![]()
Part I
Understanding Service Products,
Consumers and Markets
![]()
CHAPTER 1
Creating and Capturing Value in the Service Economy
Ours is a service economy and has been for some time.
Karl Albrecht and Ron Zemke
Thought leaders in business and service
In today’s marketplace, consumers have the power to pick and choose as never before.
From the article “Crowned At Last”,
published in The Economist, 31 March 2005
This chapter discusses the modern, ever-changing service economy, defines the nature of services, and highlights some challenges involved in marketing and managing services, and concludes with a framework for developing and implementing service strategies that establishes the structure of this book.
WHY STUDY SERVICES?
In the modern service-driven economy, marketing is taught from a manufacturing perspective in most of the business schools. Almost all marketing courses focus more on marketing manufactured products, especially consumer goods, rather than marketing services. However, a growing and enthusiastic group of scholars, consultants, and educators, including the authors of this book, have chosen to focus on services marketing and build on the extensive research conducted in this field over the past four decades.
Services Dominate the Global Economy
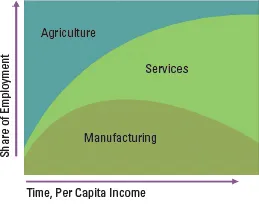
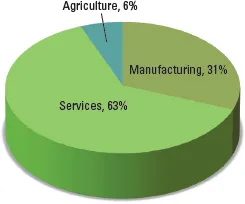
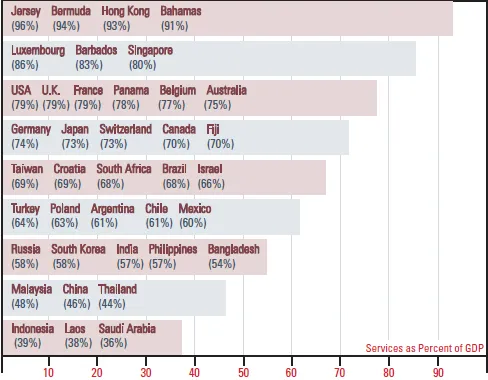
The size of the service sector is increasing in almost all countries around the world. As an economy develops, the relative share of employment between agriculture, industry (including manufacturing and mining), and services changes dramatically.1 Even in emerging economies, the service output is growing rapidly and often represents at least half of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Fig. 1.1 shows how the evolution to a service-dominated economy is likely to take place over time as the per capita income rises. In developed economies, knowledge-based services — defined as having intensive users of high technology or relatively skilled workforces — have been the most dynamic component.2 Fig. 1.2 shows that the service sector already accounts for almost two-thirds of the value of the global GDP, and Fig. 1.3 shows the size of the service sector of a few selected countries.
Figure 1.1: Changing structure of employment as an economy develops.
Source: International Monetary Fund, 1997
Figure 1.2: Contribution of services industries to GDP globally.
Source: The World Factbook 2015, Central Intelligence
Agency, www.cia.gov, accessed 22 January, 2016.
Figure 1.3: Estimated size of service sector in selected countries as a percentage of GDP.
Source: The World Factbook 2015, Central Intelligence Agency, www.cia.gov, accessed 22 January, 2016.
Most New Jobs are Generated by Services
Since the service sector is growing so rapidly in virtually all countries around the world, new job creation comes mainly from services. In fact, this shift in employment to the service sector has been seen as one of the longest and most stable of economic trends.3 Service jobs do not just refer to relatively lowly-paid frontline jobs, such as in restaurants or call centers. Rather, some of the fastest economic growth is in knowledge-based industries — such as professional and business services, education, and healthcare.4 These jobs tend to be well-paid, require good educational qualifications, and offer attractive careers. Many manufacturing firms too have moved from just bundling supplementary services with their physical products to marketing certain elements as standalone services.
There are number of leading research centers that focus on the integration of key disciplines to better equip future service professionals. Some of the leading centers include (in alphabetical order): the Center for Excellence in Service of Robert H. Smith School of Business at University of Maryland (see www.rhsmith.umd.edu/ces), the Center for Services Leadership at the W. P. Carey School of Business at Arizona State University (http://wpcarey.asu.edu/csl), and The Service Research Center at Karlstad University in Sweden (www.ctf.kau.se).
Understanding Services Offers Personal Competitive Advantage
This book is in response to the global transformation of our economies towards services, and gives an insight about distinctive characteristics of services and how they affect both customer behavior and marketing strategy. Apart from the family-owned manufacturing and agricultural business, majority of professions involve working in service organizations. The objective of the book is to make the reader aware of the service industry.
WHAT ARE THE PRINCIPAL INDUSTRIES OF THE SERVICE SECTOR?
To determine the type of industry that makes the service sector and the biggest players of the field, the best place to start with is the national economic statistics. The biggest players of the industry may include diverse sectors with services targeted to business customers, many of which are only known to people working in that industry.
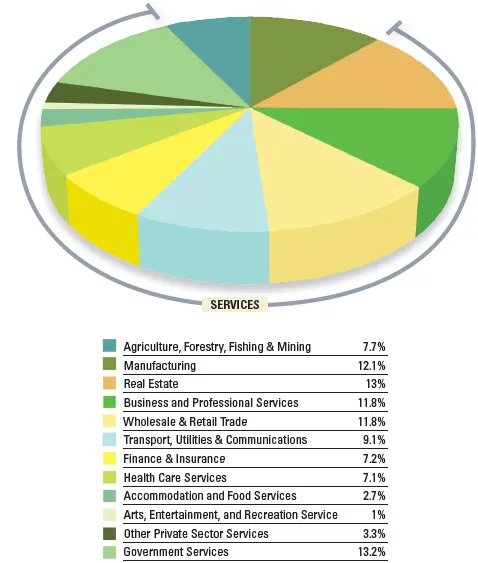
Fig. 1.4 shows how much value each of the major service industry groups contributes to the US GDP. The real estate and rental and leasing are the largest for-profit service industry sector in the US, accounting for 13% in 2013, almost one-eighth of GDP. Over 90% of this figure comes from activities such as renting residential or commercial property; managing properties on behalf of their owners; providing realty services to facilitate purchases, sales, and rentals; and appraising property to determine its condition and value. The balance is accounted for by renting or leasing a wide variety of other manufactured products, ranging from heavy construction equipment (with or without operators) to office furniture, tents, and party supplies. Another large cluster of services provides for distribution of physical products. Wholesale and retail trade accounts for about 11.8% of GDP.
Figure 1.4: Value added by Service Industry categories to US GDP.
Source: Adapted from: U.S. Department of Commerce, Bureau of Economic Analysis, GDP by Industry Accounts for 2013, 2007, www.bea.gov; accessed 22 January, 2016.
Other substantial industry sectors or subsectors include professional and business services (11.8%), finance and insurance (7.2%), and healthcare (7.1%). Accommodation and food services constitute 2.7%, while the arts, entertainment, and recreation services — which include high-profile consumer services such as spectator sports, fitness centers, skiing facilities, museums and zoos, performing arts, casinos, golf courses, marinas, and theme parks — collectively represent a mere 1% of GDP. Nevertheless, in an economy with an output of over $17.1 trillion, this last group of services was still valued at an impressive $164 billion in 2013.
POWERFUL FORCES TRANSFORMING SERVICE MARKETS
Government policies, social changes, business trends, globalization, and advances in information technology and communications in particular, are among the powerful forces transforming today’s service markets (Fig. 1.5). Collectively, these forces reshape demand, supply, the competitive landscape, and even the way customers buy and use services.
Of these forces, the dramatic development of IT and communications is perhaps the most important at the moment. Innovations in big data, cloud computing, user-generated content, mobile communications, networking technologies, artificial intelligence, and increasingly app-based self-service technologies bring their own service revolution. These technologies enable firms to deepen the relationships with their customers, offer multi-way information flow and more personalized services, improved analytics, and increase productivity and profitability.5 More importantly, these new technologies also lead to a vast array of highly innovative business models, ranging from peer-to-peer services (e.g., Airbnb for short-term accommodation and Lending Club for personal loans), integrators (e.g., Uber, connects passengers with independent drivers through apps), to crowd-based services (e.g., crowdSPRING, which, is a leading provider of logo and graphic design services).
B2B Services as a Core Engine of Economic Development6
A key driver of successful economies is their ecosystem of advanced, competitive, and innovative business services. In order to know why would business services improve the productivity of a manufacturing firm and an economy as a whole, consider the example of a large manufacturing firm with its own canteen with 100 workers, who in the national stat...