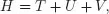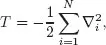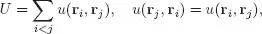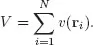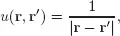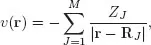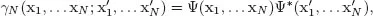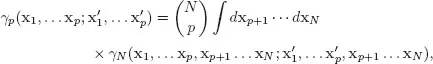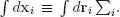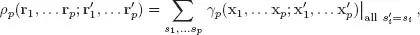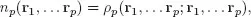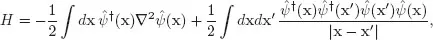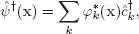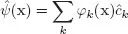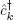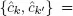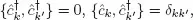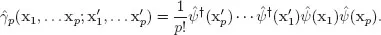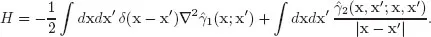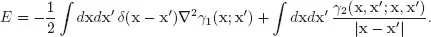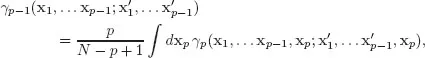![]()
Chapter 1
Low-order density matrices
1.1 Low-order spinless density matrix theory
We start by considering a generic assembly of N electrons, characterized by the Hamiltonian (in atomic units)
Here, as usual, T is the total kinetic energy operator, U denotes the electron-electron (e-e) repulsion energy operator, and V denotes the electron-nucleus (e-n) attraction energy operator, respectively. In realistic situations, one obviously has
(for a molecule, cluster, or solid characterized by M nuclei of charge ZJ, placed at fixed positions RJ, J = 1, . . . M), although the explicit functional form of u and v may be kept as indicated, in order to also embrace model systems.
The Nth-order density matrix (DM) associated with a normalized eigenfunction Ψ(x1, . . . xN) of the Schrödinger equation HΨ = EΨ is then defined as
where xi = (ri, si) is a shorthand notation for coordinates and spin variables of the ith electron. More generally, the pth-order reduced DM (pDM, with p < N) is defined by integrating out (N − p) coordinates as (see ter Haar, 1961; Holas and March, 1995, and references therein)
where, consistently with the above notation,
In cases where spin is not of interest, one considers a spin-averaged or spinless DM defined as
while the diagonal elements of the spinless DM are denoted by
with np ≥ 0. The basic quantity of interest in Density Functional Theory (DFT) is thus n(r) = n1(r) = ρ1(r; r), where the subscript ‘1’ can be omitted, for simplicity.
Expressing the Hamiltonian in second quantization as
where
are creation and annihilation quantum field operators at x, respectively, with
and
ĉk fermion creation and annihilation operators,
in the single-particle spin-orbitals
φk(
x), the reduced
pDM can be viewed as the quantum average of the operator
The same Hamiltonian can then be expressed in terms of 1DM and 2DM as
Similarly, the total (e.g. ground-state) energy of the system can be expressed as
This immediately generalizes also in presence of an external, one-body potential.
Moreover, since the Hamiltonian contains only (at most) 2-body interactions, and given the fact that a (p − 1)DM can be related to a pDM as
one can then express the total energy E as a functional of γ2 alone, i.e. of its 2-bo...