
- 252 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
eBook - ePub
About this book
This book presents a collection of problems for nonlinear dynamics, chaos theory and fractals. Besides the solved problems, supplementary problems are also added. Each chapter contains an introduction with suitable definitions and explanations to tackle the problems.
The material is self-contained, and the topics range in difficulty from elementary to advanced. While students can learn important principles and strategies required for problem solving, lecturers will also find this text useful, either as a supplement or text, since concepts and techniques are developed in the problems.
Contents:
- One-Dimensional Maps:
- Notations and Definitions
- One-Dimensional Maps
- Higher-Dimensional Maps and Complex Maps:
- Introduction
- Two-Dimensional Maps
- Complex Maps
- Higher-Dimensional Maps
- Bitwise Maps
- Fractals
- Introduction
- Solved Problems
- Supplementary Problems
Readership: Graduate students who focus on chaos, fractals and nonlinear dynamics.
One-Dimensional Maps;Complex Maps;Bitwise Maps
Frequently asked questions
Yes, you can cancel anytime from the Subscription tab in your account settings on the Perlego website. Your subscription will stay active until the end of your current billing period. Learn how to cancel your subscription.
No, books cannot be downloaded as external files, such as PDFs, for use outside of Perlego. However, you can download books within the Perlego app for offline reading on mobile or tablet. Learn more here.
Perlego offers two plans: Essential and Complete
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
We are an online textbook subscription service, where you can get access to an entire online library for less than the price of a single book per month. With over 1 million books across 1000+ topics, we’ve got you covered! Learn more here.
Look out for the read-aloud symbol on your next book to see if you can listen to it. The read-aloud tool reads text aloud for you, highlighting the text as it is being read. You can pause it, speed it up and slow it down. Learn more here.
Yes! You can use the Perlego app on both iOS or Android devices to read anytime, anywhere — even offline. Perfect for commutes or when you’re on the go.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app.
Yes, you can access Problems and Solutions by Willi-Hans Steeb in PDF and/or ePUB format, as well as other popular books in Mathematics & Applied Mathematics. We have over one million books available in our catalogue for you to explore.
Information
Chapter 1
One-Dimensional Maps
1.1Notations and Definitions
We consider exercises for nonlinear one-dimensional maps. In particular we consider one-dimensional maps with chaotic behaviour. We first summarize the relevant definitions such as fixed points, stability, periodic orbit, Liapunov exponent, invariant density, topologically conjugacy, etc.. Ergodic maps are also considered.
We use the notation f : D → C to indicate a function f with domain D and codomain C. The notation f : D → D indicates that the domain and codomain of the function are the same set.
We also use the following two definitions: A mapping g : A ↦ B is called surjective if g(A) = B. A mapping g is called injective (one-to-one) when ∀a, a′ ∈ A, g(a) = g(a′) ⇒ a = a′. If the mapping f is surjective and injective, the mapping f is called bijective.
Definition.If B ⊂ C, then f(−1)(B) is called the inverse image or preimage of B and consists of all elements of D whose image is contained in B. That is
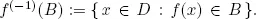
Note that the notation f(−1) does not necessarily imply that f is an invertible function.
Definition.Consider a map f : S → S. A point x* ∈ S is called a fixed point of f if
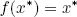
Definition.Let f : A → A and g : B → B be two maps. The maps f and g are said to be topologically conjugate if there exists a homeomorphism h : A → B such that, h ∘ f = g ∘ h.
Definition.Consider a map f : S → S. A point x ∈ S is an eventually fixed point of the function, if there exists N ∈ ℕ such that
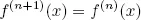
whenever n ≥ N. The point x is eventually periodic with period k, if there exists N such that f(n+k)(x) = f(n)(x) whenever n ≥ N.
Definition.Let f be a function and p be a periodic point of f with prime period k. Then...
Table of contents
- Cover Page
- Title
- Copyright
- Preface
- Contents
- Notation
- 1 One-Dimensional Maps
- 2 Higher-Dimensional Maps and Complex Maps
- 3 Fractals
- Bibliography
- Index