
- Cover
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- Contents
- Part I: Financial Econometrics and International Finance
- Part II: Econometric Theory and Methods
- Part III: Monetary, Labor and Environmental Applications
- Index