
- 284 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
About this book
This book is aimed at graduate students and researchers who are interested in the probability limit theory of random matrices and random partitions. It mainly consists of three parts. Part I is a brief review of classical central limit theorems for sums of independent random variables, martingale differences sequences and Markov chains, etc. These classical theorems are frequently used in the study of random matrices and random partitions. Part II concentrates on the asymptotic distribution theory of Circular Unitary Ensemble and Gaussian Unitary Ensemble, which are prototypes of random matrix theory. It turns out that the classical central limit theorems and methods are applicable in describing asymptotic distributions of various eigenvalue statistics. This is attributed to the nice algebraic structures of models. This part also studies the Circular β Ensembles and Hermitian β Ensembles. Part III is devoted to the study of random uniform and Plancherel partitions. There is a surprising similarity between random matrices and random integer partitions from the viewpoint of asymptotic distribution theory, though it is difficult to find any direct link between the two finite models. A remarkable point is the conditioning argument in each model. Through enlarging the probability space, we run into independent geometric random variables as well as determinantal point processes with discrete Bessel kernels.
This book treats only second-order normal fluctuations for primary random variables from two classes of special random models. It is written in a clear, concise and pedagogical way. It may be read as an introductory text to further study probability theory of general random matrices, random partitions and even random point processes.
This book is aimed at graduate students and researchers who are interested in the probability limit theory of random matrices and random partitions. It mainly consists of three parts. Part I is a brief review of classical central limit theorems for sums of independent random variables, martingale differences sequences and Markov chains, etc. These classical theorems are frequently used in the study of random matrices and random partitions. Part II concentrates on the asymptotic distribution theory of Circular Unitary Ensemble and Gaussian Unitary Ensemble, which are prototypes of random matrix theory. It turns out that the classical central limit theorems and methods are applicable in describing asymptotic distributions of various eigenvalue statistics. This is attributed to the nice algebraic structures of models. This part also studies the Circular β Ensembles and Hermitian β Ensembles. Part III is devoted to the study of random uniform and Plancherel partitions. There is a surprising similarity between random matrices and random integer partitions from the viewpoint of asymptotic distribution theory, though it is difficult to find any direct link between the two finite models. A remarkable point is the conditioning argument in each model. Through enlarging the probability space, we run into independent geometric random variables as well as determinantal point processes with discrete Bessel kernels.
This book treats only second-order normal fluctuations for primary random variables from two classes of special random models. It is written in a clear, concise and pedagogical way. It may be read as an introductory text to further study probability theory of general random matrices, random partitions and even random point processes.
Contents:
- Normal Convergence
- Circular Unitary Ensemble
- Gaussian Unitary Ensemble
- Random Uniform Partitions
- Random Plancherel Partitions
Key Features:
- The book treats only two special models of random matrices, that is, Circular and Gaussian Unitary Ensembles, and the focus is on second-order fluctuations of primary eigenvalue statistics. So all theorems and propositions can be stated and proved in a clear and concise language
- In a companion part, the book also treats two special models of random integerpartitions, namely, random uniform and Plancherel partitions. It exhibits a surprising similarity between random matrices and random partitions from the viewpoint of asymptotic distribution theory, though there is no direct link between finite models
- The limit distributions of most statistics of interest are obtained by reducing to classical central limit theorems for sums of independent random variables, martingale sequences and Markov chains. So the book is easily accessible to readers that are familiar with a standard probability theory textbook
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
Chapter 1
Normal Convergence
1.1Classical central limit theorems
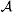
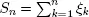

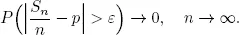
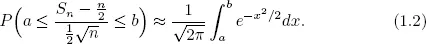
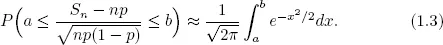
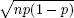
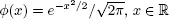
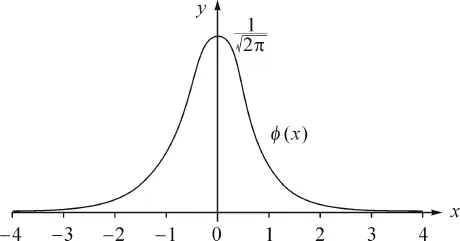
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title Page
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
- Contents
- Preface
- 1. Normal Convergence
- 2. Circular Unitary Ensemble
- 3. Gaussian Unitary Ensemble
- 4. Random Uniform Partitions
- 5. Random Plancherel Partitions
- Bibliography
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app