
Fractional Partial Differential Equations And Their Numerical Solutions
- 348 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Fractional Partial Differential Equations And Their Numerical Solutions
About this book
This book aims to introduce some new trends and results on the study of the fractional differential equations, and to provide a good understanding of this field to beginners who are interested in this field, which is the authors' beautiful hope.
This book describes theoretical and numerical aspects of the fractional partial differential equations, including the authors' researches in this field, such as the fractional Nonlinear Schrödinger equations, fractional Landau–Lifshitz equations and fractional Ginzburg–Landau equations. It also covers enough fundamental knowledge on the fractional derivatives and fractional integrals, and enough background of the fractional PDEs.
Contents:
- Physics Background
- Fractional Calculus and Fractional Differential Equations
- Fractional Partial Differential Equations
- Numerical Approximations in Fractional Calculus
- Numerical Methods for the Fractional Ordinary Differential Equations
- Numerical Methods for Fractional Partial Differential Equations
Readership: Graduate students and researchers in mathematical physics, numerical analysis and computational mathematics.
Key Features:
- This book covers the fundamentals of this field, especially for the beginners
- The book covers new trends and results in this field
- The book covers numerical results, which will be of broad interests to researchers
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Physics Background
1.1Origin of the fractional derivative
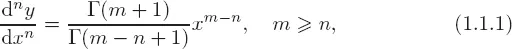

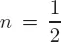
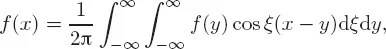
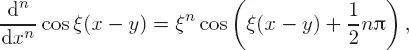
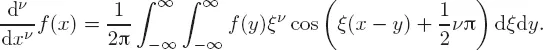
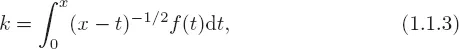
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Preface
- Contents
- 1 Physics Background
- 2 Fractional Calculus and Fractional Differential Equations
- 3 Fractional Partial Differential Equations
- 4 Numerical Approximations in Fractional Calculus
- 5 Numerical Methods for the Fractional Ordinary Differential Equations
- 6 Numerical Methods for Fractional Partial Differential Equations
- Bibliography
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app