
- 208 pages
- English
- ePUB (mobile friendly)
- Available on iOS & Android
Probability and Expectation
About this book
In China, lots of excellent students who are good at maths take an active part in various maths contests and the best six senior high school students will be selected to form the IMO National Team to compete in the International Mathematical Olympiad. In the past ten years China's IMO Team has achieved outstanding results — they have won the first place almost every year.
The author is one of the senior coaches of China's IMO National Team, whose students have won many gold medals many times in IMO.
This book is part of the Mathematical Olympiad Series which discusses several aspects related to maths contests, such as algebra, number theory, combinatorics, graph theory and geometry. This book will, in an interesting problem-solving way, explain what probability theory is: its concepts, methods and meanings; particularly, two important concepts — probability and mathematical expectation (briefly expectation) — are emphasized. It consists of 65 problems, appended by 107 exercises and their answers.
Tools to learn more effectively

Saving Books

Keyword Search

Annotating Text

Listen to it instead
Information
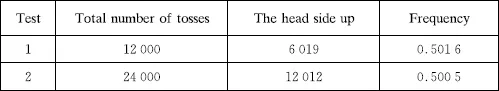
1.Coin Tossing
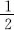
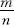
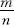
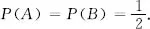
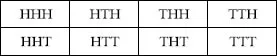
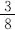
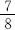
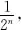
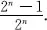
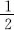
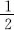
| Total number of tests | The head side up | Frequency |
| 4040 | 2048 | 0.5069 |
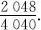
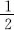
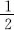
2.General Di Qing’s Coins
Table of contents
- Cover
- Halftitle
- Series Editor
- Title
- Copyright
- Introduction
- Contents
- 0. Basic Knowledge
- 1. Coin Tossing
- 2. General Di Qing’s Coins
- 3. Rolling Dice
- 4. Wei Xiao-bao’s Bet
- 5. Hold All the Trump Cards
- 6. Roll One-Spot
- 7. Red Balls and Black Balls
- 8. Same Month and Day
- 9. Integer Divisibility
- 10. Repeated Experiments
- 11. Silver Medal Dream
- 12. Fight Between Brothers
- 13. Subject Groups
- 14. More Dice
- 15. Custodian Turned Thief
- 16. Put Back or Not
- 17. Match Problem
- 18. Put Balls into Drawers
- 19. Problem of Matches
- 20. Trial in a Three-Judge Court
- 21. Win Twice in Succession
- 22. Fire Blank Shots
- 23. Catch a Turtle in a Jar
- 24. Diagnosis Rate
- 25. Running Well
- 26. Money Change Problem
- 27. Donkey versus Elephant
- 28. East Wind versus West Wind
- 29. Dowry Problem (I)
- 30. Dowry Problem (II)
- 31. Job Interview
- 32. Boxing Match (I)
- 33. Boxing Match (II)
- 34. Boxing Match (III)
- 35. Rein in on the Brink of the Precipice (I)
- 36. Rein in on the Brink of the Precipice (II)
- 37. Who Will Gamble Away?
- 38. Equal in Strength
- 39. Put All Money in One Bet
- 40. Indeterminate Equation
- 41. Throw Copper Coin onto a Small Table
- 42. Appointment of People in Hurry
- 43. Obtuse Triangle
- 44. Buffon’s Needle
- 45. Bertrand’s Paradox
- 46. Odd or Even Number
- 47. Rational or Irrational Number
- 48. Real Roots or Not
- 49. Divide the Stake
- 50. Sleeping Beauty
- 51. Number of Hits
- 52. The Suicide Club
- 53. The First Ace
- 54. How Many Pairs in Average
- 55. Many Holidays
- 56. Buy Lottery Tickets
- 57. Not to Indulge in Gambling
- 58. Social Party
- 59. Success by Trying Once or More Times
- 60. The 108 Heroes
- 61. Who is Sick?
- 62. A Fallen and Broken Rod
- 63. Broken into Three Fragments
- 64. The Number of Cross Points
- 65. Throw a Wire Ring
- Exercises
- Key to Exercises
Frequently asked questions
- Essential is ideal for learners and professionals who enjoy exploring a wide range of subjects. Access the Essential Library with 800,000+ trusted titles and best-sellers across business, personal growth, and the humanities. Includes unlimited reading time and Standard Read Aloud voice.
- Complete: Perfect for advanced learners and researchers needing full, unrestricted access. Unlock 1.4M+ books across hundreds of subjects, including academic and specialized titles. The Complete Plan also includes advanced features like Premium Read Aloud and Research Assistant.
Please note we cannot support devices running on iOS 13 and Android 7 or earlier. Learn more about using the app