
Spanning Tree Results For Graphs And Multigraphs: A Matrix-theoretic Approach
A Matrix-Theoretic Approach
- 188 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Spanning Tree Results For Graphs And Multigraphs: A Matrix-theoretic Approach
A Matrix-Theoretic Approach
About this book
This book is concerned with the optimization problem of maximizing the number of spanning trees of a multigraph. Since a spanning tree is a minimally connected subgraph, graphs and multigraphs having more of these are, in some sense, immune to disconnection by edge failure. We employ a matrix-theoretic approach to the calculation of the number of spanning trees.
The authors envision this as a research aid that is of particular interest to graduate students or advanced undergraduate students and researchers in the area of network reliability theory. This would encompass graph theorists of all stripes, including mathematicians, computer scientists, electrical and computer engineers, and operations researchers.
Contents:
- An Introduction to Relevant Graph Theory and Matrix Theory
- Calculating the Number of Spanning Trees: The Algebraic Approach
- Multigraphs with the Maximum Number of Spanning Trees: An Analytic Approach
- Threshold Graphs
- Approaches to the Multigraph Problem
- Laplacian Integral Graphs and Multigraphs
Readership: Graduate students and researchers in combinatorics and graph theory. Key Features:
- Unlike this book, very few books cover a significant amount of material about the Laplacian matrix, nor do they contain an extensive treatment of counting or optimizing the number of spanning trees
- Other works in the field do not devote to multigraphs
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Information
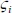
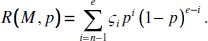
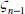
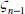
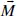
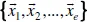
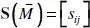
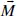

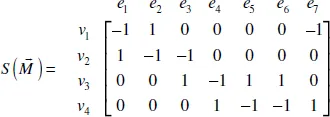
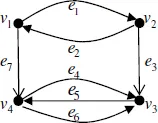
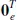
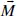
Table of contents
- Cover page
- Halftitle page
- Title page
- Copyright page
- Dedication page
- Preface
- Contents
- 0 An Introduction to Relevant Graph Theory and Matrix Theory
- 1 Calculating the Number of Spanning Trees: The Algebraic Approach
- 2 Multigraphs with the Maximum Number of Spanning Trees: An Analytic Approach
- 3 Threshold Graphs
- 4 Approaches to the Multigraph Problem
- 5 Laplacian Integral Graphs and Multigraphs
- Bibliography
- Index