
Statsnotes: Some Statistics For Management Problems
Some Statistics for Management Problems
- 320 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Statsnotes: Some Statistics For Management Problems
Some Statistics for Management Problems
About this book
Managers need access to some statistical advice from time to time to help in solving business problems. Students need access to statistical methods to support work in non-statistics courses, case studies and projects. What is needed will depend on the demands of the problem and how much statistics the manager or student already knows. The requirement is for flexible decision support.
This unique book presents statistical ideas and models in easily accessible form describing both methods and issues of application.
statsNotes are organized as a set of over one hundred notes rather than as a number of chapters. This enables managers and students to locate just what they need for the problem they have. Each note consists of a description of what to do, an example, the rationale, links to other notes.
Managers and students can choose to use as many notes as necessary, which might be just one note or a set of linked notes.
Deciding which method will be helpful depends not just on finding an appropriate statistical method but on the business context too. statsNotes provide advice at three levels:
-->
- Business fit — problems from a business viewpoint and how some statistics might help;
- Perspectives — discussion of issues with widespread implications;
- Implementation — how to use a model or method.
-->
While the range of topics covered is similar to those in introductory textbooks and courses, the focus is on management decision and the methods for dealing with risky decisions and management judgment in this book are usually found in more specialist texts.
Contents:
- Introduction and Guide
- Overview of the statsNotes
- The statsNotes
- Why Do statsNotes Look Like That?
- A Quick Guide to Definitions, Functions and Charts
Readership: Undergraduate students in finance, general management and operational management; MBA students; practicing managers.
Statistics;Management;Decision;Decision Making;Decision Sciences;MBA Key Features:
- Modular format means that readers can easily access just what they need for a particular problem
- It focuses on interaction between management problems and statistical problems
- EXCEL functions are used in preference to algebraic formulae. No prior knowledge is assumed
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
1
Introduction and guide
Statistical questions: | how to describe the judgemental forecasts and make use of them? what is the effect, if any, of linked sales? can the data we have help? how can uncertainties be combined into a forecast for the company? how should risk be assessed and presented? |
Management questions: | what should be our pricing policy? what to negotiate with our suppliers? should we drop any products and/or introduce new ones? is the risk too high? how can we manage it? |
Statistical questions: | how should data be collected? how big should the samples be? what is the best way of presenting the results? |
Management questions: | what do we do if there is a difference? how big a difference would make it worth doing anything? how sure do we need to be? |
Who should read this book
Finding what you need
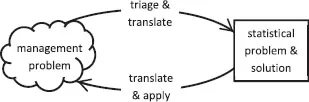
The form of the statsNotes
Perspectives: | an issue with widespread implications background for recommendations in other notes Examples {B8, D6} |
Business fit: | a problem from a business point of view shows how and why a statistical approach can help Examples {E1, G1} |
Implementation: | how to use a particular statistical model or method Examples {C1, F10} |
Table of contents
- Cover
- Halftitle
- Title
- Copyright
- Contents
- About the Author
- 1. Introduction and guide
- 2. Overview of the statsNotes
- 3. The statsNotes
- 4. Why do statsNotes look like that?
- 5. A quick guide to definitions, functions and charts
- Attribution of images
- Notes and References
- Index
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app