![]()
Blended Learning Unit: A Case of Using Facebook as a Learning Tool to Teach Gene Expression in Higher Education*
T. Pimoubol and N. Sriwattanarothai†
Institute for Innovative Learning, Mahidol University,
Nakhon Pathom, 73170, Thailand †E-mail: [email protected]
www.il.mahidol.ac.th The present study developed a prototype of blended-learning unit for enhancing students’ understanding of gene expression. Then an intervention was determined the effectiveness in enhancing understanding and the perception toward an intervention in 11 juniors from a western Thai university. In this study, students had learned gene expression using Facebook group (on-line) together with face-to-face session including (1) on-line preparing, (2) active participation in class, (3) on-line content elaboration, and (4) presentation in class. We found an intervention could support students’ in learning the gene expression as they gained better understanding and could explained those concepts. Equally important, students had highly positive perception toward an intervention. Moreover results showed that Facebook helped bridging the gap between teacher and students.
Keywords: Blended-learning, Gene expression, Active learning, Facebook.
1.Introduction
Gene expression, the most difficult topic for high school and novice college students, is the process by which information from genes are used in the synthesis of a functional gene product [1]. The process starts by genetic code interpreting, protein synthesizing, and phenotype (characteristics) generating. With the stated multilevel thinking and reasoning, it has been found to be an abstract and invisible concepts for students [2,3,4]. It also contains many technical terms and various levels of representation (macro-, micro-, and symbolic level) that is difficult for them to make the ideas tangible. Even the concepts under gene expression are complex but it worth to study how living things show various characteristics, especially how severe disorders such as cancer, diabetes, etc. developing.
Many researchers had developed the learning unit on gene expression by applying various teaching and learning approaches, for example inquiry- based learning [5], problem-based learning [1], project-based learning [6]. Not only the learning approach, visual instruction materials and media presenting gene expression concept that available both online and offline format have also considered being a part in numerous studies. Some studies integrated teaching approach with visual representation for the most effective way to teach this topic. Whether the gain better understanding after implemented those approaches, there still needed longer time than provided in the normal class. Online involving learning has then been considered an alternative way to solve this issue.
Nowadays information and communication technologies (ICT) have become an important part of learning diversity for 21st century students. It helps in searching and retrieving information from widely resources. It also benefits in learning from different modes anywhere anytime. However ICT alone could not improve students’ skills needed in this century, for example, thinking skills, science process skills, problem-solving skills, life and career skills, etc. The blended learning, a teaching strategy combining the best elements of online and face-to-face learning, has been proposed to bridge those gaps and to facilitate in collaborative learning [7, 8, 9]. Therefore this study aims to developed the blended learning unit on gene expression with the using of Facebook, the most global widely used and the most popular global social networking websites in tertiary education [10], in an online session.
To frame this study, two research questions were determined. The first question was “to what extent does an intervention enhance students’ understanding of gene expression?” while the others was “what are the students’ perception toward a developed blended-learning unit?”
2.Methodology
2.1.Research design
To determine the effectiveness of a developed blended learning unit in enhancing understanding of gene expression, a pre-experimental design that is one group pre-post test had been used. Eleven 3rd year teacher students majoring life science who voluntarily participated in the study firstly took pretest. They then learned through a developed learning unit and finally took post-test, questionnaire, and some were interviewed at the end of the unit.
2.2.A developed learning unit implementation
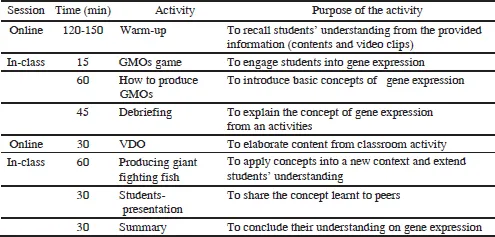
There were two modes of learning in a developed blended learning unit; Facebook, a social networking, had been used as a medium to learn in on-line session while active learning had been applied to teach during face-to-face session (Table 1). In this learning unit, Facebook group including (1) the provided content and information for reviewing students before learning in each class, (2) link to other useful online resources for more information, (3) and discussion panel via post and comment had been created by the researcher. Students were asked to join the Facebook group one-week before an intervention. They downloaded pre-test from the Facebook group and submitted to the researcher before on-line preparation. They then learned through two session of two-hour active learning activity and the on-line working/sharing with friends in between. In first two-hour class, the learning unit focused on engagement and introduction to gene expression by using GMOs game and followed by how to produce GMOs activity to introduce basic knowledge on gene expression. In the learning unit, growth hormone gene was selected to be the representative of how gene expression works in the learning unit. Each group of students was asked to produce giant fighting fish using concept of gene expression and presented in the class. In the presentation, students’ group was randomly chosen to present in the class and another group had to help their friend to complete the task. Finally post-conceptual test and questionnaire immediately administered after the intervention. Classroom observation was collected during four-hour implementation period. Moreover semi-structured interview was used to assess students’ perception at the end.
Table 1. An overview of a developed blended-learning unit on gene expression.
2.3.Research instruments
This study adopted triangulation method [11] for redeeming research quality. The assessment tools are gene expression conceptual test, questionnaire, semi-structured interview, classroom observation, and students’ document. Details of each tool are as followed;
2.3.1.Gene expression conceptual test
Gene Expression conceptual test was ten two-tier questions for assess students’ understanding in four categories, (1) transcription, (2) post-transcriptional modifications, (3) translation, and (4) application of transcription and translation. Pre-conceptual test was administrated to student five days before implementation. The same gene expression conceptual test was used as post-test after an intervention. After the normal distribution test, gene expression conceptual test score was used to determine the difference gained scores between pre-test and post-test by independent- samples t-test with SPSS version 20.
2.3.2.Students’ document
Students’ document was collected from Facebook group comment and worksheet in the class. Each student was asked to write the way to produce a giant fighting fish in worksheet using concept of gene expression includes; concept of transcription, post-transcriptional modification, concept of translation. Worksheet was analyzed by using rubric score with the maximum point of 20.
2.3.3.Questionnaire on perception
The 15-item questionnaire with Cronbach's alpha of 0.81 consists of four criteria: perception of gene expression’s understanding, perception on amusement, perception on supplementary document and perception on collaborative work. Questionnaire was used the Likert scales: I totally agree (5), I mostly agree (4), I do not know (3), I mostly disagree (2) and I totally disagree (1). The questionnaire was analyzed by using descriptive statistic.
2.3.4.Semi-structure interview
Five voluntarily students were participated in semi-structured interview consisting the questions to determine conceptual understanding and perception toward an intervention by communicated via Facebook chat. The interview data was fully transcribe and analyzed by using thematic approach.
2.3.5.Classroom observation
This study used video camera and took note to observe the behaviors and responses of the students during implementation. Data from classroom observation and students’ response was analyzed by using thematic approach.
3.Results
3.1.Gene expression conceptual test
The result of gene expression conceptual test was shown in Table 2. Students gained post-test score significantly higher than pre-test score in all those four concepts (transcription, post-transcription, translation, and application of transcription and translation (p-value = 0.001, α = 0.05). Post-transcription concept was the highest gained scores (22.80%) and application of transcription and translation was the lowest gained scores (8.04%).
Table 2. Average scores of gene expression conceptual test.
| Concept | Average Scores (Mean ± SD) |
| Pre-test | Post-test |
| Transcription (out of 6 points) | 0.42 ± 0.51 | 1.33 ± 0.45 |
| Post-Transcription (out of 4 points) | 0.77 ± 0.45 | 1.68 ± 0.06 |
| Translation (out of 4 points) | 0.41 ± 0.45 | 0.86 ± 0.71 |
| Application of Transcription and Translation (out of 6 points) | 0.79 ± 0.91 | 1.27 ± 0.94 |
When classified the pre-test score of each students, there were three groups of prior knowl...